Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Business Growth (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Why grow a business?
Many firms start small and will grow into large companies or even multi-national corporations
For example, Amazon and Dell both started in entrepreneurs' garages
Reasons why businesses grow
The owner's or manager's desire to run a large business & continually seek to grow it
The owner's desire for higher levels of market share and profitability
The desire for stronger market power (monopoly) over its customers and suppliers
The desire to reduce costs by benefiting from lower unit costs as output increases
Growth provides opportunities for product diversification
Larger firms often have easier access to finance
Internal business growth
Internal growth that is driven by organic expansion using reinvested profits or loans
It is usually achieved by:
Gaining a greater market share
Product or market diversification
Opening new outlets
International expansion (new markets)
Investing in new technology or production machinery
Examples of internal growth
Business | Explanation |
|---|---|
Apple |
|
| |
Disney |
|
Product diversification opens up new revenue streams for a business
Firms may spend money on research and development or innovation to existing products to help create a new revenue stream
Firms often grow internally to the point where they are in a financial position to integrate (merge or buy) with others
Evaluating internal growth
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
External business growth
External business growth is when a business expands by joining with or buying other businesses rather than growing on its own
A merger occurs when two or more companies combine to form a new company
The original companies cease to exist and their assets and liabilities are transferred to the newly created entity
A takeover occurs when one company purchases another company, often against its will
The acquiring company buys a controlling stake in the target company's shares (>50%) and gains control of its operations
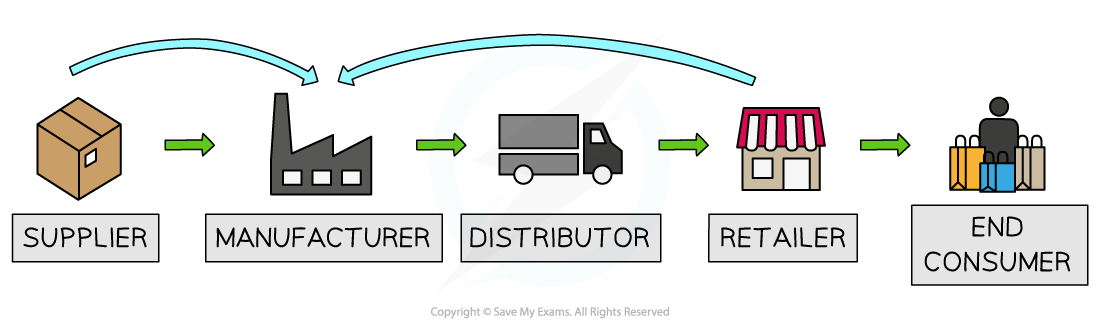
Vertical integration
Vertical integration refers to the merger or takeover of another firm in the supply chain or different stage of the production process
Forward vertical integration involves a merger with or takeover of a firm further forward in the supply chain
For example, a dairy farmer merges with an ice cream manufacturer
Backward vertical integration involves a merger with or takeover of a firm further backwards in the supply chain
For example, an ice cream retailer takes over an ice cream manufacturer
Evaluating vertical integration
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Horizontal integration
Horizontal integration is the merger or takeover of a firm at the same stage of the production process
For example, an ice cream manufacturer merges with another ice cream manufacturer
Evaluating horizontal integration
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don’t just state methods of growth (internal or external) – make sure you can explain their advantages and disadvantages, as questions often test your ability to judge which method is most suitable in a given situation
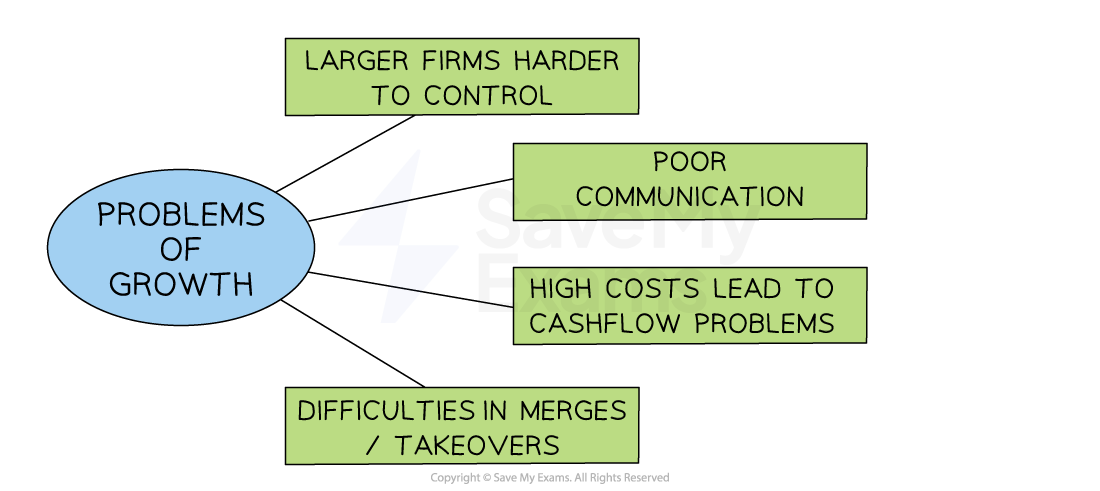
Problems of business growth
In some cases, growing the size of a business can fail to improve its profitability and can lead to cash flow and coordination problems
Problems and solutions of business growth
Poor communication
Longer chains of command and wider spans of control for managers may lead to slower decision-making times and inefficiency
Solution
Use the latest communication technologies, such as instant video calls, to improve communication between managers and workers
Decentralisation may help to delegate decision-making
Larger firms are often harder to control
As a business grows in size, it can experience diseconomies of scale such as poor co-ordination of resources
Solution
Operate as a series of smaller units which allows local or functional area managers to have more control
Increase delegation in order to empower workers and get jobs done more quickly
High costs and cashflow problems
Expansion can be very expensive as it may involve developing a new product range or buying a new factory
High costs in the short/medium term means the business may need additional finance to avoid cashflow problems
Solution
Grow slowly using profits rather than loans to fund gradual and less risky expansion
Manage cash flow carefully, making use of retained profits and short-term borrowing to counter cash flow shortfalls
Difficulties of mergers and acquisitions
A culture clash may occur if a merger or acquisition takes place between two different firms due to different management styles
Solution
Ensure good communication so employees are less likely to be resistant to change
Take time to carefully negotiate and plan mergers/acquisitions to reduce 'teething problems'

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
