Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Business Success & Failure (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Why businesses succeed
Successful businesses often share similar strengths, such as good management, strong products and enough finance
These factors help them grow, stay competitive, and meet customer needs in changing markets
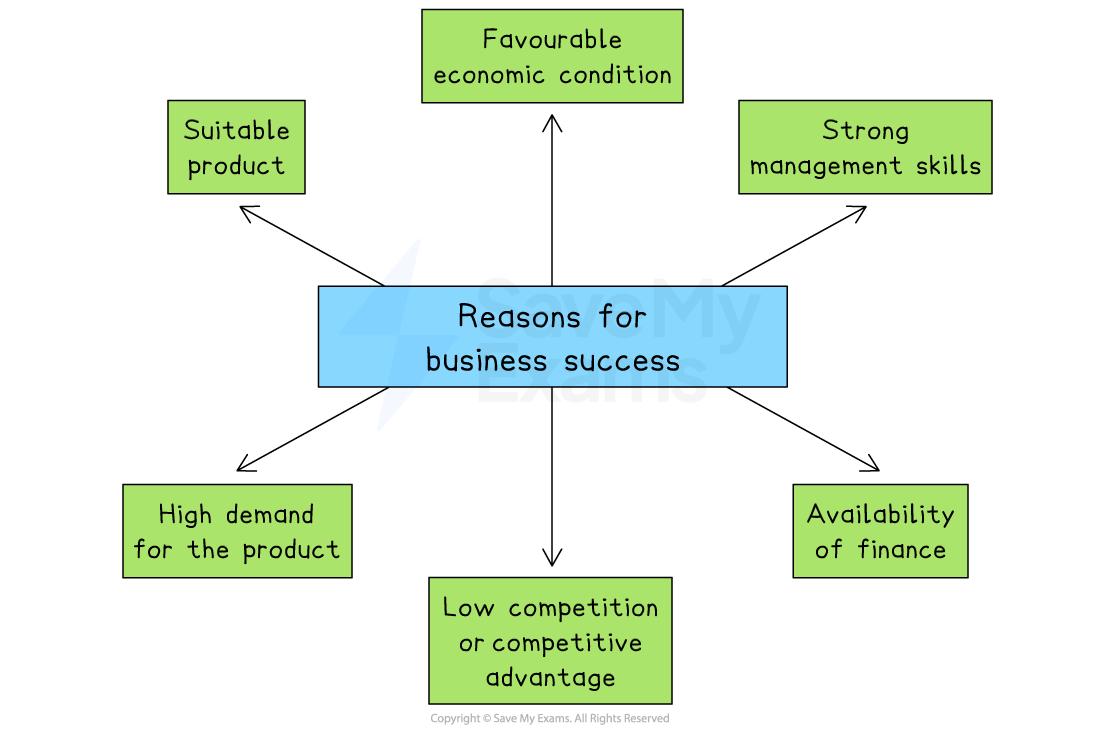
Strong management skills
Good managers make effective decisions, organise resources well and motivate employees
They plan ahead, solve problems quickly, and lead the business towards its goals
For example, Steve Jobs helped Apple succeed by making bold decisions and focusing on design and innovation
Availability of finance
Having enough money (capital) allows a business to invest in equipment, marketing, staff and product development
For example, Amazon used early investment to grow its operations and dominate online shopping
Suitable product
A successful business offers a product that solves a problem, meets customer needs or has unique features
Products must be high quality and appealing to the target market
For example, Dyson vacuum cleaners became popular by fixing problems like loss of suction
High demand for the product
When many people want the product, sales rise and the business earns more profit
Demand can increase due to trends, changes in lifestyle or special events
For example, Zoom became a global success during the COVID-19 pandemic as remote working increased
Favourable economic conditions
In a strong economy, people have more money to spend, which increases sales
Low interest rates and low inflation can also help businesses grow
For example, during economic growth periods, car manufacturers often see rising sales
Low competition or competitive advantage
Businesses succeed when they offer something better than their rivals
For example, lower prices, better quality or a strong brand
Having few competitors also gives more control over pricing and customers
For example, Nike stays successful by constantly innovating and using powerful branding
Why businesses fail
Business failure is a risk to both new and established businesses
In 2021, an average of 8% of businesses in EU countries failed
In Estonia, almost one in four businesses failed
However, in Greece, just over 2% of businesses failed
New businesses are often more at risk of failure than well-established businesses
This is often due to lack of management skills, limited experience or cashflow problems during the initial start-up phase
The volume and variety of tasks required of new business owners can be overwhelming
Market research is unlikely to be detailed, as small business owners may lack the skills to understand findings and make effective decisions
The main reasons why some businesses fail
Financial factors | Poor management |
|---|---|
|
|
External factors | Overtrading |
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don’t give vague answers like “the business failed because it was bad” – use specific factors such as poor management, lack of finance, or falling demand, and always link them to the impact on the business

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
