What is GCSE Chemistry? Student Overview
Written by: Philippa Platt
Reviewed by: Richard Boole
Published
Contents
Are you wondering what GCSE Chemistry is all about? You’re not alone! As a teacher with over 15 years of classroom experience, I’ve met countless students feeling that mix of excitement and nerves at the start. Some worry about balancing equations, others are eager for hands-on experiments. What I tell every new class is this: Chemistry can seem challenging, but with curiosity and steady effort, it becomes one of the most rewarding subjects you’ll ever explore.
This guide brings together everything you need to know:
What GCSE Chemistry covers
How exams work
The study strategies that I’ve seen unlock understanding and confidence time and time again.
What is GCSE Chemistry?
GCSE Chemistry is the science of matter and how it transforms through chemical reactions. I often say it’s the science behind everyday things like baking a cake, firework displays amd taking medicine. It’s not just about reactions in a lab, it’s about the chemistry happening all around you.
You'll study Chemistry either as part of Combined Science (also called Trilogy or Double Science) or as a standalone Triple Science. I’ve seen students flourish in both. Combined Science gives a well-balanced overview, while Triple Science lets you dive deeper into chemistry, perfect if you’re someone who has a real interest in science.
According to the (opens in a new tab)Joint Council for Qualifications (opens in a new tab), over 700,000 students take GCSE science subjects each year. This makes science one of the most popular qualification areas.
What topics will you study in GCSE Chemistry?
Core topics
Your GCSE Chemistry course covers eight main topic areas:
Atomic structure and the Periodic Table
You'll learn about atoms, elements, and how the periodic table is organised. This is the foundation for everything else in chemistry.
Bonding, structure and the properties of matter
Discover how atoms stick together and why different materials have different properties.
Chemical changes and energy changes
Explore what happens during chemical reactions and how energy is involved.
The rate and extent of chemical change
Find out what makes reactions go faster or slower, and when they stop.
Organic chemistry
Study carbon-based compounds, including fuels and important molecules.
Chemical analysis
Learn how scientists identify unknown substances and test for purity.
Chemistry of the atmosphere
Understand our planet's atmosphere and environmental issues like climate change.
Using resources
Discover how we extract materials from the Earth and use them sustainably.
These topics build on each other. So, understanding the basics helps with the more complex ideas later on.
For detailed information about each topic, check out our comprehensive GCSE Chemistry Topics guide.
How is GCSE Chemistry assessed?
GCSE Chemistry typically uses a two-paper exam system depending on the board:
Both papers test all the topics but in different combinations. This is how the topics are typically organised into the exam papers:
Frist paper | Second paper |
Atomic structure | Rates of reaction |
Bonding | Chemical analysis |
Chemical changes | Atmospheric chemistry |
Energy changes | Using resources |
Organic chemistry |
Both Foundation tier (grades 1-5) and Higher tier (grades 4-9) are available to students:
Foundation focuses on core understanding
Higher tier includes more challenging content and mathematical calculations.
The exam questions come in three main types:
Multiple choice - Quick questions testing key facts
Structured questions - Step-by-step problems with several parts
Extended response - Longer answers where you explain scientific concepts
Required practicals are hands-on experiments you'll do in lessons. You won't repeat these in your actual exams, but you'll answer questions about them. The (opens in a new tab)Department for Education (opens in a new tab) requires you to complete these practicals to ensure you develop real laboratory skills.
Key skills you'll develop in Chemistry
GCSE Chemistry isn’t just about memorising facts. The real value comes from the transferable skills you’ll develop, skills that will help you in other subjects, in further study, and in everyday life.
Scientific reasoning and problem-solving
These become second nature as you learn to think logically about chemical processes.
An example of this is looking at electrolysis (Electrolysis Exam Questions).
By breaking the problem into clear steps you train yourself to think like a chemist:
Identify the ions
Apply the rules
Predict the products
Working with chemical equations and formulae
This might seem scary at first, but it's like learning a new language that describes how atoms and molecules behave.
With practice, balancing equations becomes a logical puzzle where every atom must be accounted for.
Exam questions often reward this step-by-step approach.
Have a look at some examples of questions involving common GCSE chemical calculations.
Practical lab skills and data interpretation
These give you hands-on experience with real scientific equipment and help you understand how scientific discoveries are made.
For me as a teacher, guiding students through experiments is one of the most rewarding parts of GCSE Chemistry. It’s where abstract ideas come to life.
Even a simple flame test can spark curiosity and excitement when you see those colours appear before your eyes.
These skills are tested in required practical exam questions.
So, the more you link your practicals to your notes, the more confident and prepared you’ll feel when tackling them in an exam.
Critical thinking and applying knowledge
This includes using new scenarios to prepare you for tackling unfamiliar problems, both in science and beyond.
In exams this might look like applying your understanding of bonding, energy, or equilibria to a context you’ve never seen before
For example:
You might be told that a new compound only conducts electricity when molten
You then use your knowledge of ionic bonding, lattice strength, and equilibrium shifts to explain its behaviour.
Questions like these show examiners you understand the science, not just the memorised facts.
How to succeed in GCSE Chemistry
Understand the basics first
Chemistry is like building a house, you need solid foundations. Master the atomic structure, bonding, and Periodic Table topics first. These ideas turn up everywhere:
When you see the patterns, the rest of the course starts to click. There are patterns in:
Groups
Periods
Valency
Behaviour of metals and non-metals
Don’t rush these topics. Take time to understand why atoms behave as they do and how the periodic table is organised. Once those rules feel natural, calculations, mechanisms, and exam questions become far less intimidating.
Teacher’s tip: Build a “foundations routine” once a week:
Using the Periodic Table write electron configurations for the first 20 elements.
Use a quick flowchart to decide bonding type and predict one property that follows
For example:
Ten focused minutes like this pays off massively when topics get tougher.
Learn through practice
Regular practice with exam questions:
Builds your confidence
Helps you spot patterns in how questions are asked.
Start with simpler questions and gradually work up to more challenging ones. Each time you get something wrong, use it as a learning opportunity to strengthen your understanding.
Past papers from exam boards like (opens in a new tab)AQA (opens in a new tab), (opens in a new tab)Edexcel (opens in a new tab), and (opens in a new tab)OCR (opens in a new tab) are invaluable for this practice.
Make the most of Required Practicals
Don’t just go through the motions in practical lessons, really think about why you’re doing each step. Every experiment has a purpose, whether it’s testing for ions, measuring rates of reaction, or exploring energy changes. I always remind my students that the lab isn’t about “ticking off” an activity. It’s a chance to see the theory from your notes come alive in front of you.
In our GCSE revision notes, we have guidance on each required practical for your GCSE courses. These give practical tips, so are useful both before and after your lessons. Even something straightforward, like investigating how the concentration of acid affects the rate of a reaction, can suddenly make collision theory click in a way that reading alone can’t.
Use visual aids
Chemistry involves lots of abstract concepts that become clearer with visual representation:
Revision posters can help with chemical structures
Flashcards help you remember key facts and equations
Diagrams and flow charts can help with complex processes
For example, fractional distillation is a process you’ll often see tested in GCSE Chemistry. A great way to prepare is to be able to draw and explain how the fractionating column works. Visualising it in this way makes it much easier to recall in the exam.
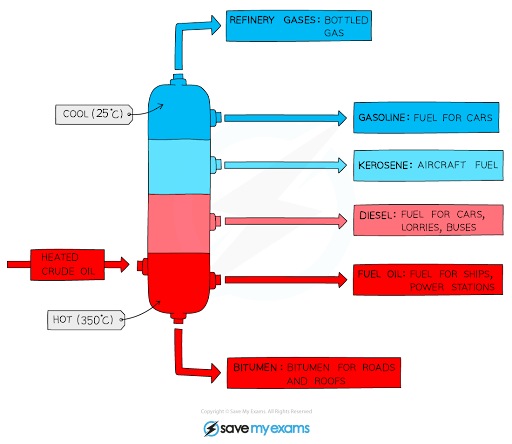
Diagram showing the process of fractional distillation to separate crude oil in a fractionating column
Many students find that colour-coding different types of information helps with memory and understanding.
In class, I often ask students to cover up a diagram they’ve drawn and then try to sketch it again from memory. It’s a quick self-test that shows you instantly which parts you’ve really understood and which bits you need to revisit.
Why study Chemistry?
Chemistry opens doors to some of the most exciting careers in science and beyond.
If you're considering A-Levels, chemistry provides excellent preparation for subjects like:
Biology
Physics
Environmental Science
Psychology
Many universities require or prefer chemistry for courses in:
Environmental studies.
Chemistry can lead to careers in pharmaceutical research, environmental consultancy, forensic science, food technology, and materials engineering. Even if you don't become a chemist, the analytical thinking and problem-solving skills are transferable.
The (opens in a new tab)Royal Society of Chemistry (opens in a new tab) reports that chemistry graduates have some of the highest employment rates among science subjects, with strong earning potential throughout their careers.
Beyond careers, chemistry helps you understand important issues like climate change, medical treatments, and sustainable technology. It makes you a more informed citizen who can evaluate scientific claims and make better decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is GCSE Chemistry hard?
Chemistry can be challenging, but it's definitely manageable with the right approach. The secret is to build your understanding step by step, instead of trying to memorise everything at once. Once you’ve got the fundamentals of atomic structure and bonding, the rest of the course starts to feel much more logical. It’s like suddenly seeing how all the pieces of a puzzle fit together. I’ve seen countless students who were struggling at first, become more confident once those foundations clicked.
Teacher’s tip: If a topic feels overwhelming, break big topics into small chunks. For example, instead of trying to learn the whole of bonding in one go, chunk it into smaller sessions:
Small wins build confidence, and before you know it, the bigger picture starts to fall into place. For more tips and information, check out this article ‘Is GCSE Chemistry Hard?’
Do I need Triple Science to take A-Level Chemistry?
While some schools prefer students to have studied separate sciences, many accept Combined Science students for A-Level Chemistry. Check with your chosen sixth form or college about their specific entry requirements.
Triple Science does provide deeper preparation, but motivated Combined Science students can succeed at A-Level with extra support.
What exam board is best for Chemistry?
AQA, Edexcel, OCR exam boards follow the same national curriculum, so content is very similar. Your school will choose based on their experience and resources.
Focus on understanding the chemistry rather than worrying about which exam board you're studying - the fundamental science is the same everywhere.
What are the best revision resources?
The most effective approach to revision really does vary from student to student, so it’s worth experimenting until you find what suits you best.
In my experience, the strongest revision plans combine different types of resources, for example, using class notes and textbooks to build understanding, past papers to practise exam technique, flashcards for key definitions, and videos or diagrams to bring abstract processes to life. Mixing these methods keeps revision fresh and helps you strengthen both your memory and your problem-solving skills.
School textbook and notes | ||
Study groups with classmates | ||
How are required practicals assessed in the exam?
You won't repeat the actual experiments in your exam, but you'll answer questions about them. These might ask about:
Method
Safety considerations
Expected results
How to improve the experiment.
Keep detailed notes about each practical, including the equipment used, safety precautions, and the scientific principles being demonstrated.
Final thoughts
GCSE Chemistry might seem daunting at first, but it’s also one of the most rewarding subjects you can study. Every lesson reveals something new about how the world works at its most fundamental level from the atoms in your body to the fuels that power our lives.
With persistence and the right support, you can not only master GCSE Chemistry but also open doors to exciting opportunities in the future. Don’t forget online resources, either. Save My Exams is full of tools designed to support your learning throughout your GCSE Chemistry course. You can:
You don’t have to use it all in one go, but work on building a habit of using what’s already available will give you a real advantage. That’s what smart preparation looks like.
After teaching Chemistry for over 15 years, I’ve seen students of every ability and background succeed. Many of these students started out doubting themselves. The biggest difference wasn’t “natural talent,” but perseverance, curiosity, and the courage to keep asking “why?” If you stick with it, Chemistry will reward you with a way of seeing the world that very few subjects can offer.
Whatever your learning style or starting point, there’s a strategy that will work for you. Embrace the journey of discovery Chemistry offers, you might be surprised by just how fascinating and empowering it becomes once the pieces start falling into place.
References
AQA GCSE Chemistry Specification (opens in a new tab)
Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Specification (opens in a new tab)
OCR GCSE Chemistry A (Gateway Science) Specification (opens in a new tab)
Joint Council for Qualifications (opens in a new tab)
Royal Society of Chemistry (opens in a new tab)
Was this article helpful?
Sign up for articles sent directly to your inbox
Receive news, articles and guides directly from our team of experts.

Share this article
 written revision resources that improve your
written revision resources that improve your