The T Lymphocyte Response (AQA A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7402
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are another type of white blood cell that
play an important part in the specific immune response
are smaller than phagocytes
have a large nucleus that fills most of the cell
are produced in the bone marrow before birth
There are two types of lymphocytes (with different modes of action)
T-lymphocytes (T cells) target and destroy abnormal or infected body cells; this is known as the cellular response
B-lymphocytes (B cells) produce antibodies that target antigens in body fluids; this is known as the humoral response
The T-Lymphocyte (cellular) response
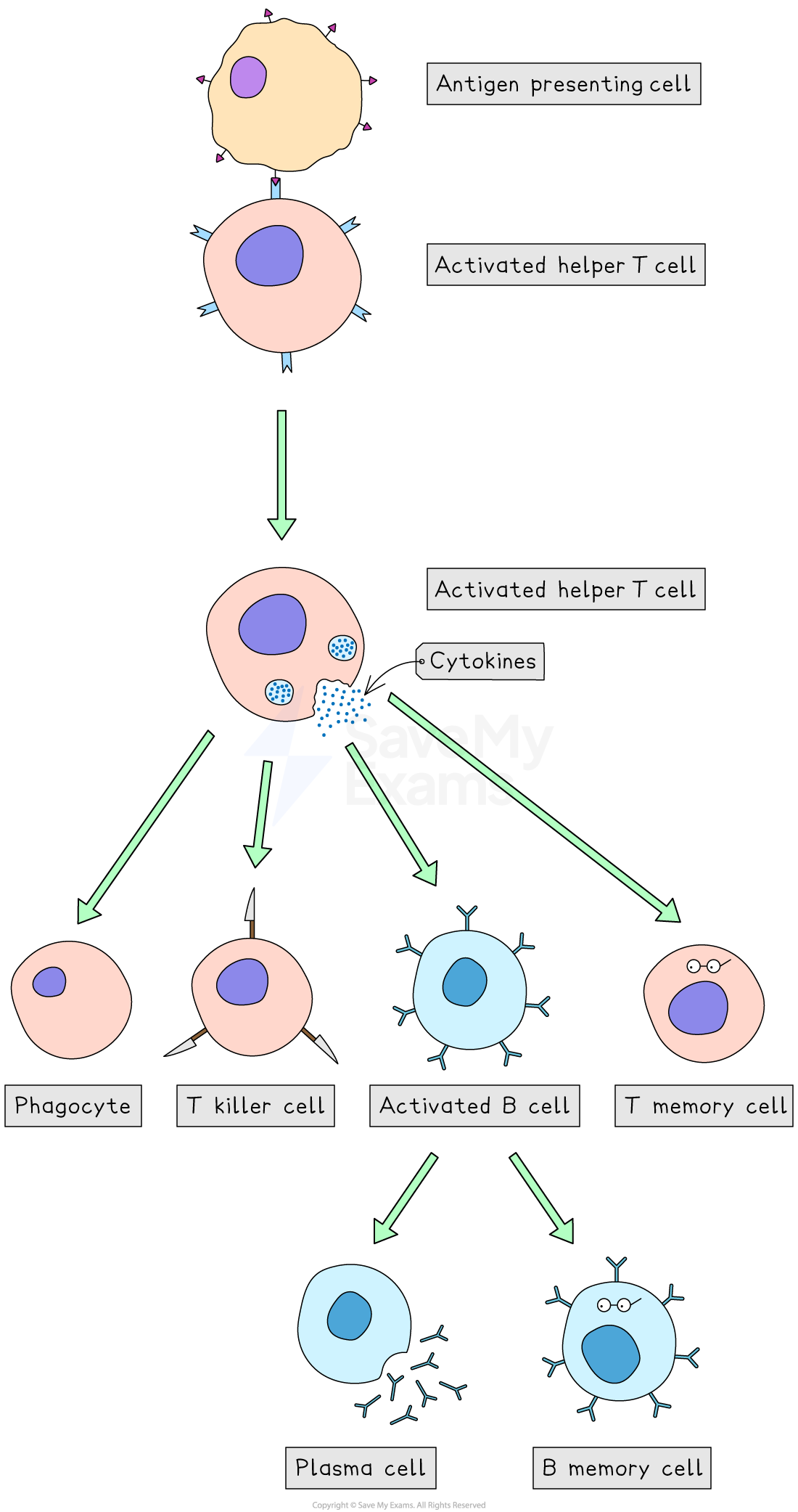
Antigen-presenting cells
An antigen-presenting cell is one of the host's cells that has been invaded by a pathogen and is displaying the antigen on its cell surface membrane
These antigens are displayed on major histocompatibility complexes (MHCs)
The role of antigen-presenting cells is to activate specific T cells that have complementary receptors to the antigen
The role of T helper cells
T helper cells (or helper T cells) are activated when they encounter (and bind to) their specific antigen on an antigen-presenting cell e.g. a macrophage
These activated helper T cells divide by mitosis to form clones
Helper T cells release cytokines, which stimulate
maturation of B-lymphocytes into antibody-secreting plasma cells
production of memory B and T cells
an enhanced rate of phagocytosis
activation of cytotoxic T cells (T killer cells)
Cytotoxic T cells
T killer cells patrol the body for infected cells displaying foreign antigens
They bind to these antigens and release toxic substances to destroy the infected cells and pathogens
Perforins create holes in the membrane, allowing toxins to enter and kill the cell

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
