The B lymphocyte Response (AQA A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7402
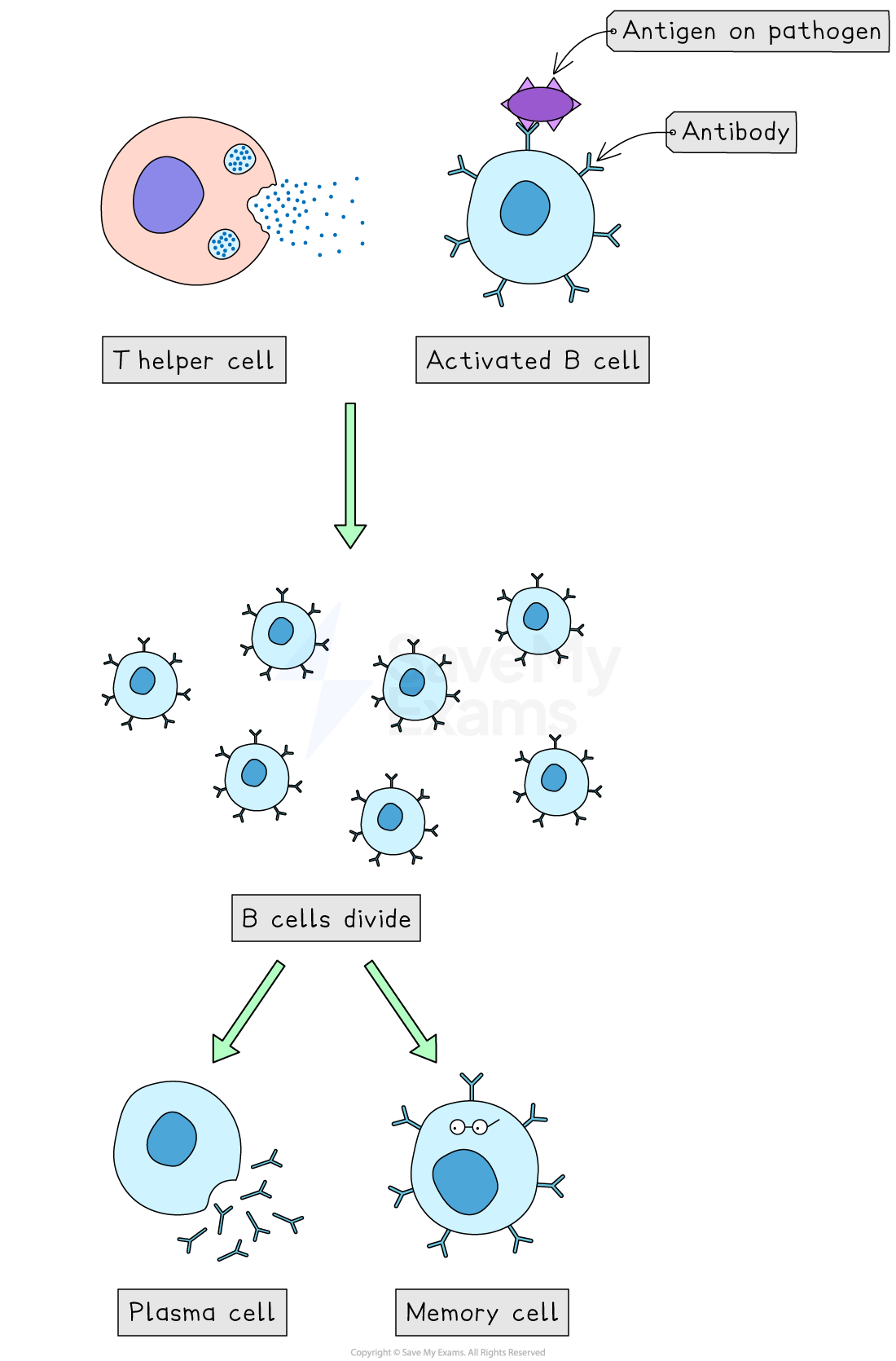
The B lymphocyte (humoral) response
Each mature B lymphocyte has a specific antibody on its surface, which acts as a receptor
Clonal selection occurs when a B cell binds to a complementary antigen
The activated B cell divides by mitosis (clonal expansion) into:
plasma cells – secrete large amounts of antibodies
memory cells – remain in circulation and provide a faster secondary response
The immune response that involves B lymphocytes and the production of antibodies is called the humoral response

Primary immune response
When an antigen enters the body, B cells are activated through two mechanisms
Antigens on the pathogen bind directly to antibody receptors on B lymphocytes
Antigen-presenting cells bind to antibody receptors on B lymphocytes
These specific B cells are activated and begin to divide by mitosis – this is called clonal selection
The B cells multiply to produce many identical copies - this is called clonal expansion
Some become plasma cells that make and release lots of specific monoclonal antibodies into the blood and tissues
Plasma cells are short-lived, but the antibodies stay in the body for some time
Other B cells become memory cells which stay in the blood and provide long-term immunity
This primary immune response is slow because it takes time to make enough antibodies
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Do not confuse these two terms, they are similar but have key differences:
Clonal selection – The process where a specific B or T lymphocyte is activated after binding to a complementary antigen
Clonal expansion – The process where the selected lymphocyte divides by mitosis to produce a large number of identical cells

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
