Glycolysis (AQA A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7402
Did this video help you?
Aerobic respiration: glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first stage of respiration and takes place in the cell cytoplasm
Oxygen is not required for glycolysis, so it can be said to be an anaerobic process
Glycolysis occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration
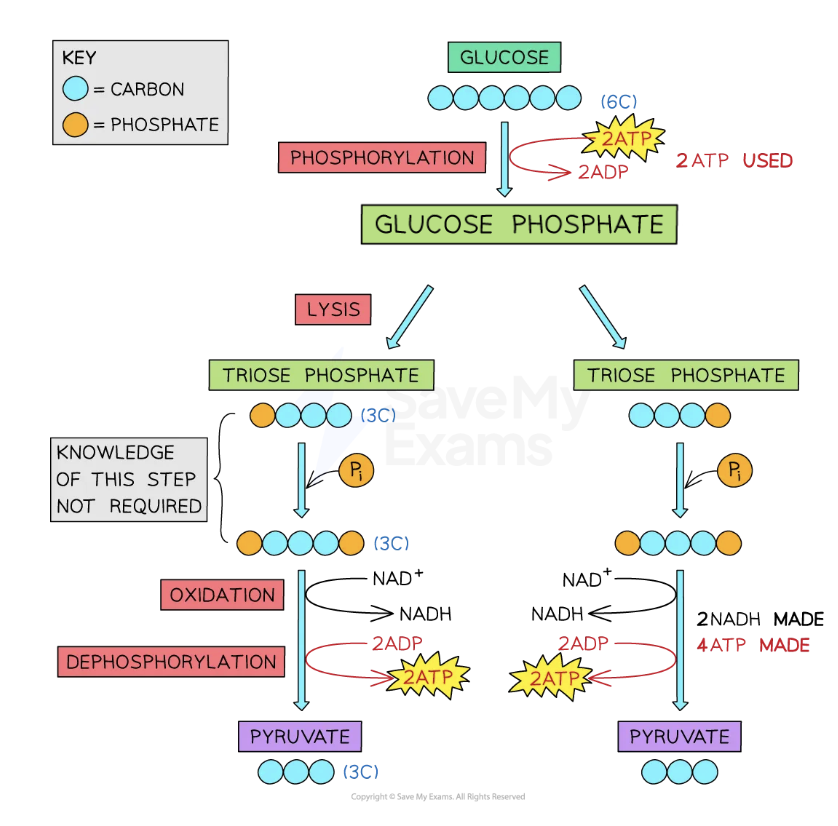
Glycolysis involves the following stages:
phosphorylation of glucose (6C) to glucose phosphate; this process requires 2 x ATP molecules
The addition of phosphate here makes glucose more reactive
splitting of glucose phosphate (6C) to produce two molecules of triose phosphate (3C)
oxidation of triose phosphate to pyruvate (3C)
Electrons and hydrogen are transferred to NAD, so 1 x NAD is reduced per molecule of triose phosphate
Phosphate groups are transferred to ADP in substrate-level phosphorylation, so 2 x ATP are produced per molecule of triose phosphate; a total of 4 x ATP
The products of glycolysis include:
2 x pyruvate (3C)
a net gain of 2 x ATP
2 x reduced NAD
Examiner Tips and Tricks
ATP is needed during glycolysis to make glucose more reactive, as it is usually a very stable molecule. As 2 ATP are used and 4 are produced during the process, there is said to be a net gain of 2 ATP per glucose molecule.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
