Ecosystems (AQA A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7402
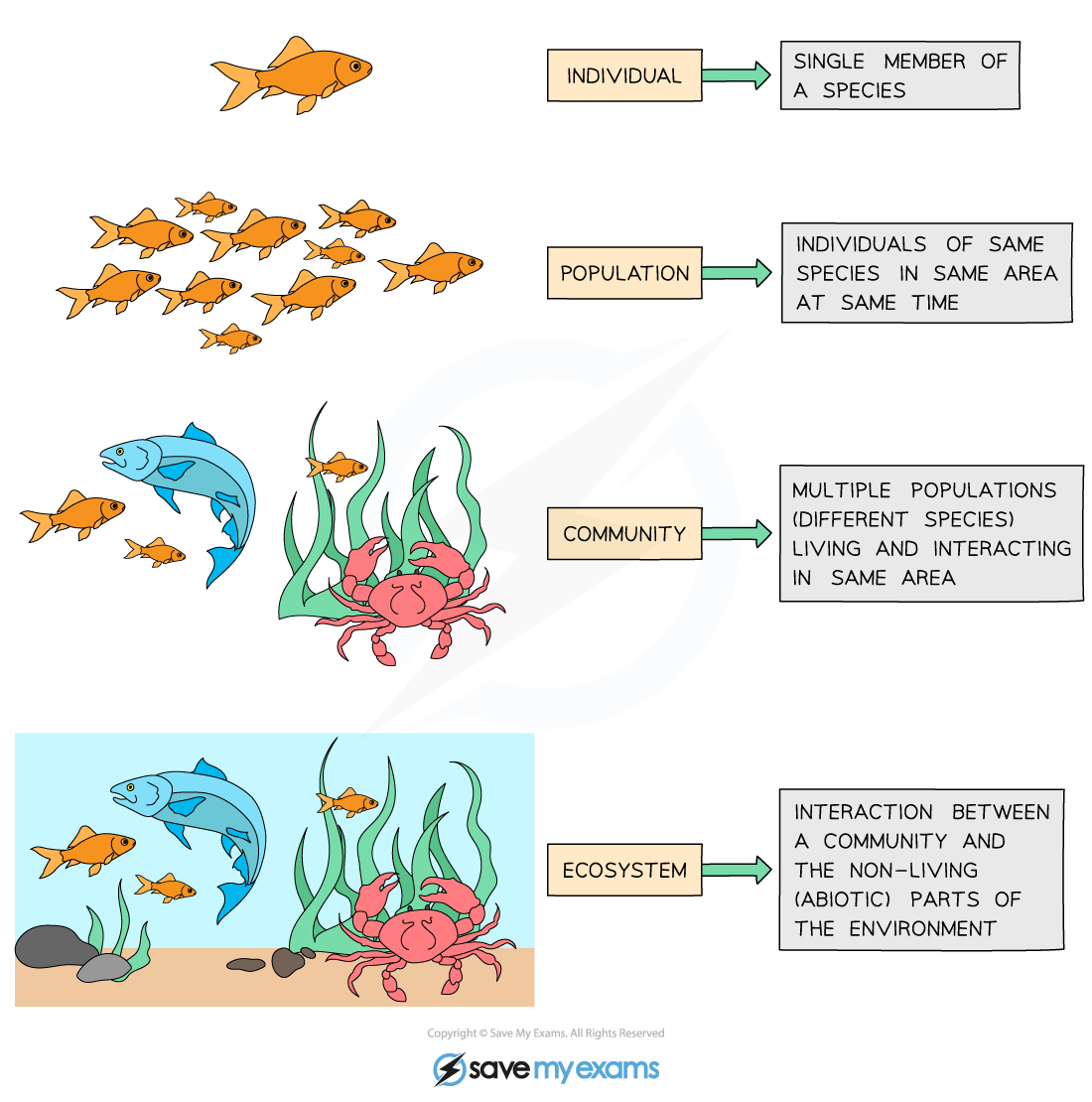
Key terms in ecology
Biotic and abiotic factors
Biotic factors are defined as:
the living components of an ecosystem that affect the survival and reproduction of organisms
Examples include:
predation
competition
disease
food availability
Abiotic factors are defined as:
the non-living components of an ecosystem that affect living organisms,
Examples include:
temperature
light intensity
pH
water availability
mineral ions
Ecosystems
An ecosystem can be defined as:
a community and its interactions with the non-living factors in the environment
There is a flow of energy within an ecosystem and the nutrients within it are recycled
E.g. in the carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycles
Ecosystems vary greatly in size and scale
E.g. both a small pond in a back garden and the open ocean could be described as ecosystems
Populations
A population is defined as:
a group of organisms of the same species living in a particular space at a particular time that can potentially interbreed
Communities
A community can be defined as:
multiple populations living and interacting in the same area
Within a community, each species depends on other species, e.g. for food, shelter and pollination
If one species is removed it can affect the whole community; this is called interdependence
Habitats
A habitat is:
the local environment in which a species normally lives
E.g. badgers, deer, oak trees and ants are all species that would live in a woodland habitat
Organisms adapt to their habitat through natural selection in order to survive and reproduce successfully
Niche
A niche is the role an organism plays in its ecosystem, including its:
use of resources
responses to abiotic factors
interactions with biotic factors
Each species has a unique niche – only one species can occupy a particular niche
If the niches of two species overlap then the species compete with each other; this can result in either:
one species outcompeting the other; the less successful species may adapt to a new niche or may become locally extinct
both populations continue to exist, but with smaller population sizes than they would have in the absence of competition
A species’ niche is determined by its adaptations:
Adaptations are structural, physiological or behavioural traits that allow survival under specific conditions
Example: Warbler species
Three North American warbler species live in the same conifer habitat
They reduce competition by feeding at different heights in the trees
This niche differentiation allows them to co-exist in the same habitat


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
