Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Product Life Cycle (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Stages of the product life cycle
The product life cycle describes the different stages a product goes through from its conception to its eventual decline in sales
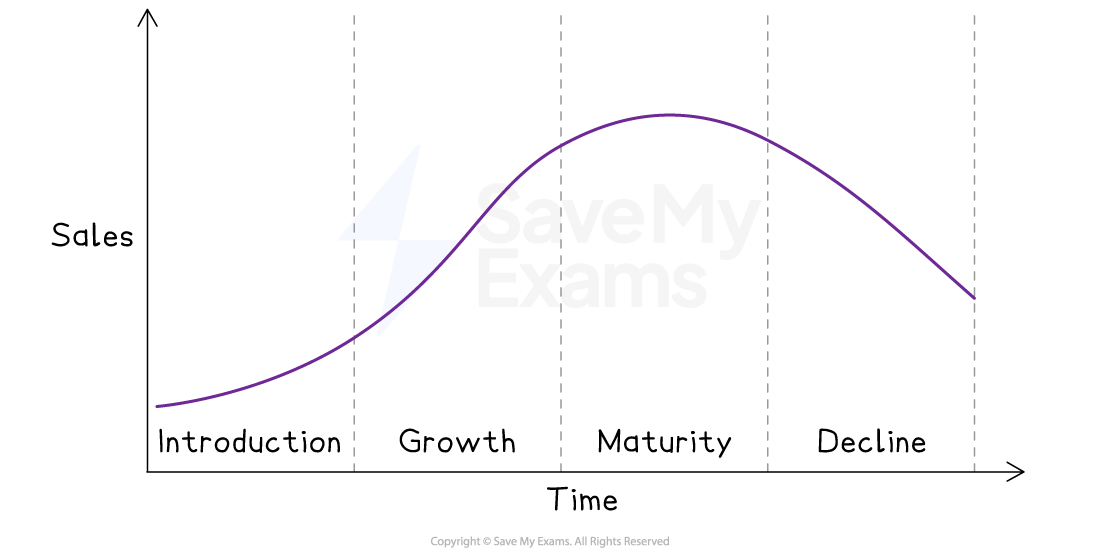
There are typically four stages in the product life cycle: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline
The product life cycle diagram
Interpreting product life cycle diagrams
Each stage of the product life cycles affects a business in different ways, such as changes in sales, profit, cash flow and how the product is marketed
By recognising which stage a product is in, businesses can make better decisions to stay competitive and profitable
Introduction
This stage begins when the product is launched
Sales grow slowly as the product is still new and not widely known
Cash flow is usually negative due to high promotion, advertising and distribution costs
Marketing focuses on building awareness and interest
Growth
Sales rise quickly as the product gains popularity
The business works to increase market share and boost production to meet demand
Cash flow often turns positive as revenue grows and costs are spread over more units
Marketing aims to stand out from competitors and build brand loyalty
Maturity
Sales remain high but growth slows due to market saturation
Cash flow is usually strong as sales continue and costs fall through efficiency and economies of scale
Marketing focuses on keeping market share and improving profits through cost-cutting or expanding into new markets
Decline
Sales fall as the product becomes outdated or replaced by newer alternatives
The business shifts to controlling the decline and cutting costs
Cash flow may turn negative due to falling sales and higher related costs
Marketing may involve discounting, clearing stock or finding new uses for the product
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful not to assume all products follow the life cycle perfectly – in exams, show awareness that some products skip stages or decline quickly, which demonstrates deeper understanding
Extension strategies
Extension strategies refer to the techniques used by businesses to extend the life of a product beyond its natural life cycle
These strategies are designed to boost sales and maintain profitability for a product that has reached the late maturity or decline stage of its life cycle
Types of extension strategies
Enter new markets
Selling the product in a new geographic area or to a new customer group
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Find new uses for a product
Promoting different ways the product can be used
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Adapt the product or packaging
Changing design, features, size or packaging to attract new interest
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Increase advertising
Launching a new advertising campaign to remind or attract customers
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Increase sales promotion
Offering discounts, loyalty rewards or competitions to increase short-term sales
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Recommending a suitable extension strategy
A business must carefully choose the right extension strategy based on its product, market and resources
Factors affecting the choice of extension strategy
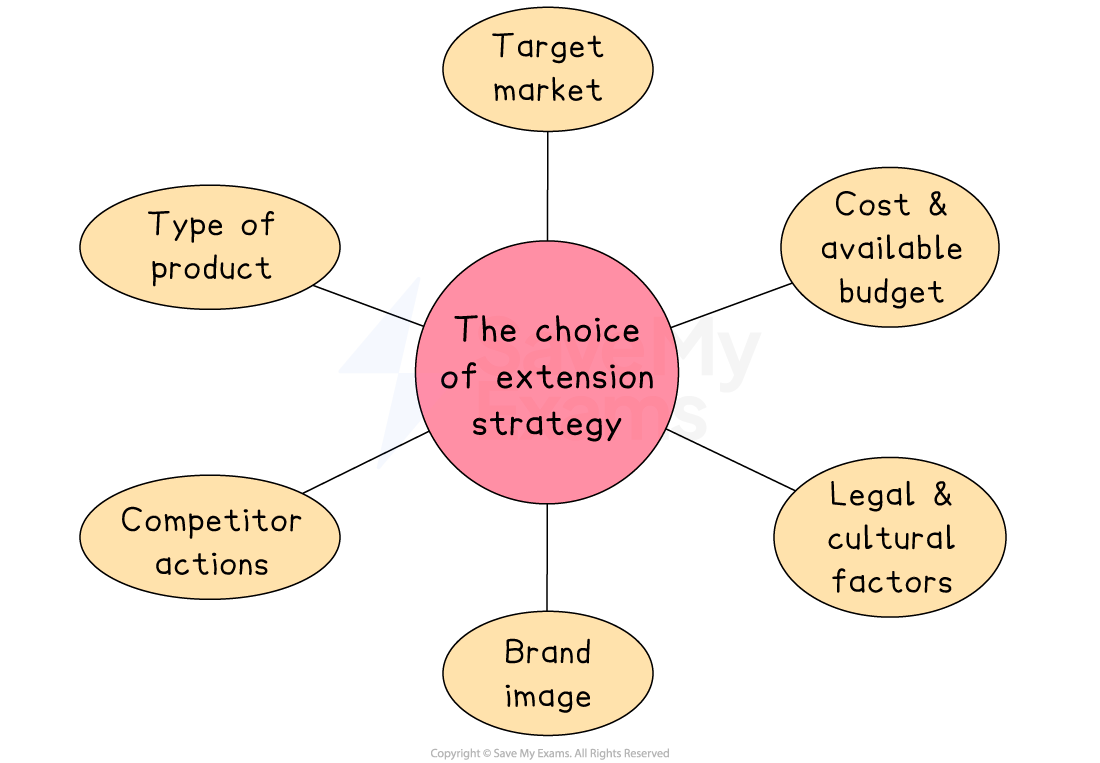
Type of product
Some products are easier to adapt than others
For example, a smartphone can be upgraded regularly, while bottled water has fewer options for change
Perishable goods or fashion items may need quicker updates to stay relevant
Target market
The business must consider who its customers are and what they want
If the target market is young and trend-sensitive, advertising or new packaging may work well
If the market is price-sensitive, sales promotions could be more effective
Cost and budget
Some strategies are cheaper than others
For example, increasing advertising or offering promotions can be done quickly but may be costly
Adapting the product or entering new markets often requires more time and money
Competitor actions
If competitors release new versions or lower prices, a business may need to respond with an extension strategy
This helps maintain market share and keeps the product competitive
Brand image
A well-known brand must protect its reputation
Some strategies, like discounts, may hurt a premium brand’s image
Legal or cultural factors
When entering new markets, the business must consider different laws and customer preferences
Packaging, promotion, or even the product itself may need to change to suit the local culture or rules
Case Study
Choco Luxe Extension Strategies
ChocoLuxe is a French luxury chocolate brand. Its Dark Caramel Crunch bar is now in the decline stage, with falling sales due to changing consumer habits

The company is considering three extension strategies
Adapting the product
Create a low-sugar version to appeal to health-conscious customers
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Entering new markets
Sell in new regions such as Asia or the Middle East
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Increased advertising
Launch a campaign highlighting ethical sourcing and premium quality
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Recommendation
ChocoLuxe should adapt the product by launching a low-sugar version, supported by fresh advertising
This approach targets current trends and builds on the brand’s strengths
Entering new markets could be explored later but is not urgent
Advertising is high cost and may not be enough to persuade customers to buy the dated product

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
