Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Factors Influencing Location Decisions (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
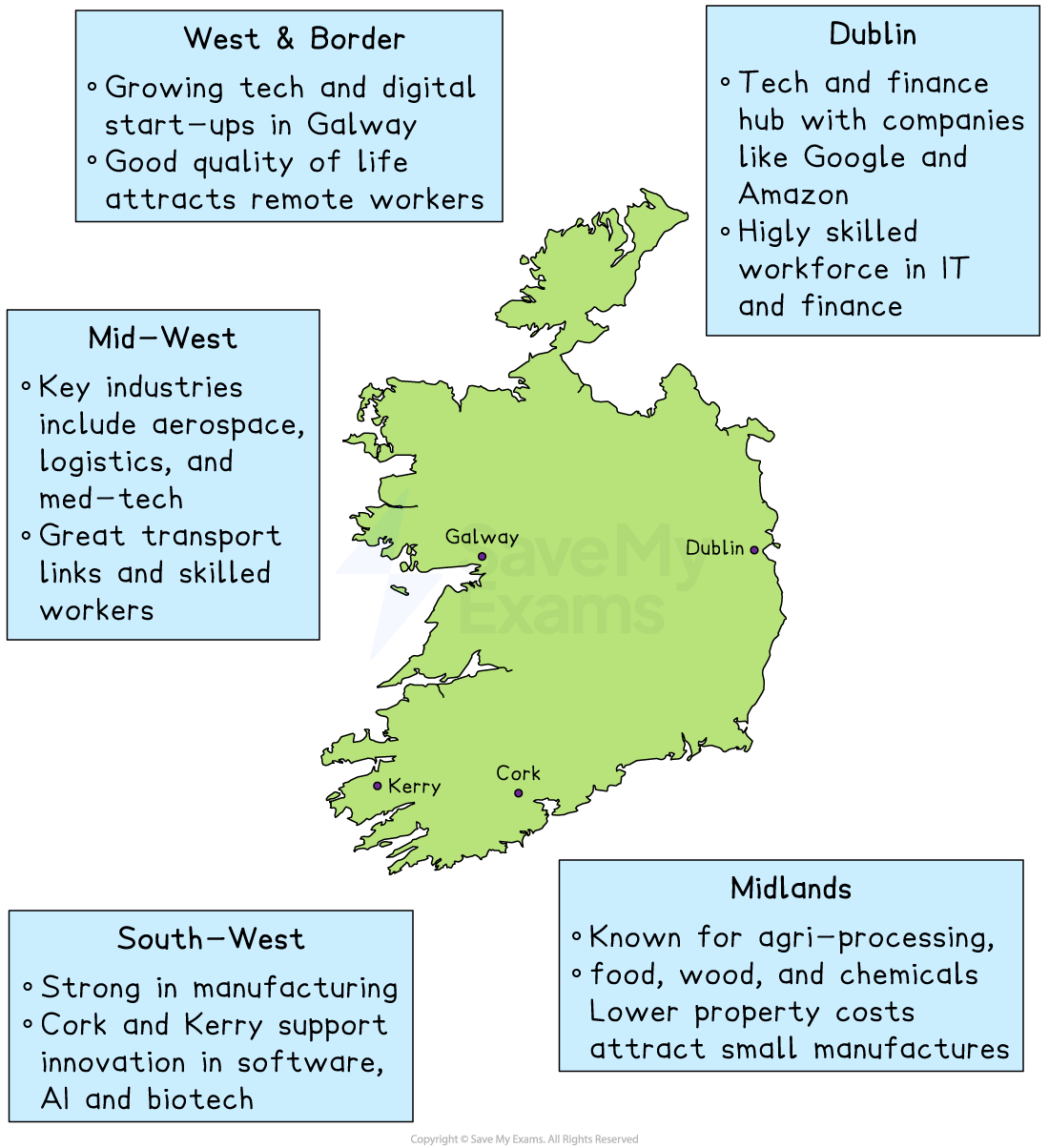
Manufacturing business locations
Location is the site from which a business decides to operate
A business will consider location if it is setting up for the first time or its existing location no longer meets its needs
A new site may become available that is more attractive to the business
For example, it has a larger staff car park or room for further expansion
Choosing a good production location can have significant impacts on a business.
A range of factors influence the location a business chooses for production
Factors affecting manufacturing business location

Proximity to the market
This refers to how close the business is to its target customers
Being near the market can reduce transport costs and make it easier for customers to access the business
Proximity to labour
This means being located near areas where skilled and qualified workers are available
Businesses often choose locations with a strong local workforce to make it easier to hire the right people and run operations efficiently
Proximity to materials
This refers to how close a business is to the raw materials or supplies it needs
Being near materials helps reduce transportation costs and ensures a steady supply
Proximity to competitors
Some businesses choose to locate near competitors to attract the same customer base or to offer something different
Others may avoid locating near competitors to reduce direct competition
The nature of the business activity
Different types of businesses have different location needs based on what they do
For example, a manufacturing plant may need large space and delivery access, while a law firm may need a smaller, more central office
For example, a factory needs room for machinery and deliveries, while a law office needs a professional, easy-to-access location
Infrastructure
This includes transport links and electronic networks like internet connections
Good transport is essential for businesses that deliver physical goods
Fast and reliable internet is key for online businesses
For example, an online fashion retailer needs a location close to the motorway for quick delivery and fast service, helping it compete in the market
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don’t assume “low costs” are always the main factor – examiners expect you to recognise that priorities differ, e.g. a factory may focus on raw materials while a retailer prioritises customer access
Service businesses locations
Businesses in the service sector consider further factors when determining a suitable location
Proximity to customers is very important for retail businesses
Premises must be accessible and convenient so a location with a car park or close to transport links is likely to be attractive
Locating in areas with high footfall, such as on a high street or in a shopping mall, is a popular choice for retailers
In some cases, a location may be chosen to take advantage of a shared customer base or a particular reputation
Examples include bookshops on London's Charing Cross Road and luxury fashion brands on New York's Fifth Avenue
Climate and geographical factors can be a key factor for some specialist service providers
For example. businesses that offer ski instruction are located in mountainous areas with high annual snowfall
Services businesses that do not rely on passing trade may locate in out-of-town premises
Rent and business rates tend to be lower
Incentives for job creation such as grants may be available from local authorities
In addition, businesses are likely to avoid locating in areas with high levels of anti-social behaviour and crime, as this could impact insurance costs
Factors to consider when choosing a country to produce in
When a business chooses which country to locate operations in, such as manufacturing, customer support or regional headquarters, it must consider a range of factors
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Trade barriers |
|
Financial incentives |
|
Labour costs & skills |
|
Corporate tax rates |
|
Access to raw materials |
|
Market access |
|
Political/legal environment |
|
Infrastructure quality |
|
Case Study
Why Multinationals Choose Ireland
Many multinational companies are increasingly choosing Ireland as a base for both service and manufacturing business operations
Very low corporation tax rate of around 12.5%
Access to a highly educated, English-speaking workforce that fits technology or R&D roles
Open immigration policies attract global skilled workers in technology, healthcare and ICT sectors
Strategic location that gives easy access to both the US and European markets
Strong infrastructure and legal environment with stable government and EU membership
Recommending an appropriate business location
When a business is choosing between possible locations, it must recommend one option and then justify (explain why) that choice using evidence
Steps in the process
Identify the options – e.g., two different sites or two different countries
Weigh up the advantages and disadvantages of each option
Consider the type of business – e.g., manufacturer vs. service provider
Think about long-term success – costs, customer access, and growth potential
Make a clear recommendation – state which option is better
Justify with reasoning – link back to the case study data (e.g. “This site is closer to customers, which is more important than slightly higher rent, because it increases sales”).
What to include in a justification
Costs: Which option keeps costs lower in the long run?
Revenue: Which location gives better access to customers or markets?
Suppliers: Is one location closer to raw materials or supply chains?
Labour: Are skilled workers available?
Competition: Is one site less competitive, or does clustering with rivals increase customers?
Government: Are there incentives (e.g. tax breaks, grants)?
Risk & future growth: Which location offers better potential to expand or adapt?
Case Study
Choosing a New Production Location for Sabores del Sol
Background:
Sabores del Sol is a successful Spanish company producing ready meals and Mediterranean snacks. Rising production costs in Spain and growing demand across Europe mean the business needs to open a new international production facility.

The company is considering three possible countries: Poland, Vietnam, and Mexico.
Option 1: Poland
Benefits
Lower labour costs than Spain
Member of the EU → no trade barriers when exporting across Europe
Strong transport links throughout Europe
Skilled workforce with experience in food manufacturing
Drawbacks
Labour costs are rising gradually
Language and cultural differences
Regional bureaucracy may cause delays
Option 2: Vietnam
Benefits
Very low labour costs, ideal for mass production
Strong government support for foreign investment
Access to rapidly growing Asian markets
Expanding industrial infrastructure
Drawbacks
Long distance from Spain → higher shipping costs and delivery times
Less reliable logistics compared to Europe
Language and cultural differences could create training and communication problems
Option 3: Mexico
Benefits
Competitive labour costs and skilled food processing sector
Trade advantages when exporting to the US and Latin America
Good access to fresh raw materials
Growing export and manufacturing reputation
Drawbacks
Long distance from Spain → higher shipping costs to Europe
Political instability and safety concerns
Complex regulations in some regions
Recommendation and Justification
Poland is the most suitable location for Sabores del Sol
It offers lower production costs than Spain, while still providing a skilled workforce
Being inside the EU means there are no tariffs or trade barriers, which supports smooth and cost-effective exports to Sabores del Sol’s main market in Europe
Its strong transport links ensure reliable delivery across the continent
Vietnam and Mexico provide lower labour costs, but both are much further from Europe. This means longer delivery times, higher shipping costs, and supply chain risks, which are significant disadvantages for a company aiming to grow in the European ready-meals market
Conclusion
Poland offers the best balance of cost savings, skilled labour, and easy access to European customers. It is a low-risk, strategic choice that matches the company’s growth objectives

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
