Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Production Processes: Lean Production (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Lean production techniques
Lean production involves the minimisation of the resources used in production
Less time is required as the production process is organised in the most efficient way
Fewer materials are used, as there is a focus on waste reduction
Less labour is used, as lean production is typically capital intensive
The space required for production is reduced as a result of just-in-time inventory management
A small number of trusted suppliers work closely with the business
The use of lean production is likely to lead to a competitive advantage
Lower unit costs are achieved due to minimal wastage so prices may be lower than those offered by competitors
Better quality of output is likely as a result of supplier reliability and carefully managed production processes
1. Just-in-time inventory control
Just-in-time (JIT) is a lean production technique where raw materials are not stored on-site but ordered as required and delivered by suppliers at the moment they are required for production
Close relationships with suppliers need to be developed to ensure reliable delivery and communication
Locating the business close to suppliers can reduce transport time and costs
2. Continuous improvement (Kaizen)
Kaizen involves taking continuous steps to improve productivity through the elimination of all types of waste in the production process
Changes are small and ongoing rather than significant one-off’s
They are constantly reviewed to ensure that they achieve the desired positive impact on productivity
Kaizen requires a long-term management commitment to change
Kaizen (continuous improvement)

Elements of Kaizen commonly include
Zero defects in manufacturing
High levels of automation
High levels of cooperation between workers and management
Staff training and computer inventory management systems may also reduce wastage, as fewer errors are likely to be made
Evaluating the use of lean production
Lean production has several advantages for businesses aiming to reduce waste and improve efficiency
However, the initial implementation and ongoing monitoring of lean production has some significant drawbacks
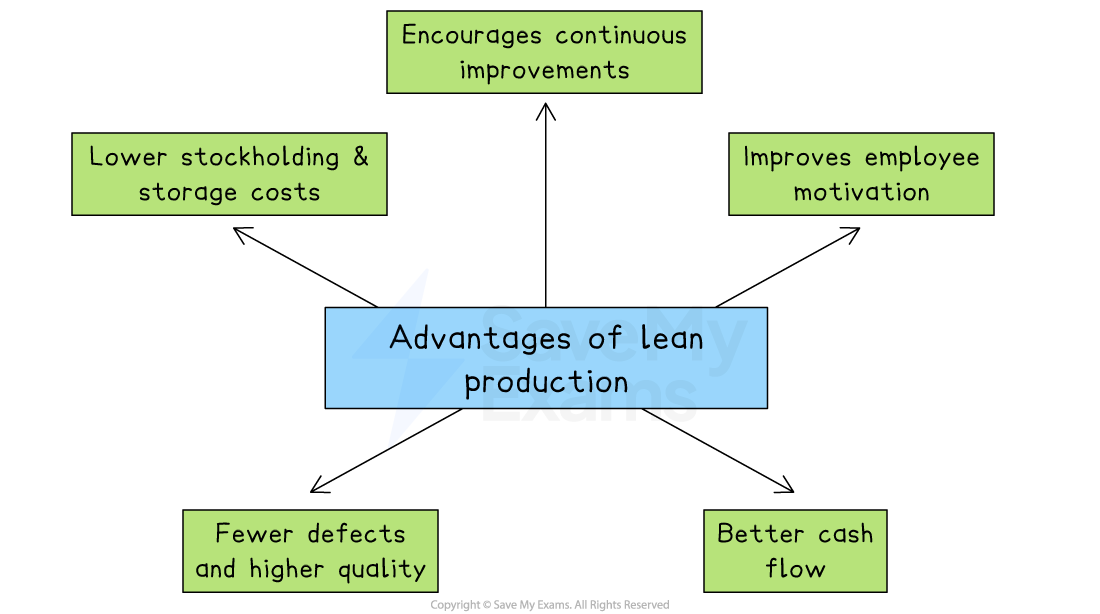
Advantages of lean production
Lean production helps to lower stockholding and storage costs
Just-in-Time (JIT) systems reduce the need to keep large amounts of inventory
Storage space can be used for more productive activities, such as extra work areas or machinery
It encourages continuous improvement
Employees regularly suggest small changes that help reduce waste and improve quality
This process allows problems to be identified and solved early
Employee motivation is likely to improve under lean production
Workers are encouraged to work in teams and take responsibility for improvements
Being involved in decision-making can make staff feel valued and more committed
Lean production improves cash flow
Because less money is tied up in stock, more cash is available for other business needs
This can help the business invest in areas like marketing, training, or technology
It can lead to fewer defects and higher product quality
Lean methods focus on doing things correctly the first time to avoid waste
This results in more efficient production and greater customer satisfaction
Disadvantages of lean production
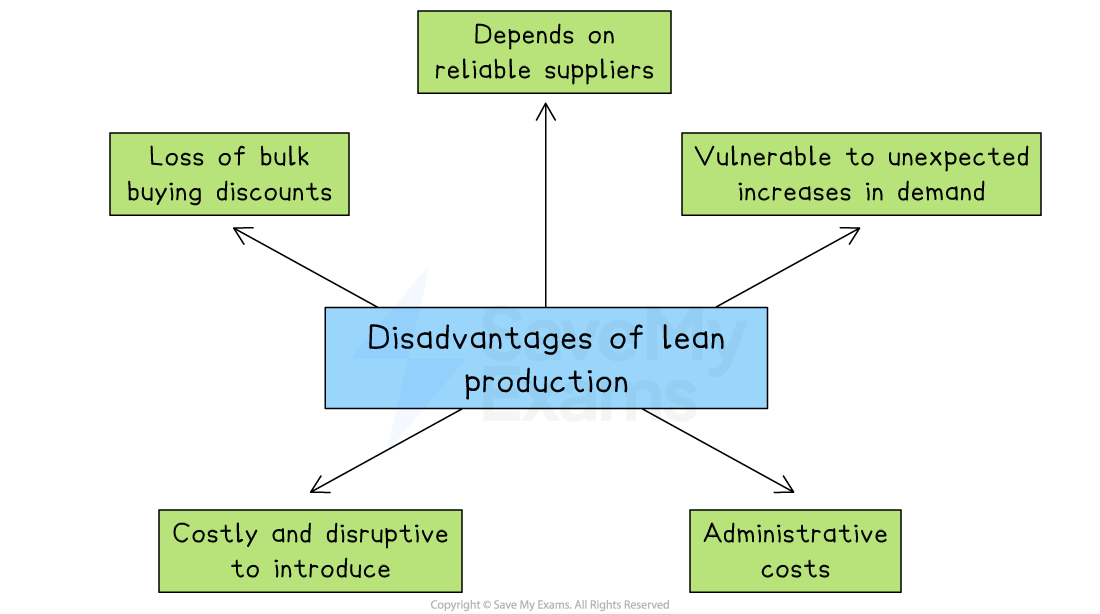
Lean production makes it harder to gain bulk buying discounts
Since businesses place smaller orders more often, they may pay more for components and raw materials, increasing unit costs
It reduces the ability to respond quickly to unexpected increases in demand
With little or no stock kept in reserve, businesses may miss sales opportunities
This can lead to dissatisfied customers or a damaged reputation
The system depends heavily on reliable suppliers
If a delivery is late or poor in quality, production may come to a complete stop
Businesses must develop strong and dependable supplier relationships
Introducing lean production can be costly and disruptive
It often requires big changes to the organisational structure and workflow
Employees may need extra training, which takes time and money
There are increased administrative costs due to frequent ordering
Managing more orders creates extra paperwork and workload for staff
This can raise overall office and back-office expenses
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common misconception is that lean production is always positive – strong answers recognise possible drawbacks, such as supply delays with Just-in-Time or employee resistance to continuous improvement

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
