Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
The Use of Technology in the Production of Goods & Services (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
The impact of technology on production methods
Technology has changed how businesses produce goods and services
It can make production faster, cheaper and more accurate, but also comes with some challenges
Advantages and disadvantages of technology in production
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Computer-aided manufacture (CAM)
Computer-Aided Manufacture (CAM) is the use of computers to control and assist with production activities
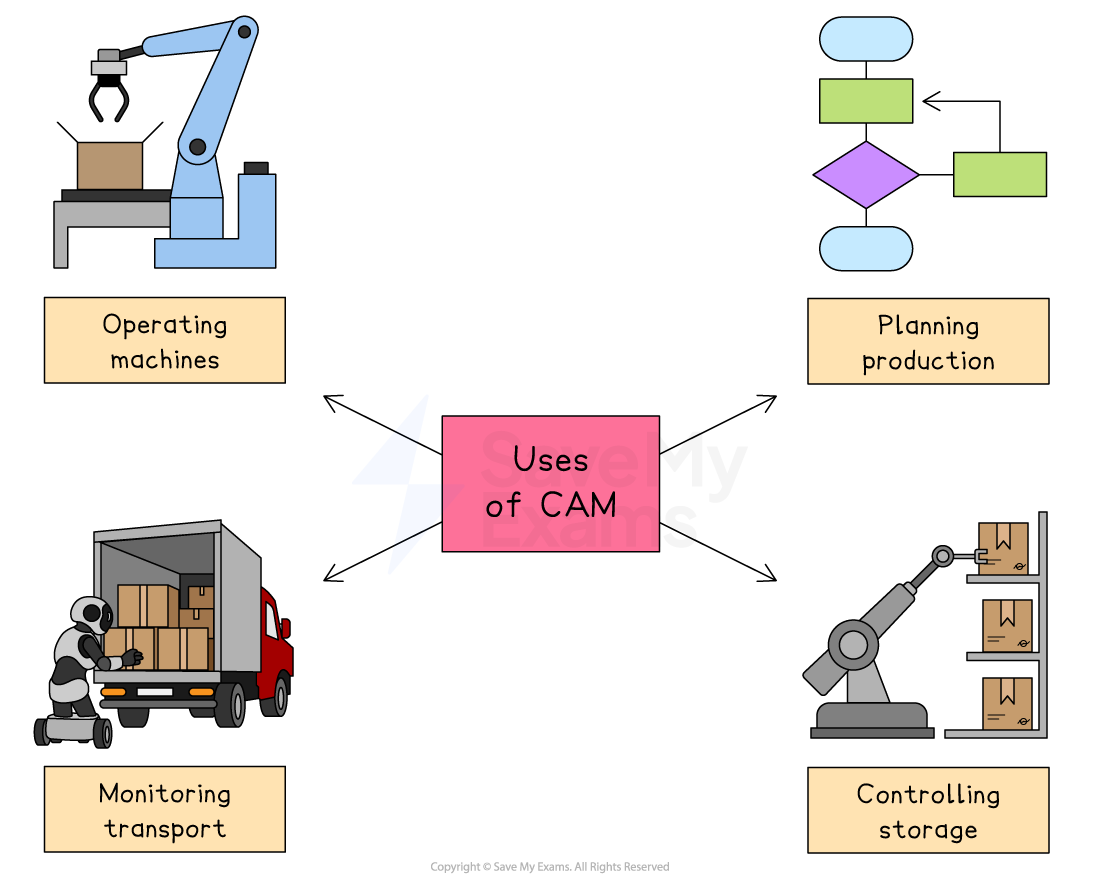
Uses of computer-aided manufacture
Operating machines
CAM controls machinery such as cutters, drills or robotic arms, ensuring tasks are completed quickly, accurately, and with consistent quality
Planning production schedules
CAM software helps plan when and how products will be made, reducing delays and making sure resources are used efficiently
Monitoring transport
CAM systems can track the movement of materials and products, helping ensure they reach the right stage of production on time
Controlling storage
CAM helps manage inventory by tracking how much stock is available, where it is stored, and when new materials need to be ordered
3D printing
Digital designs are uploaded and the 3D printer produces the product with minimal labour costs
Digital printers have been used to print car engines, houses, food and replacement limbs
The impact of 3D printing on production
Impact | Explanation |
|---|---|
Cost |
|
Productivity |
|
Quality |
|
Flexibility |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Examiners value awareness that technology is constantly evolving – mention that businesses must keep up with new developments to stay competitive and avoid falling behind rivals

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
