Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Communication Barriers (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Introducing communication barriers
Barriers to communication hinder the flow of information, leading to potential misunderstandings, conflicts and inefficiency
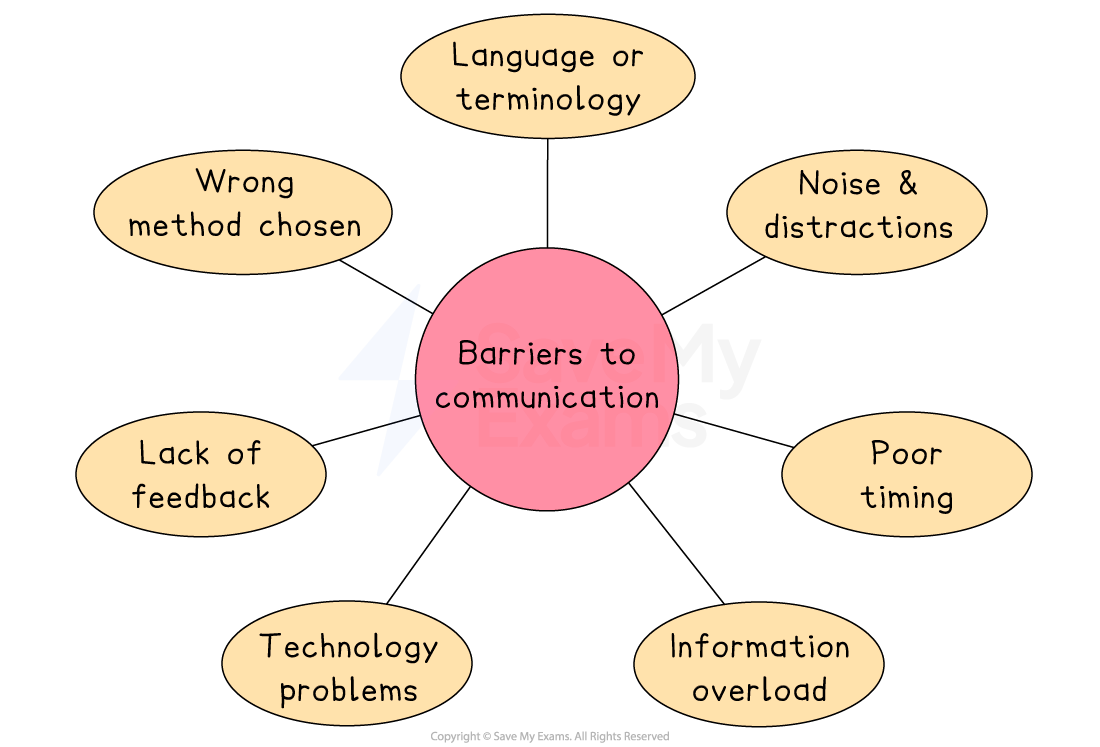
Main barriers to communication
Problems caused by communication barriers
Language or terminology
When employees use complex or technical language that others do not understand, the message can be misunderstood or ignored
For example, a manager sends an email with financial jargon that non-finance staff cannot follow, leading to confusion about budget limits
Poor timing
Messages sent at the wrong time can be missed or cause stress
For example, telling employees about a major change at the end of a busy shift may lead to frustration or lack of attention
Information overload
If people are given too many messages at once, they may ignore or forget important details
For example, a long email covering ten topics may result in staff missing a key update about health and safety
Noise and distractions
Background noise or interruptions make it difficult to focus on the message
For example, announcements made in a loud factory might not be heard clearly by workers.
Technology problems
Delays or failures in communication systems can stop messages from being delivered or received
For example, an important video meeting is missed because the link didn’t work or the internet connection failed
Lack of feedback
If no feedback is given, the sender cannot be sure the message was understood correctly
For example, a team leader sends a task by email but receives no reply, leading to delays in completing the work
Wrong method chosen
Using the wrong communication method for the message or audience can cause misunderstandings
For example, posting a notice about a sudden meeting change may not reach all employees in time
How can communication barriers be reduced or removed?
Barrier | Solution |
|---|---|
Language or terminology |
|
Poor timing |
|
Information overload |
|
Noise and distractions |
|
Technology problems |
|
Lack of feedback |
|
Wrong method chosen |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When writing about barriers, don’t stop at identifying them – stronger answers explain how they can be reduced or removed, linking solutions directly to the problem given in the question

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
