Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Policies Used To Reduce Unemployment (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0455 & 0987
Demand and supply-side solutions
Demand-side unemployment is caused by a lack of total demand in the economy and this is often related to a recession in the economic cycle
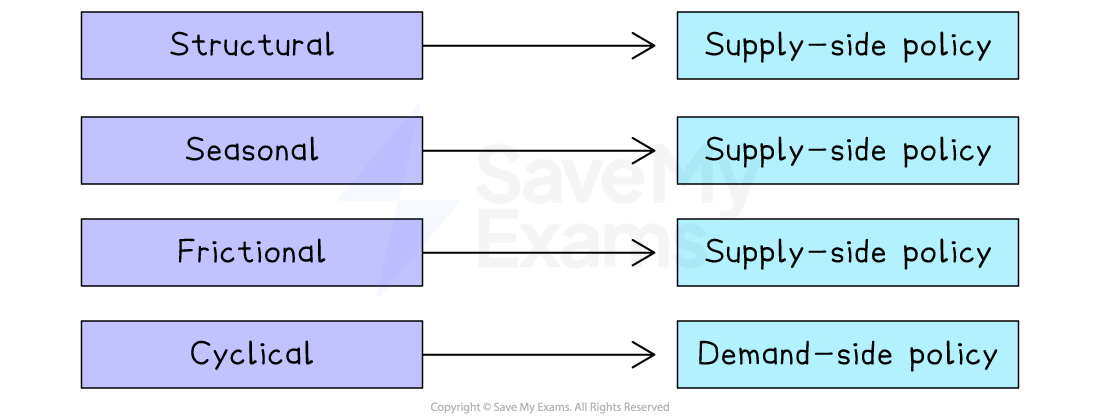
Frictional, seasonal and structural unemployment emerge from factors affecting the supply side of the economy
The appropriate government interventions to alleviate different types of unemployment depend on whether they stem from demand-side or supply-side factors
Type of policy to use for each cause of unemployment
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always link the policy to the type of unemployment in the question. For example:
Cyclical unemployment → demand-side policies work best
Structural unemployment → supply-side policies are more effective
Demand-side policies
Expansionary fiscal policy and expansionary monetary policy aim to increase total (aggregate) demand in an economy
The demand for labour is derived from the demand for goods/services
If total demand for goods and service increases there will be a higher demand for labour, leading to lower unemployment
Total demand can be increased through any policy which increases one of the components of real gross domestic product (rGDP)
Examples of demand-side policies to reduce unemployment
Broad policy type | Specific policy | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Expansionary fiscal policy |
|
|
Expansionary fiscal policy |
|
|
Expansionary fiscal policy |
|
|
Expansionary monetary policy |
|
|
How effective are demand-side policies?
Demand-side policies are very effective at dealing with unemployment caused by a fall in total (aggregate) demand
They are not effective at dealing with frictional and structural unemployment
One conflict caused by expansionary policy is that demand-pull inflation is likely to occur
Expansionary monetary policy tends to increase inequality in the distribution of income, as the poor are usually unable to benefit from it (banks do not necessarily lend to the poorest households)
Supply-side policies
Supply-side policies aim to improve the quantity and/or the quality of the factors of production, thereby raising potential output
If output increases then firms will require more workers to produce that output and unemployment may fall
Examples of supply-side policies used to reduce unemployment
Specific supply-side policy | Explanation |
|---|---|
The government reduces trade union power |
|
The government reduces regulation on the oil and banking industries |
|
The government introduces new long term training subsidies for students of green technology |
|
Effectiveness of supply-side policies
Supply-side policy tends to be long-term
E.g. reducing trade union power is a long-term process, as is training
It is most effective in dealing with unemployment caused by frictional and structural unemployment
It does not help deal with unemployment caused by demand-side issues e.g. a recession

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
