Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
The Types & Consequences of Unemployment (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0455 & 0987
Types of unemployment
There are specific causes of unemployment
Understanding the cause is helpful as each cause may require different solutions to be implemented
Types of unemployment
Type | Explanation |
|---|---|
Seasonal |
|
Frictional |
|
Structural |
|
Cyclical |
|
The consequences of unemployment
Unemployment can have serious impacts on individuals, producers/firms, the government, and the wider economy
The effects are often connected
For example, a loss of income for individuals reduces spending, which lowers firms’ sales, leading to lower tax revenue for the government
The effects of unemployment, especially long-term unemployment, are extremely damaging
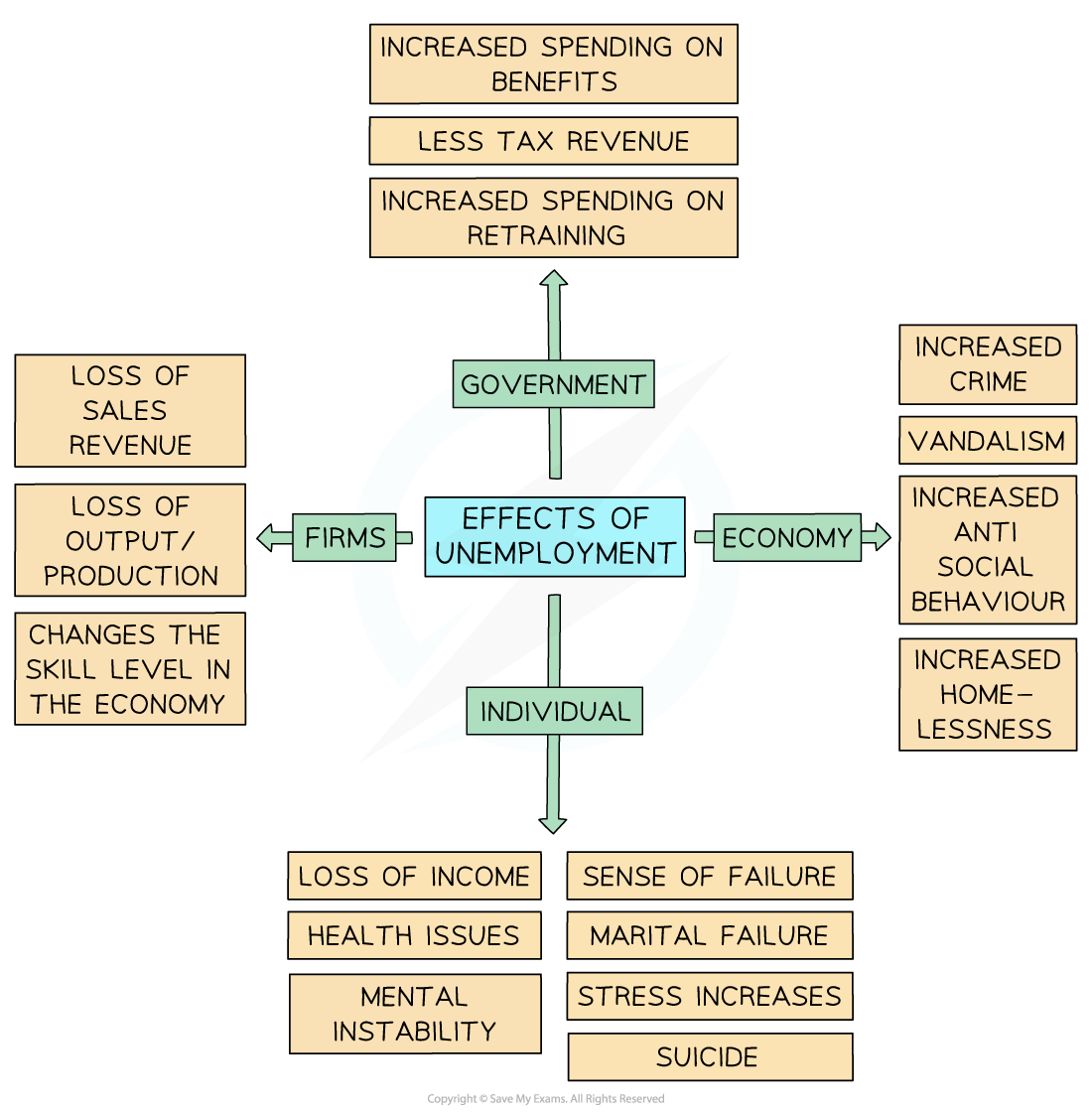
Impact on individuals
Loss of income
Unemployed people cannot earn wages, reducing their ability to buy goods and services
Sense of failure
Being without work can harm self-esteem and confidence
Health issues
Physical and mental health can suffer due to financial pressure and inactivity
Mental instability
Anxiety and depression can increase during long periods of unemployment
Marital breakdown
Financial stress can lead to relationship problems
Stress and suicide
Extreme cases of unemployment-related stress may lead to suicide
Impact on producers/firms
Loss of sales revenue
Unemployed consumers spend less, reducing firms’ income
Loss of output
Fewer workers mean lower production levels
Lower skill levels
If unemployment lasts a long time, workers lose skills, reducing the quality of the labour force
Impact on government
Increased spending on benefits
More people claiming unemployment or welfare payments
Lower tax revenue
Less income tax, corporation tax and sales tax is collected
Increased spending on retraining
Governments may need to fund programmes to help people back into work
Impact on the economy
Increased crime and vandalism
Unemployment can lead to higher crime rates due to financial desperation or social unrest
Increased anti-social behaviour
Frustration and exclusion from the labour market can cause social problems
Increased homelessness
Without income, some people may lose their homes

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
