Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Causes & Consequences of Inflation (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0455 & 0987
The causes of inflation
An increase in the general price level in an economy can be caused by demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, or imported inflation
1. Demand-pull inflation
Demand-pull inflation is caused by excess demand in the economy
Total (aggregate) demand is the sum of all expenditure in the economy
rGDP = Consumption (C) + Investment (I) + Government spending (G) + Net Exports (X-M)
If any of the four components of rGDP increase, there will be an increase in the total demand (AD) in the economy, leading to an increase in the general price level
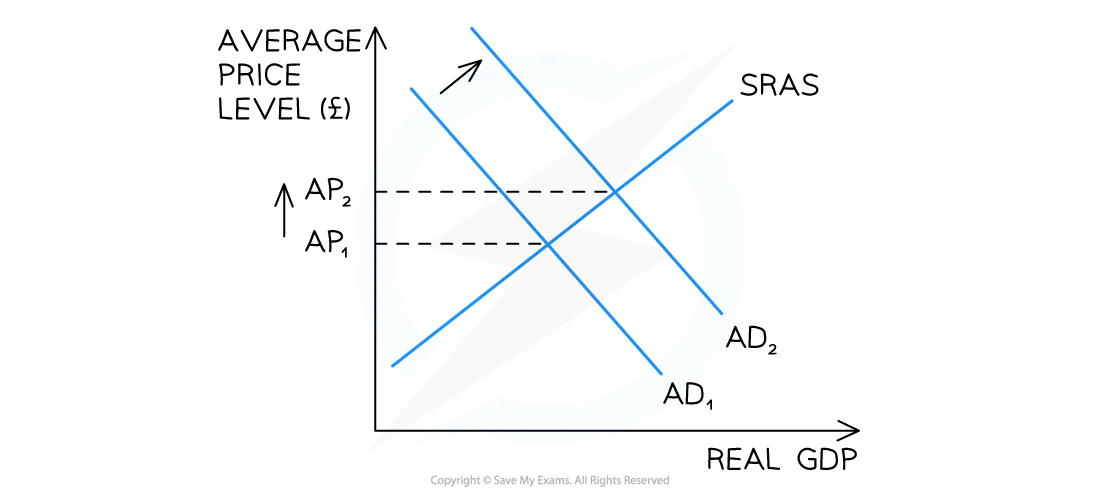
Diagram analysis
If any of the four components of AD increase, there will be a shift to the right of the AD curve from AD1 → AD2
This causes the average price level to increase from AP1 → AP2
Demand-pull inflation has occurred
An example of demand-pull inflation
If the Central Bank lowers the base rate, there is likely to be increased borrowing by firms and consumers
This will result in an increase in consumption and investment, which will increase the rGDP
It is likely to lead to a form of demand-pull inflation
2. Cost-push inflation
Cost-push inflation is caused by increases in the costs of production in an economy
If any of the costs of production increase (labour, raw materials etc.), or if there is a fall in productivity, the total supply will decrease
With less supply, prices rise, leading to an increase in the general price level
Cost-push inflation has occurred
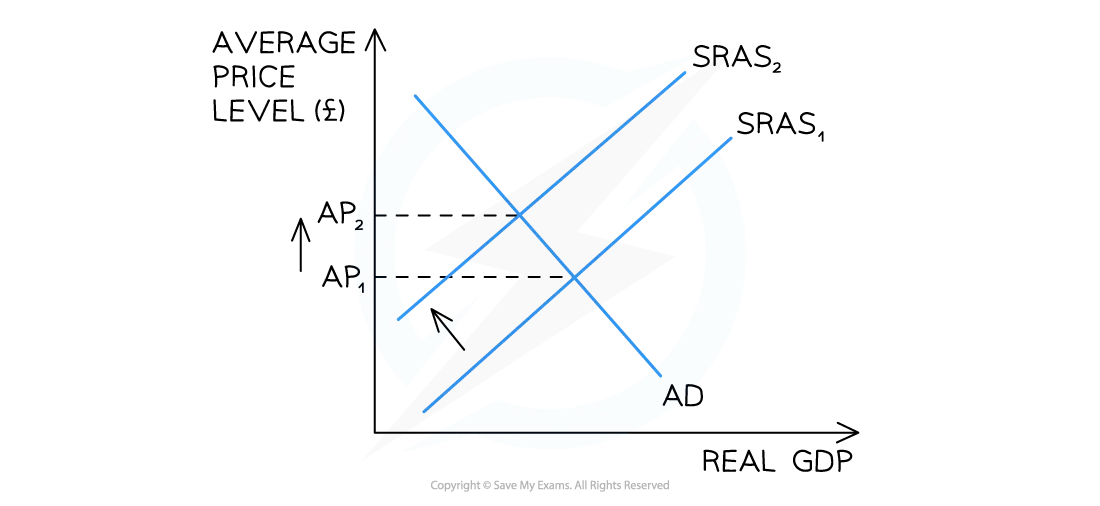
Diagram analysis
If any of the costs of production increase (labour, raw materials etc.), or if there is a fall in productivity, there will be a shift to the left of the SRAS curve from SRAS1→SRAS2
This increases the average price level from AP1 → AP2
Cost-push inflation has occurred
An example of cost-push inflation
Trade unions negotiate higher wages for workers
The wage increases represent an increased cost of production for firms
With the inputs, firms now produce less and supply reduces, leading to higher general price levels
Cost-push inflation has occurred
3. Imported inflation
Imported inflation happens when the prices of goods and services that a country imports go up, causing overall prices in the domestic economy to rise
If a country relies on imports for raw materials, fuel or food, any increase in global prices raises production costs for domestic firms
For example, if the price of imported oil rises, transport and production costs increase in many industries
This leads to higher prices for a wide range of goods.
Higher costs are usually passed on to consumers as higher prices, leading to cost-push inflation
A fall in the exchange rate (weaker currency) can also lead to imported inflation
A weaker currency makes foreign goods more expensive, even if the foreign price hasn’t changed
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Imported inflation is external — caused by global price changes or exchange rate movements, not by domestic demand or changes to domestic costs of production
The consequences of inflation
Inflation means that the general price level is rising over time. It reduces the purchasing power of money and can affect different groups in different ways
The effects on savers, lenders and borrowers
Group | Effect of inflation | Why? |
|---|---|---|
Savers |
|
|
Lenders |
|
|
Borrowers |
|
|
The effects on firms and consumers
Firms | Consumers |
|---|---|
|
|
The effects on workers and the government
Government | Workers |
|---|---|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember, governments want some inflation – usually 2-3% – as this is a sign of economic growth. However, inflation in excess of that is harmful in many of the ways described above.
When evaluating inflation, a considerable positive for many governments is the fact that it erodes the value of government debt. This may be difficult to grasp, but if a government has a lot of debt, it may actually be happy to let inflation run at a higher level for a period of time. The trade-off is that everyone in the economy who is not a 'borrower' is worse off, and if inflation is high, it can lead to social unrest and economic instability.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
