Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Indicators of Living Standards (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0455 & 0987
Real GDP per head (capita)
Economic development is the sustainable increase in living standards for a country, typically characterised by increases in life span, education levels, and income
There are many measures of living standards
Single indicators, e.g., real gross domestic product per capita, number of doctors/1000 people; infant mortality rate, and % of the population with access to clean drinking water
Composite indicators such as the Human Development Index (HDI)
The distinction between real, nominal and per head GDP
Nominal GDP
In economics, the use of the word 'nominal' refers to the fact that the metric has not been adjusted for inflation
Nominal GDP is the actual value of all goods and services produced in an economy in a one-year period
There has been no adjustment to the amount based on the increase in general price levels (inflation)
Real GDP
Real GDP is the value of all goods and services produced in an economy in a one-year period - and adjusted for inflation
For example, if nominal GDP is $100bn and inflation is 10% then real GDP is $90bn
Real GDP per head (capita)
This metric take the real GDP and divides it by the number of people in the population
It shows the mean wealth of each citizen in a country
This makes it easier to compare standards of living between countries
For example, Switzerland has a much higher GDP per capita than Burundi
The advantages and disadvantages of real GDP per capita
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When an exam question uses the phrase 'at constant prices', it is referring to real GDP. For example, a question may read, 'Explain what is meant by a rise in GDP at constant prices.' This requires you to define real GDP and then explain the rise.
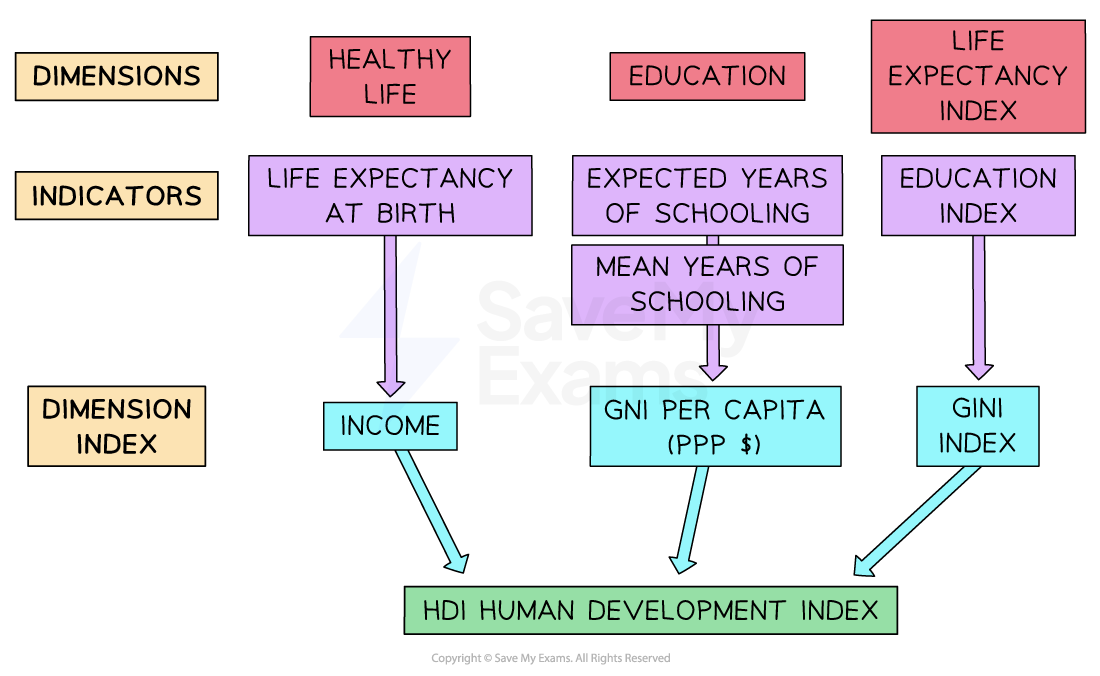
The human development index (HDI)
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a measure used to compare the development levels of different countries, not just based on income, but also on health and education
Developed by the United Nations, the Human Development Index is a combination of 3 indicators
Health – measured by life expectancy at birth
Education – measured by average years of schooling and expected years of schooling
Income, as measured by the real gross national income per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP)
Each indicator is given equal weighting in the index
The index ranks countries on a score between 0 and 1
A score closer to 1 means a higher level of human development
A score closer to 0 means a lower level of human development
Examples of HDI values
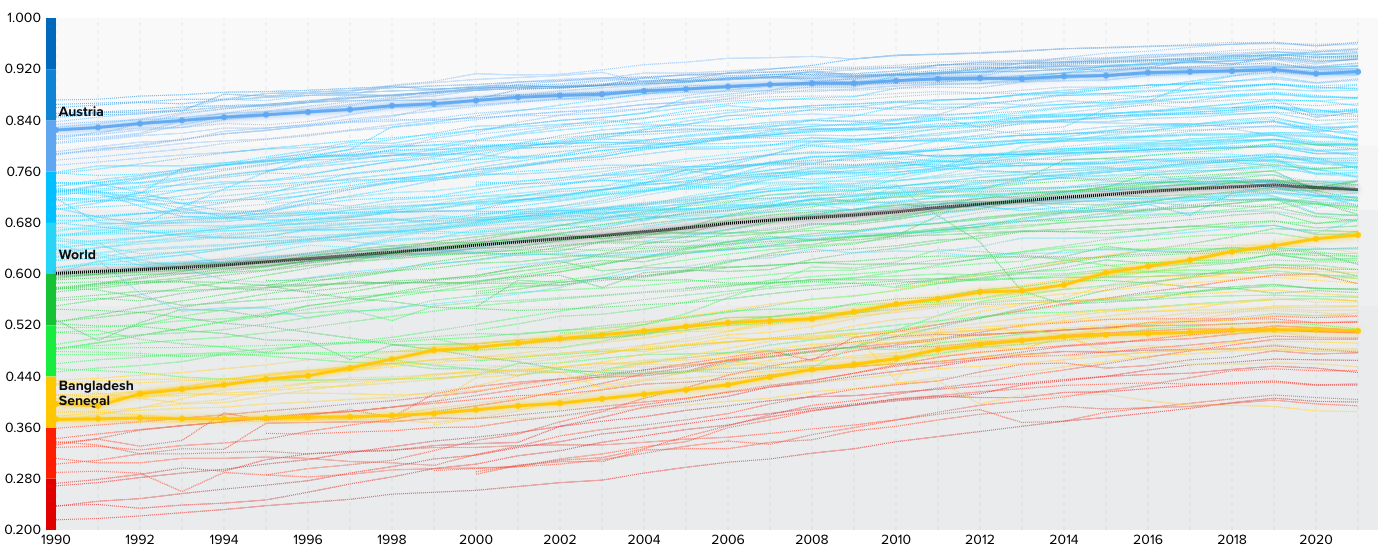
Source: UNDP Data Centre (opens in a new tab)
A value of less than 0.550 is considered low development, e.g. Senegal was at 0.514 in 2021
A value of 0.550-0.699 is considered medium development, e.g., Bangladesh was at 0.667 in 2021
A value of 0.700-0.799 is considered high development; e.g., Thailand was at 0.777 in 2021
A value ≥ 0.800 is considered very high development, e.g. Austria was at 0.918 in 2021
The advantages and disadvantages of using the HDI
One of the main advantages is that the HDI is a composite indicator which provides a more useful comparison metric than single indicators do
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
