Why Did Unemployment Continue? (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE History): Revision Note
Exam code: 0470 & 0977
Summary
The New Deal was very expensive and was fiercely criticised by its opponents. However, Roosevelt was still reelected by a large margin in 1936. Despite this, concerns about the New Deal and its failure to conquer unemployment continued to grow.
It was the outbreak of the Second World War in 1939 that finally dragged America completely out of the Great Depression and secured its economic recovery.
Limitations of the New Deal
When Roosevelt became president in 1933, there were 12.8 million unemployed Americans
By 1941, that number had been slashed to 5.6 million
Considering the expense and effort of the New Deal, 5.6 million was still a large number
Unemployment never fell below 10 per cent during the 1930s
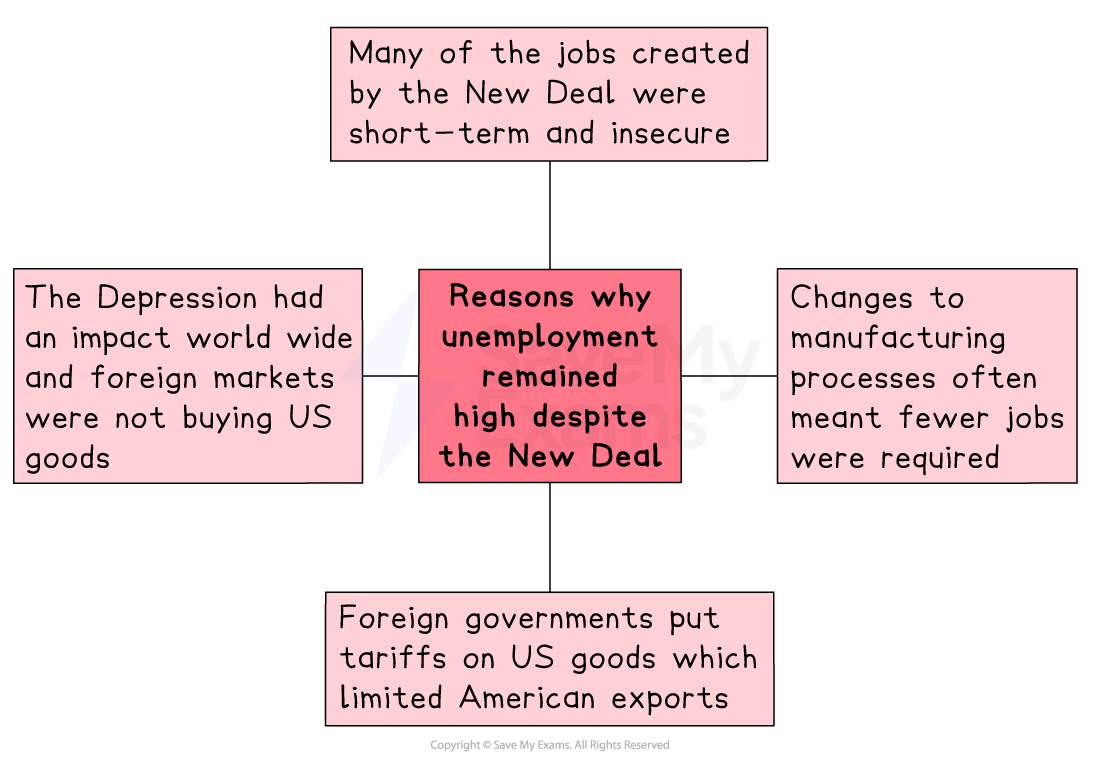
There are several reasons for this including:
Short-term and insecure jobs
Improvements in manufacturing meant that fewer workers were needed
The Depression meant that fewer goods were purchased
Tariffs on US goods affected exports
Consumer spending
Unemployment remained high, and wages remained low
This meant that many American workers did not have the disposable income to purchase consumer goods
As a result, sales of consumer goods such as cars, radios, vacuum cleaners and refrigerators were low
This led to the closure of businesses that made these goods and contributed to the persistently high unemployment figures
The Second World War
By the late 1930s, many people were beginning to fear that the New Deal had failed
They worried that the US would soon return to an economic depression
The outbreak of war in 1939, and the US’s entry into the war in 1941, changed all that
Factories that had been built to make cars were soon making thousands of planes, tanks and guns
Farmers who had been struggling to sell their crops suddenly found there was a rapid increase in the demand for food to feed the soldiers and sailors
Farmers were also able to sell their produce to countries such as Britain and the Soviet Union that were most affected by the war
Coal and oil were in enormous demand, and the iron and steel industries also boomed
The combined effect of booming industry and agriculture and the large number of people joining the armed forces almost eliminated unemployment
By 1944, there were just 670,000 unemployed Americans
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The three question types on this paper require you to write specific things. Make sure you give the examiner what they ask for!
Describe → Give key facts in short, clear sentences. No explanation needed.
Explain → Show why or how, with cause–effect links.
How far do you agree? / Do you agree? → Present both sides, then give a supported judgement.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
