Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Causes & Consequences of Economic Growth (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0455 & 0987
Causes of economic growth
Economic growth is the increase in the output of goods and services in an economy over time, usually measured by the rise in real gross domestic product (GDP)
Growth can be short-term (from better use of existing resources) or long-term (from an increase in productive capacity)
1. A change in total demand
Actual economic growth occurs when there is an increase in the quantity of goods and services produced in an economy in a given period of time - using existing resources
If any component of real GDP increases (consumption, investment, government spending, net exports), there will be an increase in total demand
This type of growth is short-run — it uses up idle resources but does not expand capacity permanently

Any movement from Point E towards the PPC boundary represents actual economic growth and is caused by an increase in output (rGDP)
Diagram explanation
Previously unused factors of production are now being employed
This is demonstrated by a shift from inside the production possibilities curve (PPC) such as Point E, towards the boundary of the PPC
At any given point in time, the actual economic growth may be less than the potential growth available to the economy
2. An increase in the quantity of resources
More resources allow the economy to produce more goods and services in the long run
Some factors that lead to an increase in resources include:
More workers from population growth or immigration
The discovery of new raw materials
Increased capital stock from business investment
More land brought into production for example through land reclamation such as that carried out in The Netherlands
This type of long-term growth expands the productive potential of the economy, shifting the production possibility frontier (PPF) outward
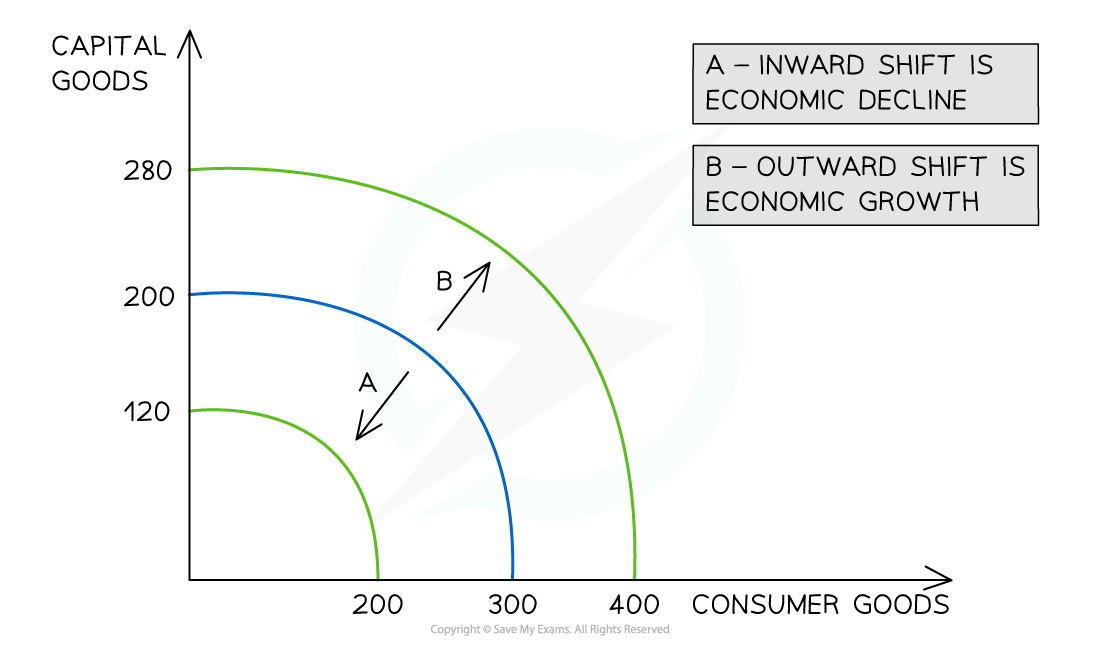
Diagram explanation
Economic growth occurs when there is an increase in the productive potential of an economy
This is demonstrated by an outward shift of the entire curve represented by B
More consumer goods and more capital goods can now be produced using all of the available resources
3. An increase in the quality of resources
Higher-quality resources mean greater efficiency and productivity
Some factors that lead to an increase in the quality of resources include:
Better education and training improving workforce skills
Investment in advanced technology
Improved infrastructure such as transport, communications and energy
Health improvements increasing worker efficiency
These lead to sustainable long-term growth without inflationary pressure
This type of long-term growth expands the productive potential of the economy, shifting the production possibility frontier (PPF) outward
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember this distinction, as MCQ often checks for this understanding:
Growth caused by a change in total demand is represented by a movement from within the existing PPC towards its boundary
Growth caused by a change in the quantity or quality of the factors of production (supply-side growth) moves the entire PPC curve outwards
The consequences of economic growth
Economic growth is considered to be the main contributor to an improvement in the standards of living
Due to the negative aspects of economic growth, there is much controversy about maintaining it as a central macroeconomic aim
Instead, arguments for a focus on societal well-being are gaining traction
The advantages and disadvantages of economic growth
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
