Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Business Impacts on the Environment (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Pollution
Some industrial processes generate pollutants, including air and water emissions, hazardous waste and chemical byproducts
The disposal of these pollutants can harm ecosystems, wildlife and human health
For example, the burning of fossil fuels releases large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere
Food and consumer goods manufacturers account for 60% of worldwide greenhouse gas emissions
Single-use plastics are also a huge concern
They produce toxic chemicals when they break apart
This causes pollution and harms animals, such as marine turtles, who become entangled in plastic found in the sea
Depletion of resources
Natural resources, such as water, energy and raw materials, are used in business operations
Excessive consumption of these resources can lead to their depletion
Materials and products may be sourced from environmentally sensitive areas
Industries like logging, agriculture, and construction contribute to deforestation in locations such as South America
This has a significant impact on biodiversity and contributes to global warming
Why businesses respond to environmental issues
More businesses are taking action to reduce their environmental impact
This is partly due to growing public concern
According to a 2023 UK survey, over 80% of consumers said they were more likely to buy from a company that takes sustainability seriously
Governments are also introducing stricter environmental laws, and pressure from stakeholders like customers, employees and investors is increasing
Reasons to respond to environmental issues
Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
Improved reputation |
|
Increased sales |
|
Legal requirements |
|
Pressure from stakeholders |
|
Cost savings |
|
Competitive advantage |
|
Access to new markets |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Many students think environmental responsibility only increases costs. Remember, it can also be an opportunity—such as attracting eco-conscious customers or gaining a competitive edge. Examiners reward answers that recognise both challenges and benefits
How businesses respond to environmental issues
With growing concern about climate change, pollution and resource use, many businesses are taking action to reduce their environmental impact
These actions can help businesses save money, follow the law and build customer trust
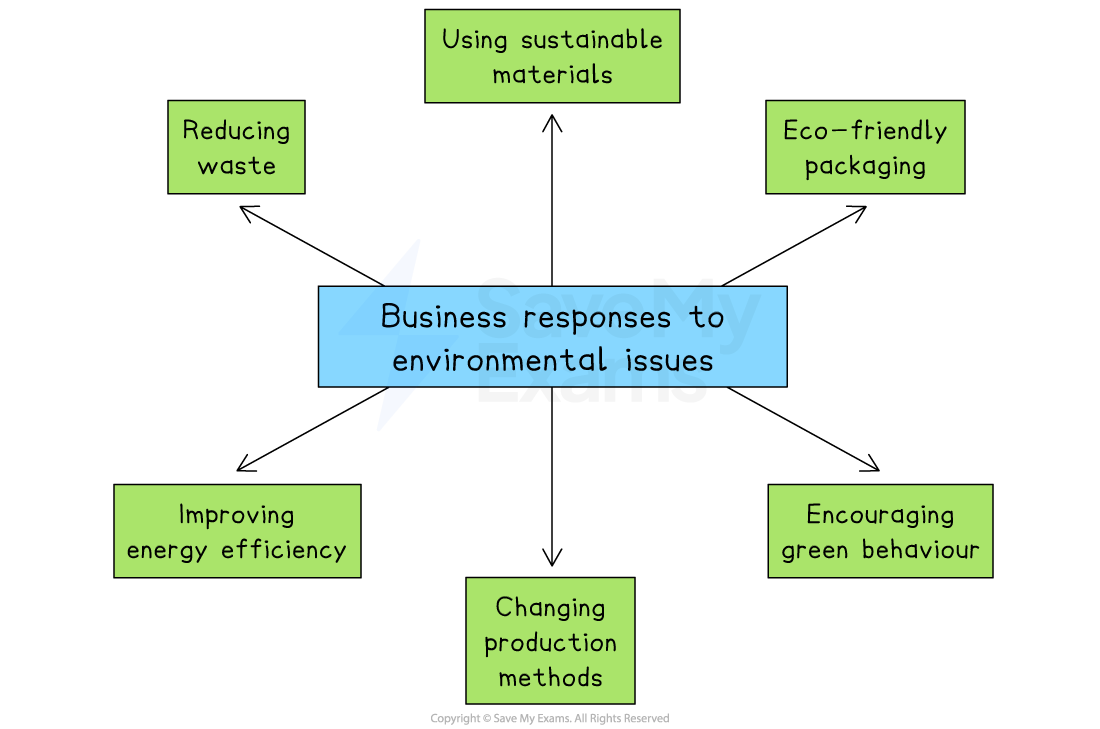
Business responses to environmental issues
Reducing waste
Businesses can reduce, reuse and recycle materials to cut down on landfill waste and pollution
Improving energy efficiency
Installing energy-saving equipment, such as LED lighting or solar panels, helps reduce electricity use and lower carbon emissions
Using sustainable materials
Switching to recycled or eco-friendly materials can reduce environmental damage and appeal to green customers
Changing production methods
Businesses may invest in cleaner technology or reduce harmful emissions during manufacturing to lower their overall environmental footprint
Eco-friendly packaging
Using biodegradable or recyclable packaging helps reduce plastic waste and limits environmental harm
Encouraging green behaviour
Businesses can promote eco-friendly habits, such as offering discounts for reusable bags or encouraging employees to cycle or walk to work
Case Study
Danone's Steps To Reduce Its Environmental impact
Danone, known for brands like Activia and Evian, has taken major steps to reduce its environmental impact, especially in food production and packaging

Actions
It has committed to becoming carbon neutral by 2050 and has already achieved carbon neutrality in several of its factories
The company works with farmers to support sustainable agriculture, using fewer chemicals and protecting soil health
It has invested heavily in plant-based products, such as dairy-free yoghurts and drinks, which generally have a lower environmental footprint than animal-based alternatives
Danone is redesigning its packaging to use 100% recyclable, reusable or compostable materials by 2025, with several water brands already using bottles made entirely from recycled plastic
Outcome
These actions help Danone meet legal requirements, reduce its carbon footprint and build a strong reputation with environmentally aware consumers
Effects of legal controls on business activity and the environment
Governments pass environmental laws to reduce damage caused by business activity. These laws affect:
How businesses produce
What they produce
Where they produce or sell
The costs of doing business
1. How businesses produce
Legal controls may ban or restrict harmful production methods (e.g., limits on factory emissions, rules on waste disposal)
Businesses may need to invest in cleaner technology, filters, or recycling systems
Impact: Higher production costs, but safer working and living environments
2. What businesses produce
Certain products may be banned if they harm the environment (e.g., plastic bags, toxic chemicals)
Businesses may be forced to redesign or switch to sustainable alternatives
Impact: Higher R&D costs, but opportunities to innovate and appeal to eco-conscious consumers
3. Where businesses produce or sell
Firms may be prevented from locating near protected areas (e.g., national parks, residential zones)
Laws may restrict selling in markets where environmental standards are not met (e.g., exporting to the EU with strict rules)
Impact: Limits expansion but protects communities and ecosystems
4. Influence on costs
Area of Impact | Examples | Effect on business costs |
|---|---|---|
Compliance costs |
|
|
Fines and penalties |
|
|
Product redesign |
|
|
Reputation & sales |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
