ELISA (AQA AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7401
ELISA
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) uses antibodies to detect the presence and quantity of a specific antigen or antibody in a sample
In an ELISA test:
An enzyme is attached to antibodies
When this enzyme reacts with a certain substrate, a coloured product is formed, causing the solution in the reaction vessel to change colour
If a colour change occurs, this shows that the antigen or antibody of interest is present in the sample being tested (e.g. blood plasma)
There are different types of ELISA test:
Direct ELISA tests use a single antibody that is complementary to the antigen being tested for
Indirect ELISA tests use two different antibodies (known as primary and secondary antibodies)
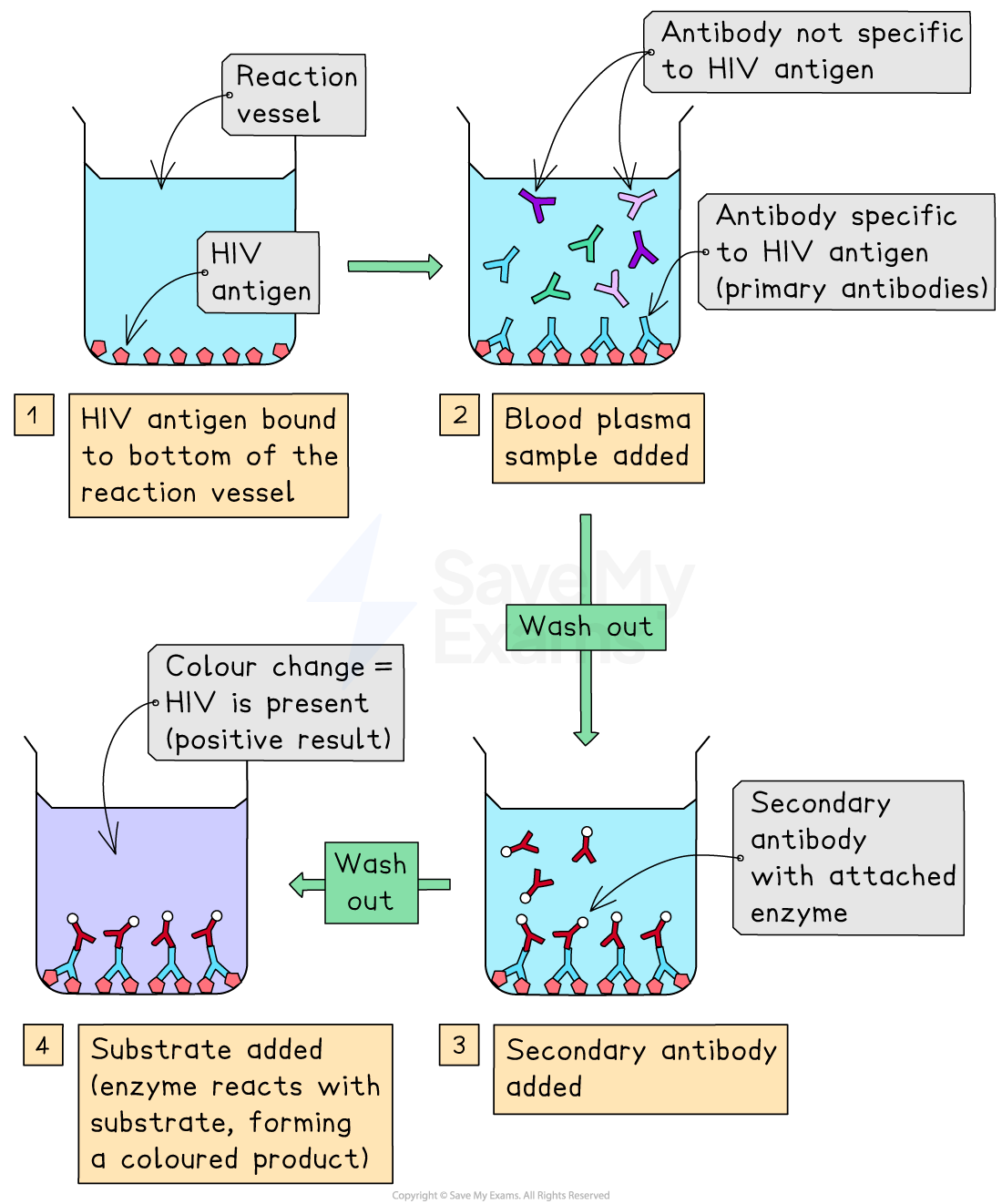
Example: indirect ELISA for HIV diagnosis
An indirect ELISA test can be used to test whether a patient has antibodies to HIV:
HIV antigens are fixed to the bottom of the test well
Patient's blood plasma is added – if HIV-specific antibodies are present, they bind (primary antibodies) to the HIV antigens
The well is washed to remove unbound antibodies
Secondary antibodies with an enzyme attached are added – they bind to the primary antibodies
Another wash step removes unbound secondary antibodies
This step avoids a false-positive test
A substrate is added – if the enzyme is present, a colour change occurs
A colour change indicates the patient has HIV-specific antibodies, meaning they are infected with HIV

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
