pH (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
The pH Scale
What is the pH scale?
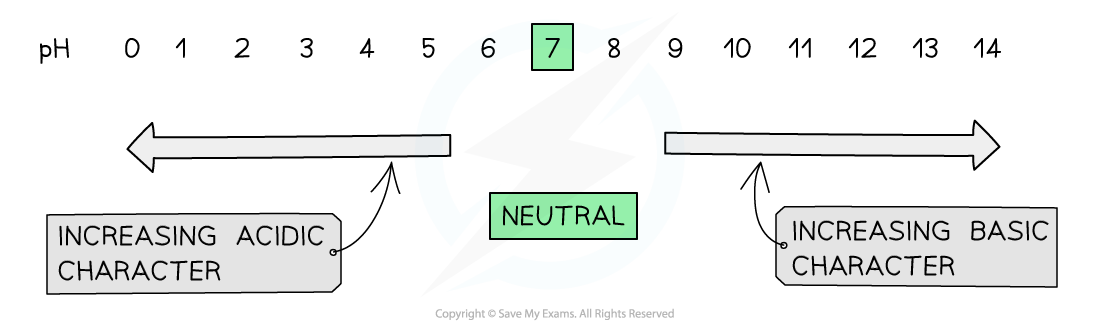
The pH scale is a numerical scale used to measure acidity or alkalinity
It runs from below 0 to above 14
All acids have pH values of below 7
The lower the pH, the more acidic the solution is
All alkalis have pH values of above 7
The higher the pH, the more alkaline the solution is
A solution with a pH of exactly 7 is described as being neutral
The pH Scale
What are some common acids and alkalis?
Common acids | Common alkalis |
|---|---|
Sulfuric acid, H2SO4 | Sodium hydroxide, NaOH |
Hydrochloric acid, HCl | Ammonia, NH3 |
Vinegar (ethanoic acid), CH3COOH | Baking powder |
How do we measure pH?
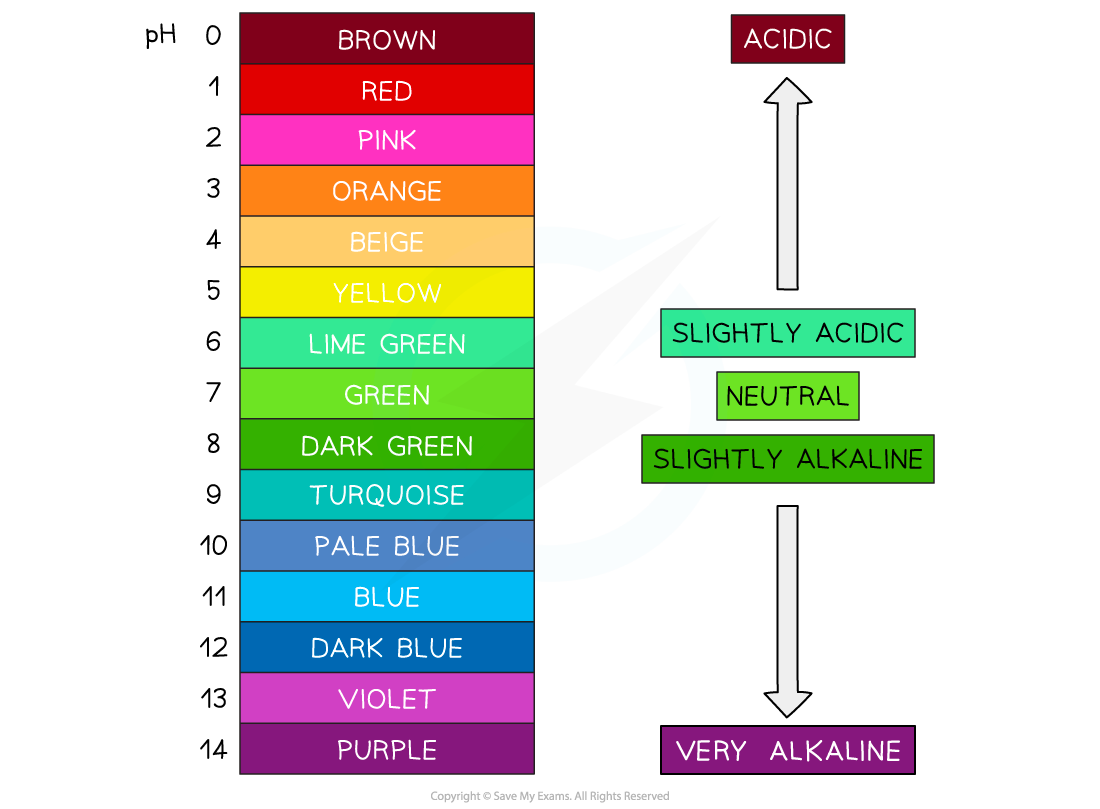
Universal indicator is a wide range indicator and can give only an approximate value for pH
It is made of a mixture of different plant indicators which operate across a broad pH range and is useful for estimating the pH of an unknown solution
A few drops are added to the solution and the colour is matched with a colour chart which indicates the pH which matches with specific colours
Universal indicator colours vary slightly between manufacturers so colour charts are usually provided for a specific indicator formulation
Colour range of universal indicator
Worked Example
The following table shows the pH of some substances.
Substance | pH |
|---|---|
lemon juice | 2.2 |
limewater | 10.5 |
saliva | 6.3 |
milk of magnesia | 10.1 |
What is the most alkaline substance?
[1]
What is the most acidic substance?
[1]
Name the substances which is closest to neutral.
[1]
Answers:
The highest pH in the table is 10.5, which is the most alkaline substance
So, the most alkaline substance is limewater [1 mark]
The lowest pH in the table is 2.2, which is the most acidic substance
So, the most acidic substance is lemon juice [1 mark]
pH 6.3 is closest to neutral / pH 7
So, the substance closest to neutral is saliva [1 mark]
Hydrogen & Hydroxide Ions
Hydrogen ions
Acids have pH values of below 7, have a sour taste (when edible) and are corrosive
Acids are substances that can neutralise a base, forming a salt and water
Acidic solutions have a higher concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) than hydroxide ions (OH-)
The presence of H+ ions is what makes a solution acidic
For example, hydrochloric acid
HCl (aq) → H+ (aq) + Cl– (aq)
Hydroxide ions
Alkalis have pH values of above 7
When a base is water-soluble it is referred to as an alkali
They are substances which can neutralise an acid, forming a salt and water
Alkaline solutions have a higher concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) than hydrogen ions (H+)
The presence of the OH– ions is what makes the aqueous solution an alkali
For example sodium hydroxide
NaOH (aq) → Na+ (aq) + OH– (aq)
Neutral solutions
A neutral solution has equal concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions
When [H+] = [OH−], the pH = 7
Pure water is a neutral solution
H2O (l) ⇌ H+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
Type of solution | Relative ion concentration | pH range | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Acidic | [H+] > [OH-] | Below 7 | HCl (aq) → H+ (aq) + Cl– (aq) |
Neutral | [H+] = [OH-] | 7 | H2O (l) ⇌ H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) |
Alkaline | [H+] < [OH-] | Above 7 | NaOH (aq) → Na+ (aq) + OH– (aq) |

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
