Properties of Ionic Compounds (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
Melting & boiling points of ionic compounds
Ionic compounds are typically crystalline solids at room temperature
They have very high melting and boiling points
This property is a direct result of their giant ionic lattice structure
In the solid state, the positive and negative ions are held in a fixed, rigid lattice by strong electrostatic forces of attraction (the ionic bonds)
To melt or boil an ionic compound, this strong lattice structure must be broken apart, allowing the ions to become free to move
Breaking these powerful ionic bonds requires a very large amount of energy
Since a lot of heat energy is needed, the temperature at which the substance melts or boils is very high
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When explaining the high melting and boiling points of ionic compounds, you must refer to the energy needed to overcome the "strong electrostatic forces of attraction" between the ions, or state that "strong ionic bonds must be broken".
Avoid mentioning "molecules" or "intermolecular forces" as these do not exist in an ionic lattice.
Solubility of ionic compounds
Many ionic compounds are soluble in water
When a soluble ionic compound is added to water, a specific process occurs:
The water molecules are attracted to the positive and negative ions on the surface of the ionic lattice
These attractions are strong enough to pull the ions away from their fixed positions, causing the strong ionic lattice to break apart
The individual ions are now free to move within the water
Water molecules surround these separated positive and negative ions
Dissolving ionic compounds
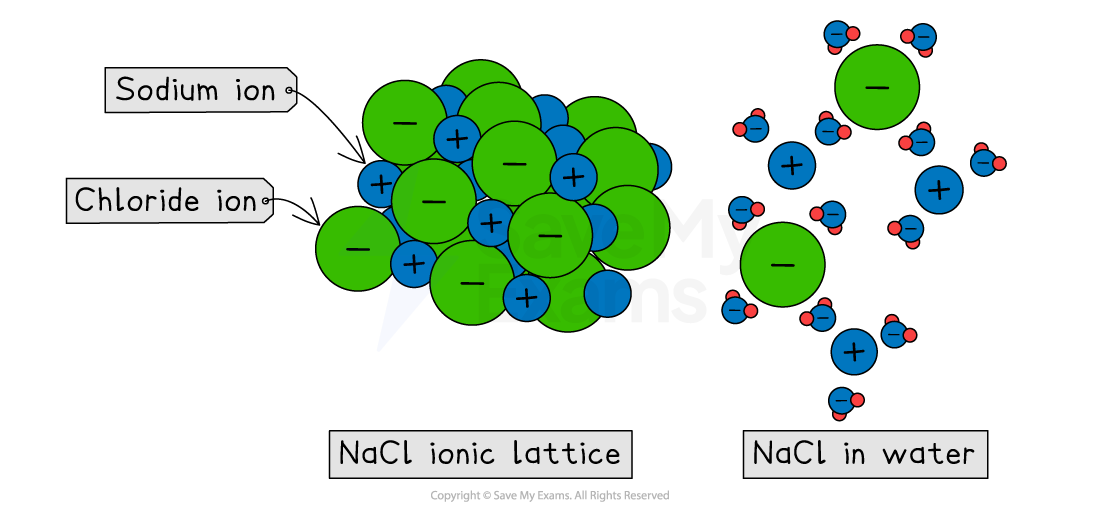
Ionic compounds are generally insoluble in covalent solvents (like oil or hexane)
The particles in covalent solvents are not able to overcome the strong electrostatic forces holding the ionic lattice together
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is important to be precise when describing what happens during dissolving. The key phrases are that the "lattice breaks down" or "ions are separated" and that the free ions become "surrounded by water molecules".
Avoid saying the compound "melts" or that the ions "disappear".
Electrical conductivity of ionic compounds
For any substance to conduct electricity:
It must contain charged particles
These charged particles must be free to move and carry a current
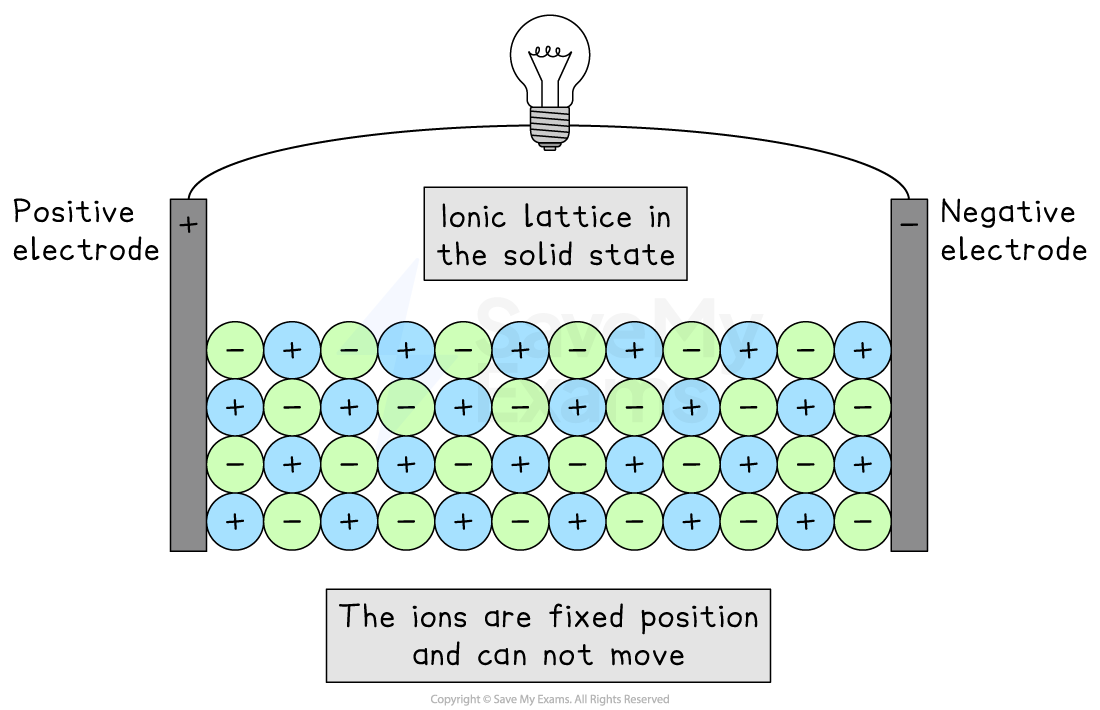
In the solid state
Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity when solid
An ionic lattice does contain charged particles (positive and negative ions)
So, it meets the first condition for conducting electricity
However, in the solid lattice, these ions are held in fixed positions by strong ionic bonds and are not free to move
Since the charged particles cannot move, solid ionic compounds cannot conduct electricity
When molten or in solution
Ionic compounds can conduct electricity when molten (melted) or dissolved in water
When an ionic compound melts or dissolves, the strong lattice structure breaks down
This releases the ions, so they are now free to move
Because the substance now has charged particles (ions) that are free to move, it can conduct electricity
How conduction works
When an electric current is passed through a molten ionic compound or an ionic solution, the ions move in a specific way:
The positive ions are attracted to and move towards the negative electrode
The negative ions are attracted to and move towards the positive electrode
This directed movement of charged ions is the flow of electricity
Conductivity of ionic compounds
ANIMATION
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When explaining conductivity, you must mention both conditions. A common error is to just say "it contains ions". This is not enough for the mark.
For a solid: "It contains ions, but they are not free to move."
For a liquid/solution: "It contains ions which are free to move."

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
