Factors Affecting Rates of Reaction (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
Increasing rates of reaction
There are four main ways to speed up a chemical reaction:
Increase the temperature
Increase the concentration of a reactant solution
Increase the surface area of a solid reactant
Use a catalyst
All these factors work by increasing the frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles per second
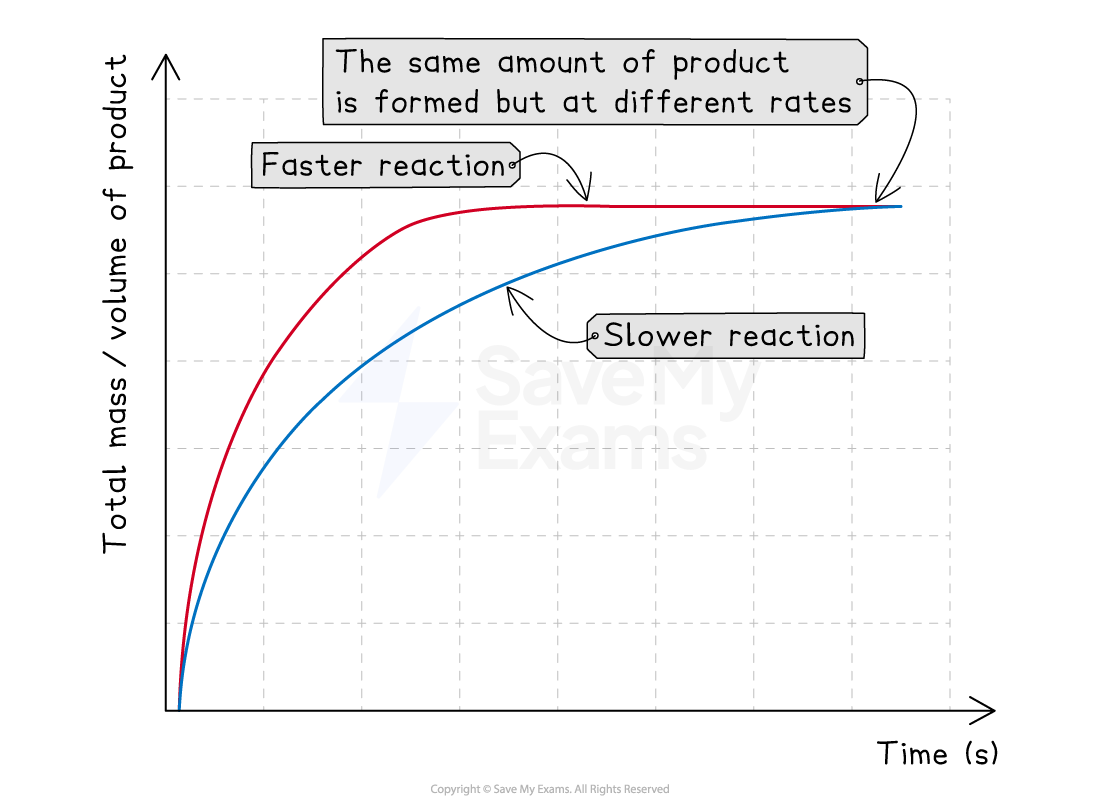
How the factors look on a graph
When you change the temperature, concentration or surface area, you change the speed of the reaction
However, you still make the same total amount of product
This has a predictable effect on the shape of a reaction rate graph:
Faster reactions:
Have a steeper curve
Finish quicker
This means that the curve on the graph levels out sooner
Slower reactions:
Have a less steep curve
Take longer to finish
This means that the curve on the graph takes longer to level out
Explaining the factors (collision theory)
1. Increasing concentration
If you increase the concentration of a reactant, the reaction gets faster
Why it gets faster:
A higher concentration means there are more reactant particles in the same volume
This leads to more frequent collisions between particles
This increases the number of successful collisions per second
The rate of reaction increases
Examiner Tips and Tricks
For concentration, the best answers mention that there are "more particles per unit volume"
This phrase is better than "in the same volume" because it shows a high level of understanding
2. Increasing temperature
If you increase the temperature of the reaction, the reaction gets faster
Why it gets faster:
A higher temperature gives the reactant particles more kinetic energy
This means the particles move faster
This leads to more frequent collisions
The collisions are also more energetic, so more of them are successful
The rate of reaction increases
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that increasing the temperature has two effects:
It makes collisions more frequent (particles move faster)
It make collisions more energetic (more likely to be successful)
Mentioning both shows a deeper understanding
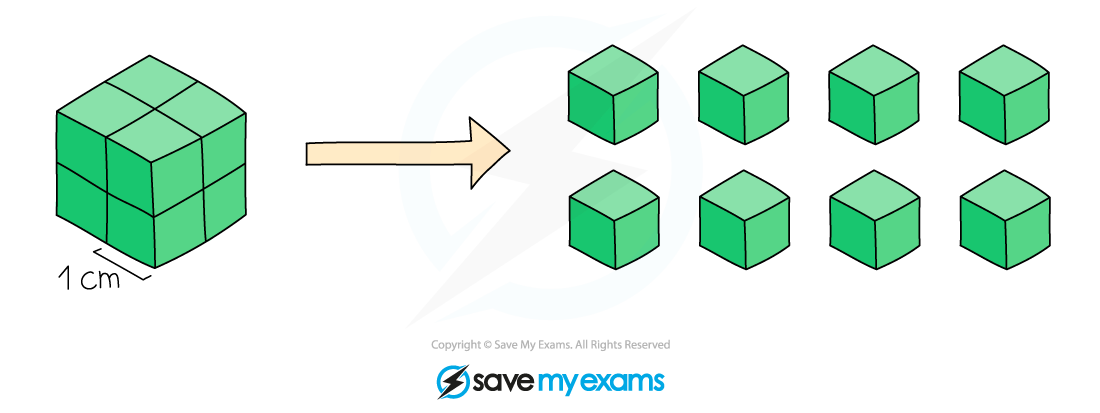
3. Increasing surface area
If you increase the surface area of a solid reactant, the reaction gets faster
Why it gets faster:
Breaking a solid lump into a powder increases the surface area
This means more reactant particles are exposed at the surface
This leads to more frequent collisions between particles
This increases the number of successful collisions per second
The rate of reaction increases
4. Using a catalyst
Adding a catalyst increases the rate of reaction
Why it gets faster:
A catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway that allows the reaction to happen more easily
This increases the number of successful collisions per second
The rate of reaction increases
Worked Example
A student heated the reaction mixture to a higher temperature. Explain why this would increase the rate of reaction.
[2]
Answer:
At a higher temperature, the particles have more kinetic energy and move faster
AND
This leads to more frequent collisions
[1 mark]
The collisions are also more energetic, meaning a higher proportion of them will be successful
[1 mark]
A good 2-mark answer to this "explain" question links the change to the effect on particle collision and would talk about collision frequency and collision energy
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The syllabus focuses on increasing the rate, but an exam question could easily ask why decreasing the concentration slows a reaction down
Just reverse the logic:
Lower concentration
→ fewer particles in the same volume
→ less frequent collisions
→ slower rate
When explaining concentration or surface area, don't just say "there are more collisions."
To get full marks, you need to be more precise
Use the key phrase "more frequent collisions" or "more collisions per second"
How Catalysts Work
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction but is not used up in the process
This means a catalyst can be recovered chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction and used again
Catalysts are very important in industry
They save money by allowing reactions to happen faster or at lower, less energy-intensive temperatures
SQA example: The Haber process uses an iron catalyst to make ammonia
The catalyst "shortcut"
You can think of a chemical reaction as a journey over a mountain.
The energy needed to get the reaction started is like the effort of climbing the mountain
A catalyst works by providing an alternative reaction pathway that is easier to follow
It's like finding a tunnel that goes through the mountain instead of having to climb over the top
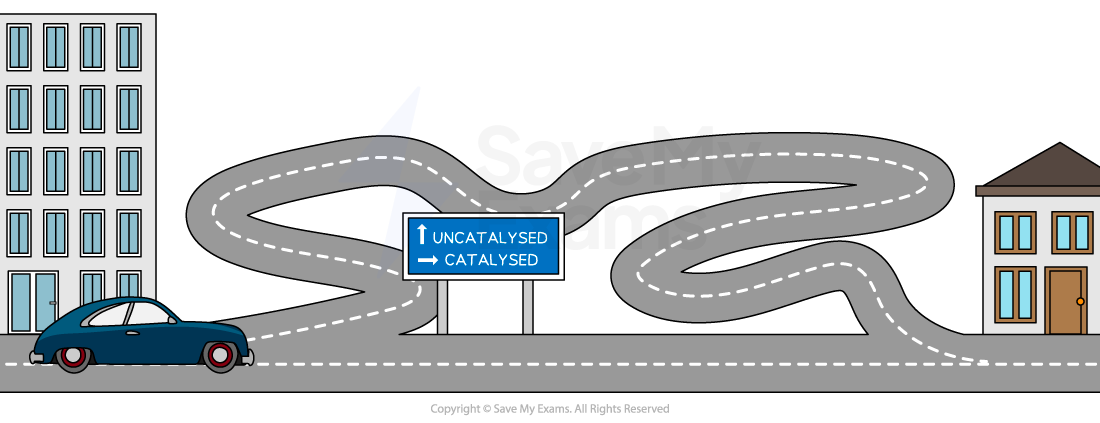
Since the catalyst provides an easier route, more particles have enough energy to react at any given moment
This increases the number of successful collisions per second
Therefore, the rate of reaction increases
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember two key things about catalysts:
They increase the rate of reaction
They are not used up and the final amount of product made is unchanged

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
