Calculate Enthalpy Changes Using ΔHc⦵ (HL) (DP IB Chemistry): Revision Note
Calculate enthalpy changes Using ΔHcꝊ
The standard enthalpy change of combustion is
The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of the substance burns completely under standard conditions
We can use enthalpy of combustion to find an unknown enthalpy change using a Hess cycle
In this type of cycle, the combustion products are always placed at the bottom of the diagram and the arrows should be pointing downwards
Energy cycle including combustion products
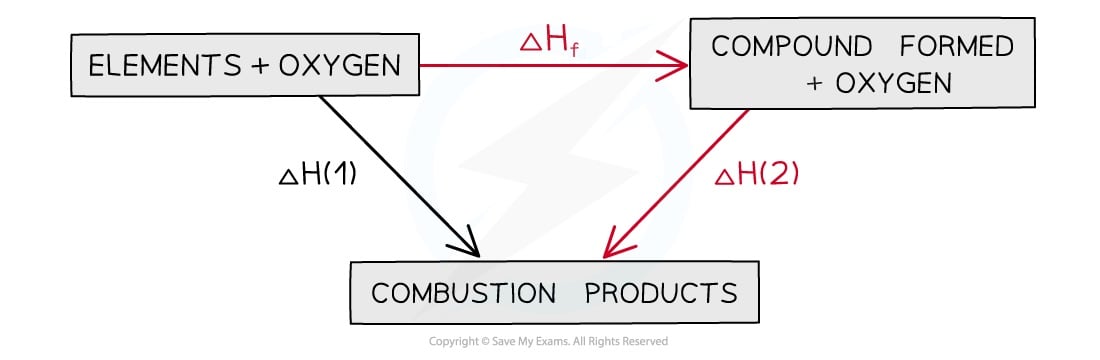
The general expression for ΔHꝊr is therefore:
ΔHꝊr = ∑ΔHcꝊ(reactants) - ∑ΔHcꝊ(products)
Worked Example
Using the data provided, calculate the standard enthalpy change of formation, ΔHf, of propanone.
3C (s) + 3H2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → CH3COCH3 (l)
Substance | C (s) | H2 (g) | CH3COCH3 (l) |
|---|---|---|---|
∆HCө / kJ mol–1 | -394 | -286 | -1821 |
Answer:
Step 1: Write the balanced equation

Step 2:Write the combustion products below the equation

Step 3: Draw downward pointing arrows from each substance to its combustion product

Step 4: Write the appropriate values on the arrows and multiply by the number of moles

Step 5: In a cycle, go from the reactants to the products, changing the sign of the value if the arrow points in the opposite direction

ΔHfө = -1182 - 858 + 1821 = -219 kJ mol-1
The sign on -1821 needs reversing as the cycle goes in the opposite direction to the arrow pointing to the combustion products
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don't forget to make sure the number of atoms of each element is balanced when drawing your cycle
Using Hess's Law to solve ΔHc⦵ & ΔHf⦵ problems
Using Hess's Law to solve ΔH⦵f problems
Standard enthalpy changes of formation, ΔH⦵f can also be used to calculate standard enthalpy changes of reactions, ΔH⦵
The overall equation will be:
ΔH⦵f (reactants) + ΔH⦵r = ΔHθf (products)
Which rearranges to:
ΔH⦵r = ΔH⦵f (products) - ΔH⦵f (reactants)
Be careful to count up all the atoms you need to use, and make sure they are written as they occur in the elements in their standard state
Diagram to show the Hess's Law cycle for calculating ΔH⦵ from ΔH⦵f data

Using Hess's Law to solve ΔH⦵c problems
Standard enthalpy changes of combustion, ΔH⦵c can also be used to calculate standard enthalpy changes of reactions, ΔH⦵
The overall equation will be:
ΔH⦵c (products) + ΔH⦵r = ΔH⦵c (reactants)
Which rearranges to:
ΔH⦵r = ΔH⦵c (reactants) - ΔH⦵c (products)
Diagram to show the Hess's Law cycle for calculating ΔH⦵ from ΔH⦵c data


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
