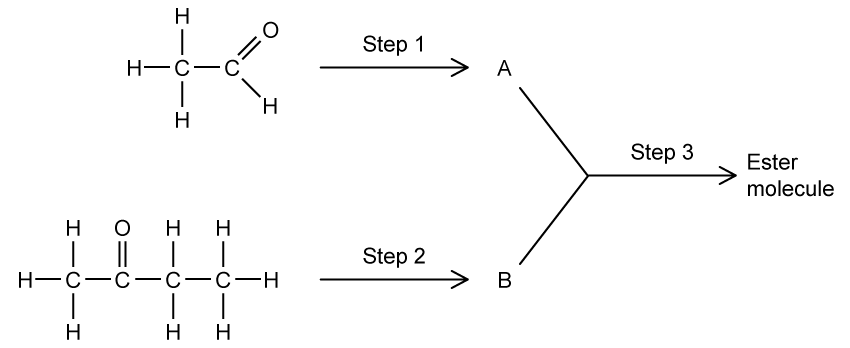
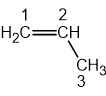
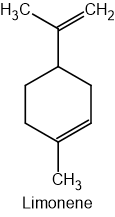
The chemistry of many metal halides is dominated by their behaviour as Lewis acids and their ability to form complex ions with ligands, such as the cyanide ion (CN-).
The cyanide ion, CN-, is a powerful ligand.
i) Draw the Lewis structure for the cyanide ion.
[1]
ii) Deduce, with a reason, which atom in the cyanide ion is more likely to donate the electron pair to form a coordinate bond with a metal ion.
[1]
Silver chloride, AgCl, is an ionic solid with a high melting point that is insoluble in water. However, it will dissolve in an aqueous solution of potassium cyanide due to the formation of the linear dicyanidoargentate(I) complex ion.
Deduce the formula of the dicyanidoargentate(I) ion.
Explain why solid silver chloride has a high melting point.
Aluminium chloride also exhibits coordinate bonding, existing in the gas phase as a dimer, Al2Cl6.
Draw the structure of the Al2Cl6 dimer, using an arrow (→) to clearly indicate one of the coordinate bonds.
Explain why molten aluminium oxide, Al2O3, is an electrical conductor, whereas molten aluminium chloride is not.
Was this exam question helpful?