Constant & Variable Velocity (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Vectors & constant velocity
How can I model motion with constant velocity using vectors?
The formula for the position vector of an object is
is the position vector of the starting point
is the velocity for the constant velocity
is the time since the object first left the starting point
An object moves in a straight line if the velocity is constant
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This formula is not given in the formula booklet. However, this is just the vector equation of a line where is a point on the line of motion and
is the direction of motion.
Worked Example
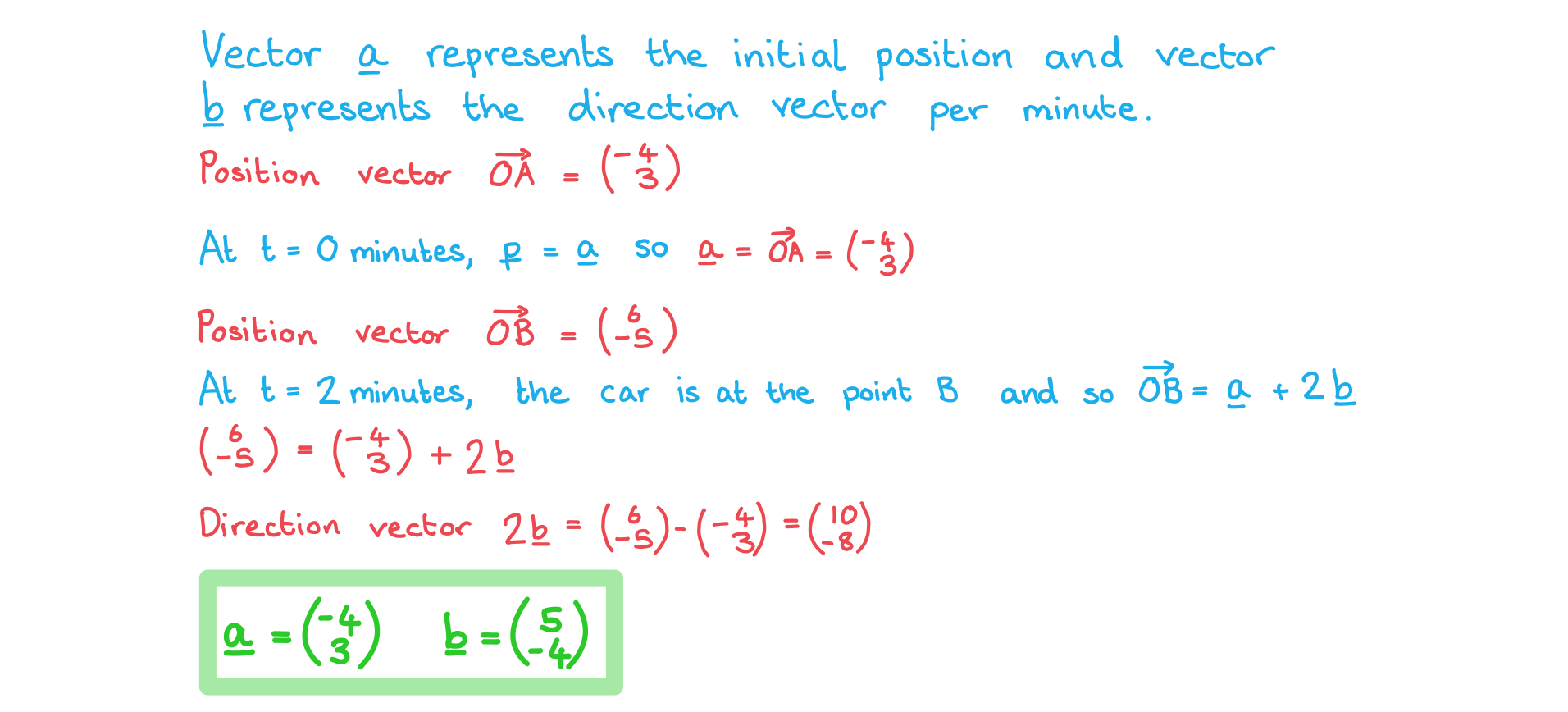
A car, moving at constant speed, takes 2 minutes to drive in a straight line from point A (-4, 3) to point B (6, -5).
At time t, in minutes, the position vector (p) of the car relative to the origin can be given in the form .
Find the vectors a and b.
Answer:
Did this video help you?
Vectors & variable velocity
How can I model motion with variable velocity using vectors?
Variable velocity is represented by a vector whose components are functions of time
This means the position vector and acceleration vector are also functions of time
What is the connection between displacement and velocity vectors?
Velocity is the rate of change of the position
Differentiate the position vector to find an expression for the velocity vector
Integrate the velocity vector to find an expression for the position vector
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don't forget to include a constant of integration for each component. To find the full expression, you need to know the position vector of the object at a specific time. More information is given in the calculus section.
What is the connection between acceleration and velocity vectors?
Acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity
This means it is the second derivative of the position
Differentiate the velocity vector to find an expression for the acceleration vector
Differentiate the position vector twice to find an expression for the acceleration vector
Integrate the acceleration vector to find an expression for the velocity vector
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don't forget to include a constant of integration for each component. To find the full expression, you need to know the velocity vector of the object at a specific time. Also, you can integrate the acceleration vector twice to find the position vector. You need to know the position vectors at two different times to find the full expression.
Worked Example
A ball is rolling down a hill with velocity . At the time
the position vector of the ball is
.
a) Find the acceleration vector of the ball's motion.
Answer:
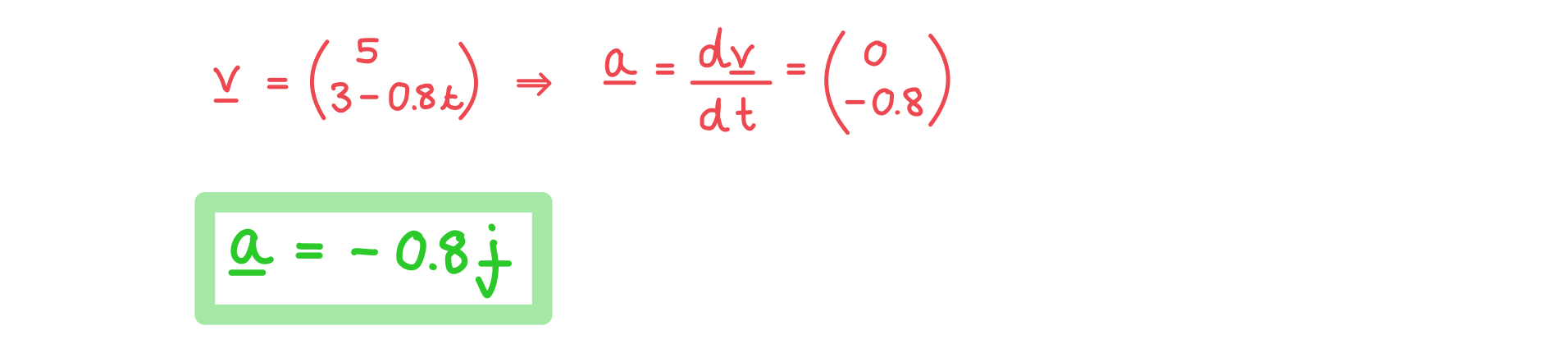
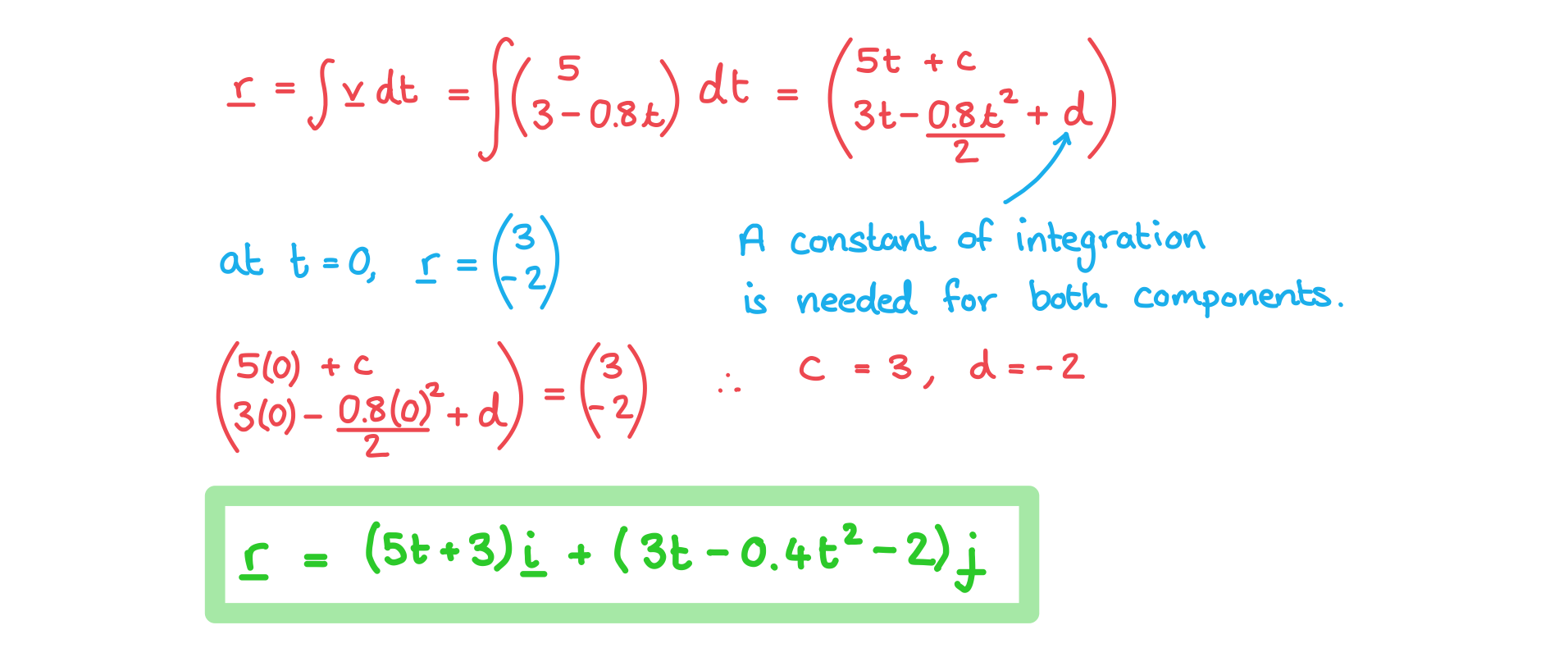
b) Find the position vector of the ball at the time, .
Answer:

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
