Introduction to Complex Numbers (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Cartesian form
What is an imaginary number?
Up until now, equations like
have “no real solutions”
The solutions are
but you cannot square root a negative number
To extend this idea, mathematicians have defined one of the square roots of negative one as
This is called an imaginary number
The square roots of other negative numbers can be found by rewriting them as a multiple of
using
e.g.
What is a complex number?
Complex numbers have both a real part and an imaginary part
For example:
The real part is 3
The imaginary part is 4
The imaginary part does not include the '
'
Complex numbers are often denoted by
The real part of
is
The imaginary part of
is
The set of all complex numbers is given the symbol
Complex numbers can have one part
e.g.
is purely real
and real numbers are a subset of complex numbers
e.g.
is purely imaginary
and imaginary numbers are a subset of complex numbers
Two complex numbers are equal if, and only if, both the real and imaginary parts are identical.
For example,
and
are not equal
What is Cartesian form?
The form
is known as Cartesian form
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This is the first form of a complex number given in the formula booklet.
In general, for
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Your GDC must be in 'complex mode' to give outputs that are complex numbers. It may also call Cartesian form 'rectangular form'.
Worked Example
(a) Solve the equation
Answer:
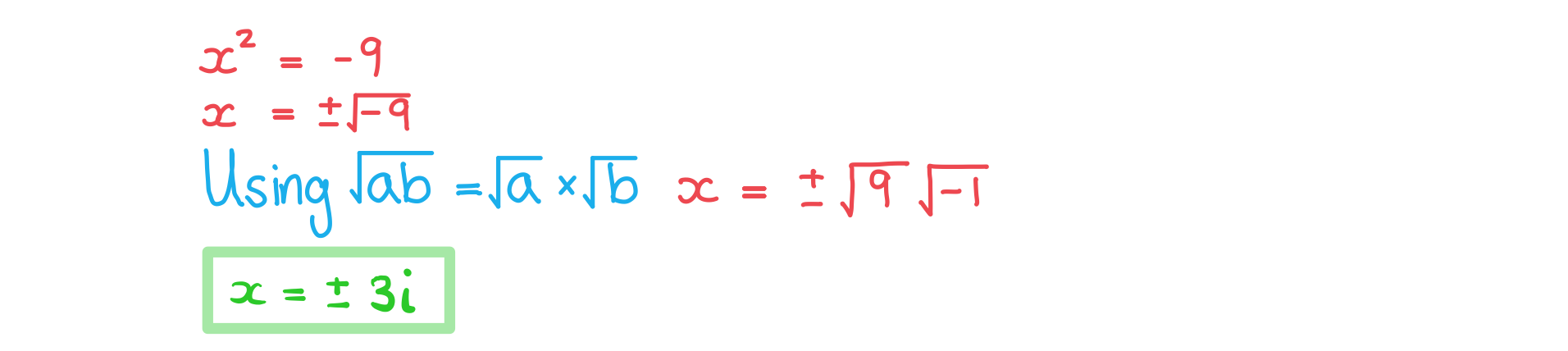
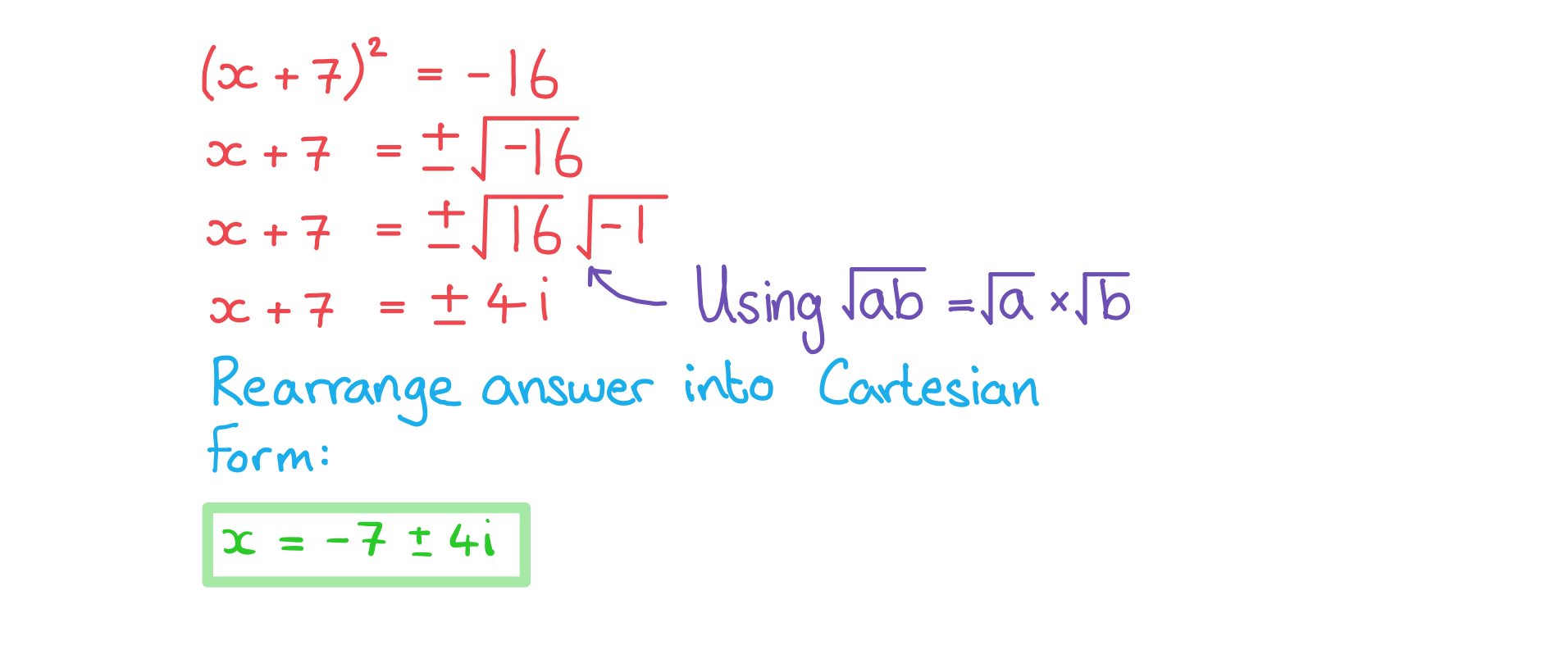
(b) Solve the equation , giving your answers in Cartesian form.
Answer:

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
