A student carried out an experiment to determine the enthalpy of hydration for anhydrous magnesium sulfate, MgSO4.
The student used the following two reactions.
Reaction 1 The dissolving of anhydrous magnesium sulfate in water:
MgSO4 (s) + aq → MgSO4 ( aq) ΔH1
Reaction 2 The dissolving of hydrated magnesium sulfate in water:
MgSO4·7H2O (s) + aq → MgSO4 (aq) ΔH2
The enthalpy of hydration, ΔHhyd, is the enthalpy change for the reaction:
MgSO4 (s) + 7H2O (l) → MgSO4·7H2O (s)
The student's method for Reaction 1 involved adding a known mass of anhydrous magnesium sulfate to a known volume of water in a polystyrene cup and recording the temperature change.
Explain why a polystyrene cup is used for this experiment and why it is often placed inside a glass beaker.
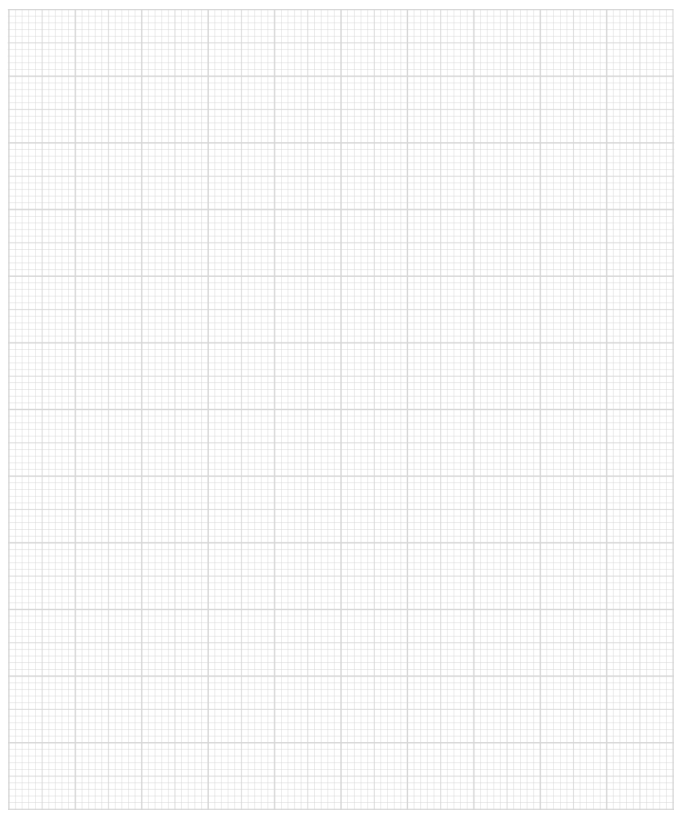
The student's results for Reaction 1 are shown in Table 1. The anhydrous magnesium sulfate was added at time t = 180 s.
Table 1
Time / s | Temperature / °C |
|---|---|
0 | 21.5 |
60 | 21.5 |
120 | 21.5 |
180 | - |
240 | 29.5 |
300 | 29.0 |
360 | 28.5 |
420 | 28.0 |
Plot a graph of temperature against time on the grid provided.
Use your graph to determine an accurate value for the temperature change, ΔT.
Show your working on the graph.
The student used 4.82 g of anhydrous magnesium sulfate (Mr = 120.3) and 50.0 cm3 of water in the experiment in 01.2.
The student had already determined that the enthalpy change for Reaction 2, ΔH2, was +18.0 kJ mol-1.
Use your answer from 01.2 and the data provided to calculate the enthalpy of hydration, in kJ mol-1, for anhydrous magnesium sulfate.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J g-1 K-1. Assume the density of water is 1.00 g cm-3.
The main source of error in this calorimetry experiment is heat loss to the surroundings.
State how this source of error would affect the calculated value for the enthalpy of hydration, ΔHhyd. Explain your answer.
Was this exam question helpful?