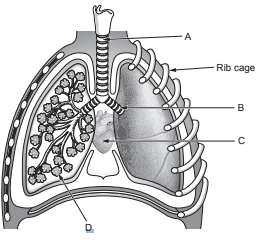
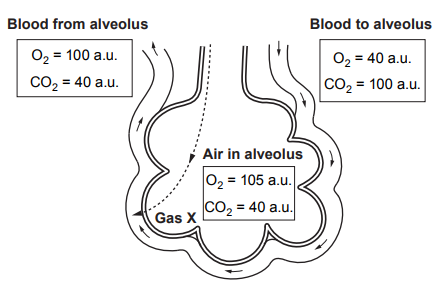
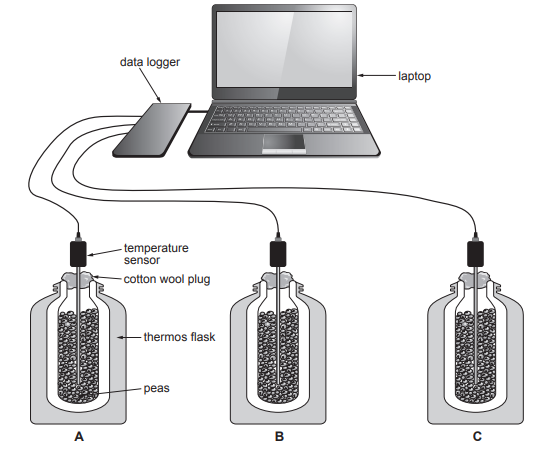
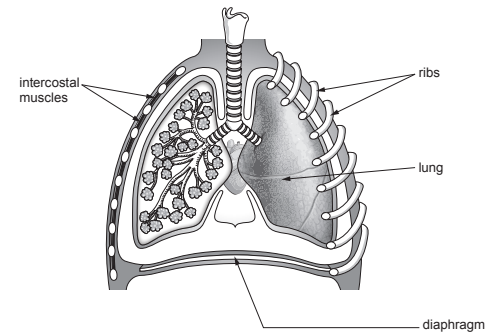
Image 2.1 shows a part of the respiratory system where gas exchange takes place.
Image 2.1
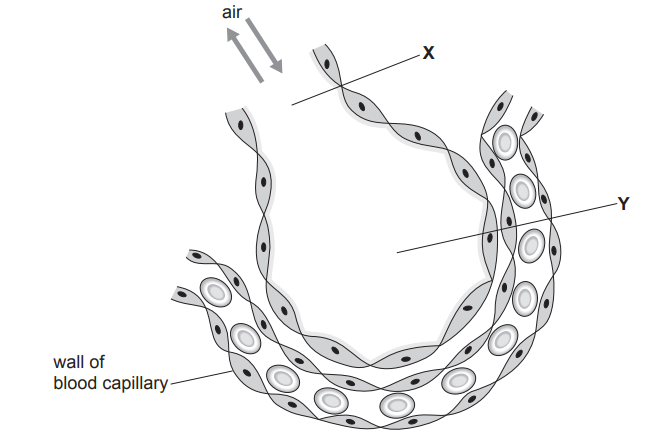
Name structures X and Y in Image 2.1. Choose words from the list below.
bronchus alveolus bronchiole trachea
X ……………….........................................……..
Y ……………….........................................……..
(i) Underline the correct term from the brackets to complete each of the following sentences:
[3]
I. The gas that moves from the air into the bloodstream is
( carbon dioxide / oxygen / nitrogen ).
II. The process that describes how the gas moves from the air into the bloodstream is
( respiration / osmosis / diffusion / photosynthesis ).
III. The process that releases energy in cells is
( respiration / osmosis / diffusion / photosynthesis).
(ii) Describe two ways that the part of the respiratory system shown in Image 2.1 is adapted for gas exchange.
[2]
Table 2.2 shows the percentage of gases in inspired and expired air
Table 2.2
Gas | Inspired air (%) | Expired air (%) |
Nitrogen | 78 | ............... |
Oxygen | 21 | ............... |
Carbon dioxide | ............... | 4 |
Complete Table 2.2 by adding the missing percentages to the empty boxes from the list below:
0.04 16 78 21 4
Was this exam question helpful?