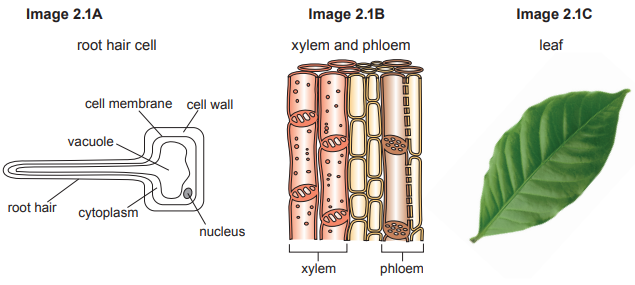
Image 8.1 shows a fertiliser that is used when growing tomato plants.
Image 8.1

State three nutrients that this fertiliser may contain.
Tony grows tomato plants in his greenhouse. He designed an investigation to see if using fertiliser made a difference to the mass of his tomatoes. He grew one tomato plant adding the fertiliser once a week and left one plant without fertiliser. After three months he measured the mass of 10 tomatoes from each plant.
Identify the independent and dependent variables for the investigation.
Independent variable ……….........................................………...............................…….. Dependent variable ……….........................................………...............................……..
Table 8.2 shows the results for the experiment.
Table 8.2
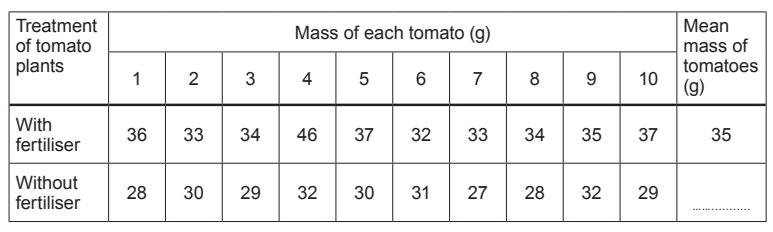
(i) Tony calculated the mean mass of tomatoes grown with fertiliser without including an anomalous result.
Circle the anomalous result in Table 8.2.
[1]
(ii) Calculate the mean mass of tomatoes grown without fertiliser. Write your answer in Table 8.2 to the nearest whole number.
[2]
Space for working:
(iii) State the conclusion that Tony can make from the results in Table 8.2.
[1]
(i) Tony ensured that this investigation was a fair test. State one variable that Tony would have controlled.
[1]
(ii) Each tomato plant produced many tomatoes, from which Tony chose ten.
Suggest why this step in Tony’s method could have caused inaccuracies in his results, and what he could have done to improve the investigation.
[2]
Reason for inaccuracies
Suggestion for improvement
Was this exam question helpful?