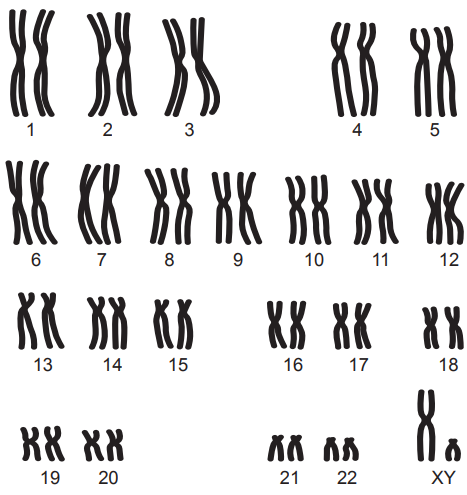
Image 6 shows the stages of genetically modifying a soya bean crop plant to become herbicide resistant.
Image 6
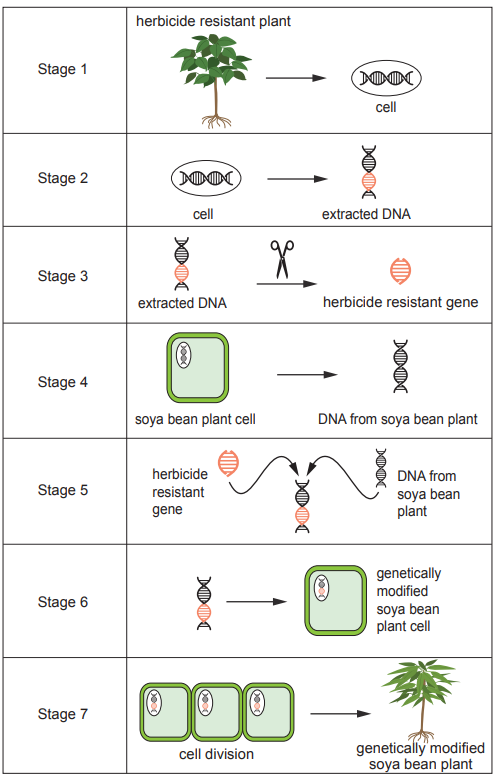
Use Image 6 to describe what is happening in each of the stages 1–7 during the process of genetic modification.
Include one advantage and one disadvantage of genetically modified (GM) crops in your answer
Was this exam question helpful?