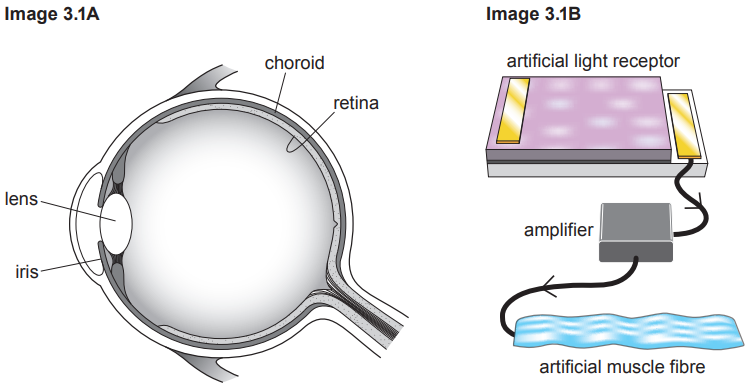
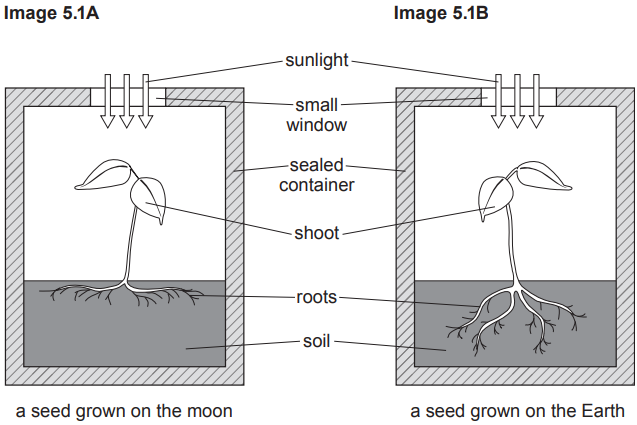
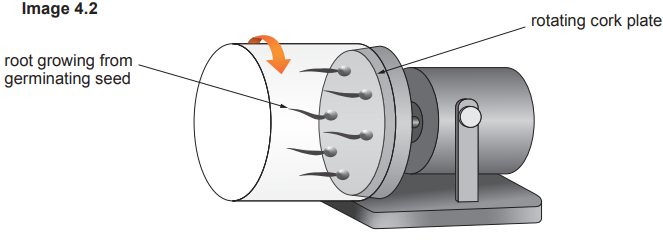
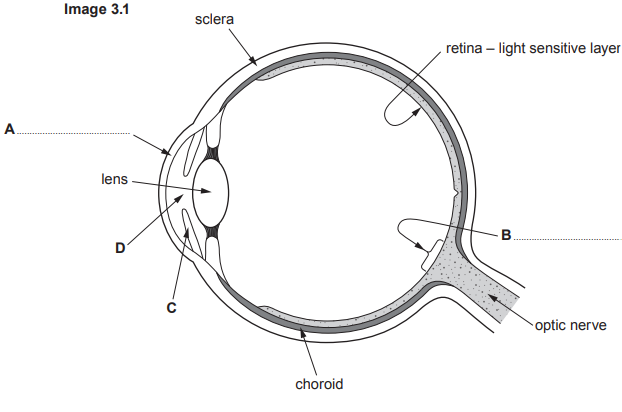
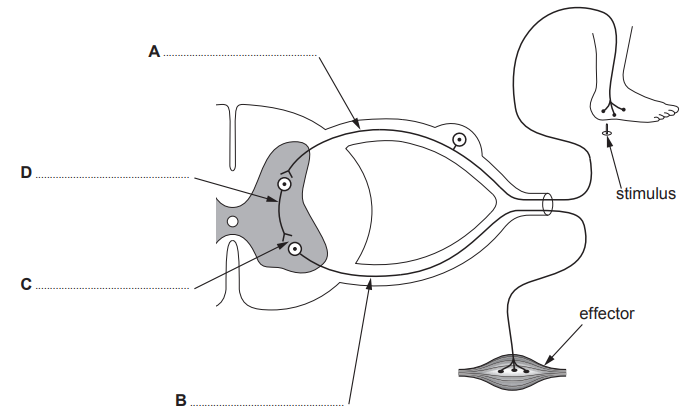
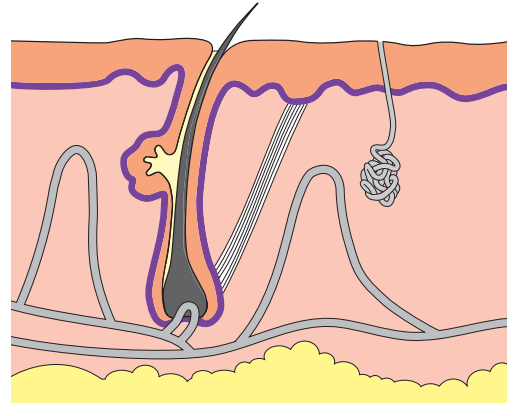
In Type 2 diabetes the body tissues do not respond to insulin.
The main risk factors are obesity, lack of regular exercise, family history and age.
The condition can be diagnosed by blood tests to measure glucose levels or by testing urine for glucose.
There are no drugs that can cure Type 2 diabetes.
However, a drug called metformin improves the response of the body tissues to insulin.
(i) Choose words from the list below to fill in the gaps in the sentences.
[4]
liver pancreas stomach glycogen hormone starch
Insulin is a .................... that is produced in the ...................... . It travels in the blood to the ....................... and causes glucose to be converted to.........................
(ii) Use the information provided to complete Table 4.1 by writing true or false next to each of the statements.
[4]
Table 4.1
Statement | True/False |
Type 2 diabetes is caused by too much insulin being produced. | |
Metformin works by reducing the response of the body tissues to insulin. | |
Being overweight is a risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. | |
Type 2 diabetes can be cured with medication | |
Only lifestylechoices affect the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. |
(iii) Doctors may prescribe metformin tablets to help treat Type 2 diabetes. Suggest two lifestyle changes the doctor may also advise.
[2]
Graph 4.2 shows the number of people with Type 2 diabetes per 1000 of the population between 2014 and 2024.
Graph 4.2
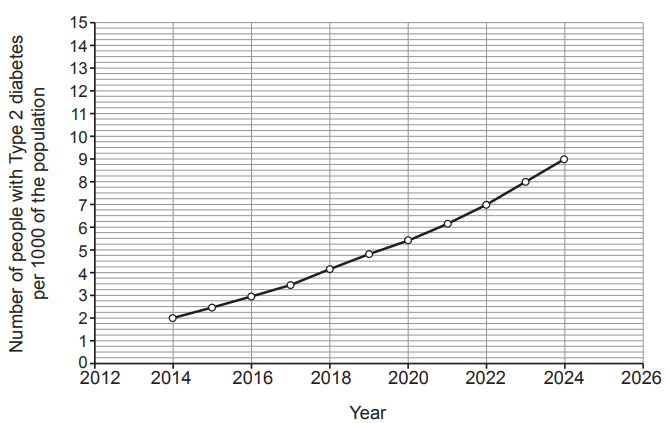
(i) Describe the trend shown in Graph 4.2 between 2014 and 2024.
[1]
(ii) Use the information in Graph 4.2 to calculate the difference in the number of people with Type 2 diabetes per 1000 of the population between 2014 and 2024.
[1]
Difference per 1000 of the population between 2014 and 2024 =...............
(iii) Use your answer to part (b)(ii) and the following equation to calculate the percentage change in the number of people that have Type 2 diabetes per 1000 of the population between 2014 and 2024.
[2]
Percentage change =.................
iv) Use Graph 4.2 to estimate the number of people per 1000 of the population that will have Type 2 diabetes in 2026 if the current trend continues. Show on Graph 4.2 how you arrived at your answer.
[1]
Number of people per 1000 of the population that will have Type 2 diabetes in 2026 =................
(i) Underline the chemical solution that can be used to test for glucose in urine.
[1]
Biuret reagent Benedict’s reagent Iodine
(ii) State what colour the solution would turn if the person had diabetes.
[1]
Was this exam question helpful?