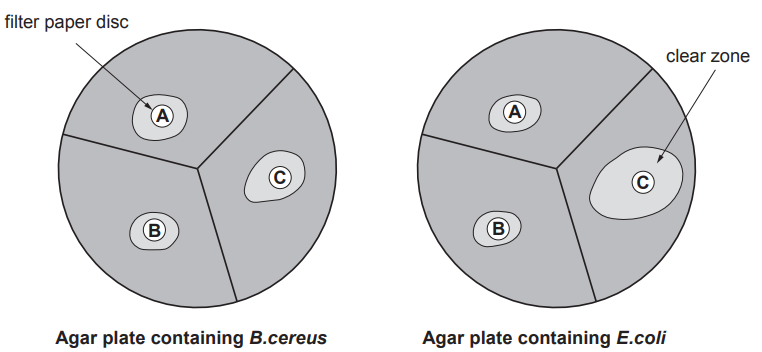
Mair investigated four antibiotics (A, B, C and D) to compare how effective they were at killing bacteria.
She set up four agar plates with bacteria growing on them.
She placed a filter paper disc containing a different antibiotic in the centre of each plate.
She put the plates in an incubator.
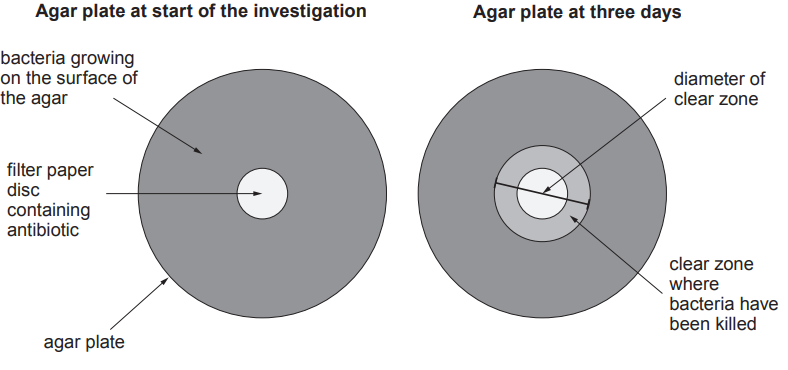
After three days, she measured the diameter of the clear zone where bacteria had been killed.
She calculated the area of the clear zone.
Image 6.1
Mair used aseptic techniques to set up the agar plates.
(i) Explain why it was necessary for her to use sterilised forceps to place the filter paper discs on the agar.
[1]
(ii) Describe how she would have made sure that no bacteria from the environment could enter the agar plates after the filter paper discs were placed on the agar.
[1]
Circle the most suitable temperature for the incubator in a school laboratory from the choice below.
10°C 25°C 37°C 60°C
Table 6.2 shows Mair’s results.
Table 6.2
Antbiotic A | Antibiotic B | Antibiotic C | Antibiotic D | |
Area of clear zone on agar plate (mm2) | 270 | 360 | ............... | 450 |
(i) The radius of the clear zone for antibiotic C was 11 mm.
Complete Table 6.2 by calculating the area of the clear zone for antibiotic C, using the formula below, where r = radius.
Area of circle = (
= 3.14)
Give your answer to the nearest whole number.
[3]
(ii) Use the data in Table 6.2 to complete Bar chart 6.3 by:
[3]
I. adding the scale for the area of the clear zone .
II. drawing bars for antibiotics A, B and C and labelling your bars.
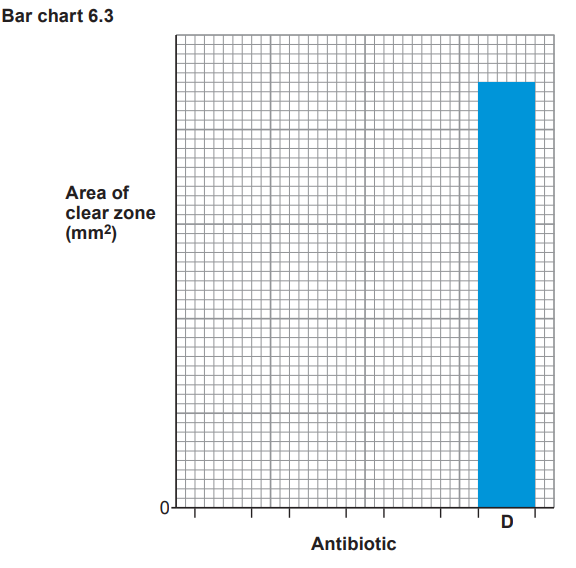
(iii) From Bar chart 6.3, state which one of the antibiotics was the most effective and explain the reason for your choice.
[3]
Antibiotic ..............................
Reason ......................................
(i) State how Mair could check that her results were reproducible.
[1]
(ii) Suggest one way in which the investigation could be extended to give more information about the effects of antibiotics on the growth of bacteria.
[1]
Was this exam question helpful?