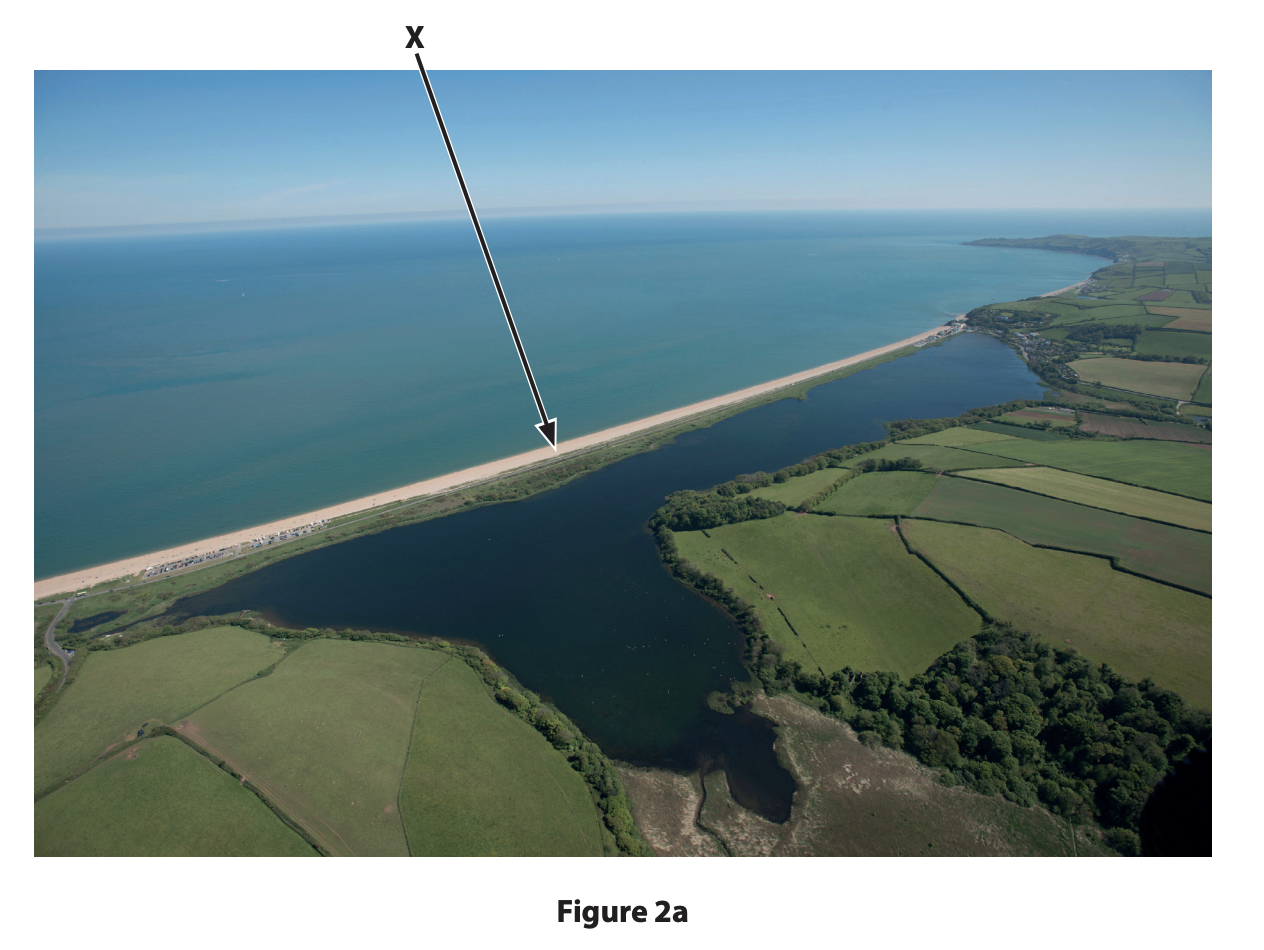

Coastal erosion and deposition create distinctive landscapes.
Study Figure 2a in the Resource Booklet.
Identify landform X.
bar
headland
spit
wave cut platform
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 1GA0

Coastal erosion and deposition create distinctive landscapes.
Study Figure 2a in the Resource Booklet.
Identify landform X.
bar
headland
spit
wave cut platform
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Define the term slumping.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Explain one way seasonal changes in the UK’s weather can affect rates of coastal erosion.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

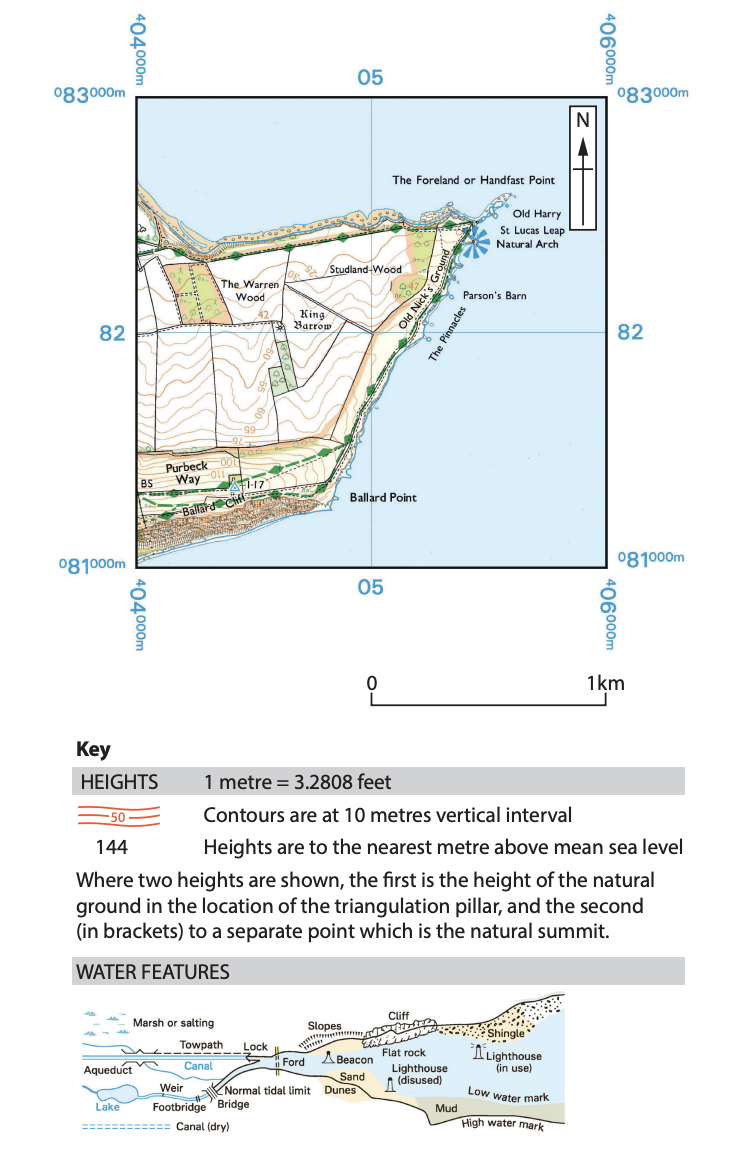
Figure 2c
Study Figures 2b and 2c in the Resource Booklet.
Examine the role of different physical processes in the formation of the coastal landforms shown in Figures 2b and 2c.
You must use evidence from Figures 2b and 2c in your answer
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Coastal landscapes are constantly being changed by different processes.
Name one type of mass movement.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
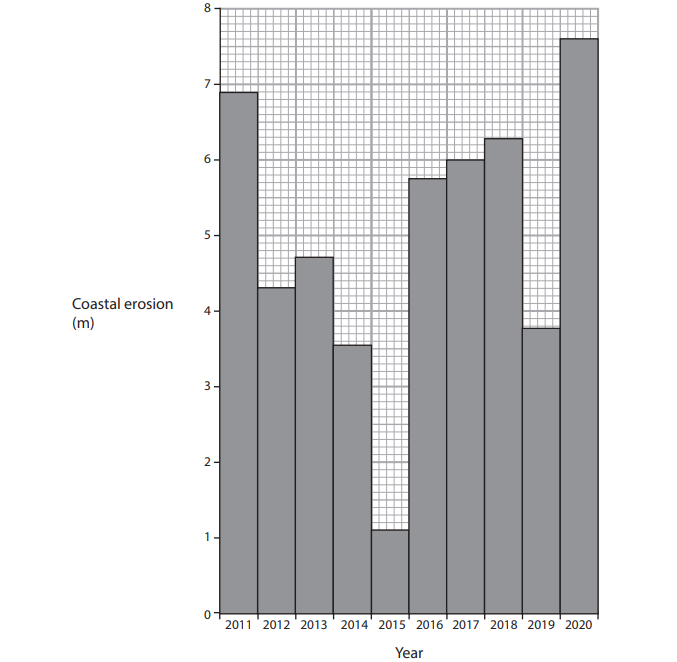
Figure 2a
Annual amount of coastal erosion at Withernsea, England
Study Figure 2a in the Resource Booklet.
Identify the year with the greatest amount of coastal erosion.
2012
2015
2017
2020
Choose your answer
Explain one reason why rates of coastal erosion may change over time.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
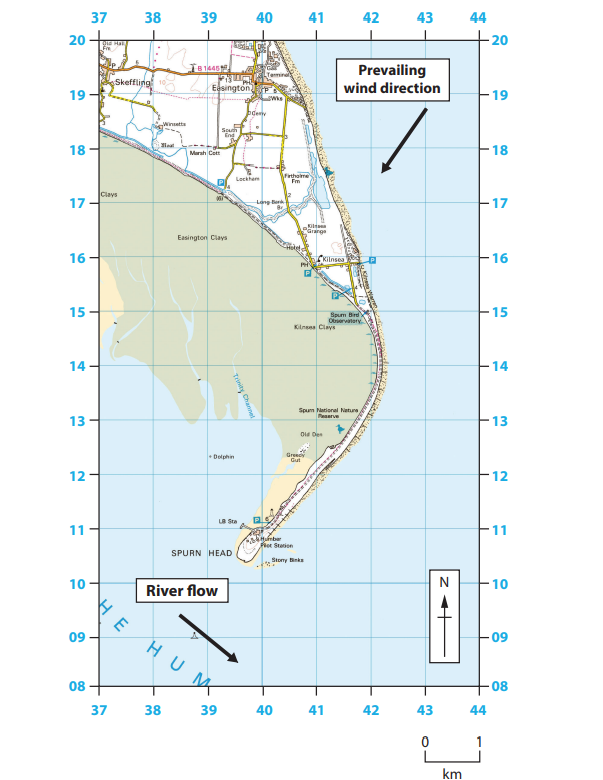
Figure 2b
A spit in East Yorkshire, England
Key for Figure 2b

Figure 2c
An aerial photograph of a spit in East Yorkshire, England
Study Figures 2b and 2c in the Resource Booklet.
Examine the role of physical processes in the formation of the spit shown in Figures 2b and 2c.
You must use evidence from Figures 2b and 2c in your answer.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
You have studied a coastal landscape as part of your geographical investigation.
Name of your fieldwork location
Explain one way your investigation helped you understand how coastal processes affect people.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Coastal landscapes are constantly being changed by physical processes.
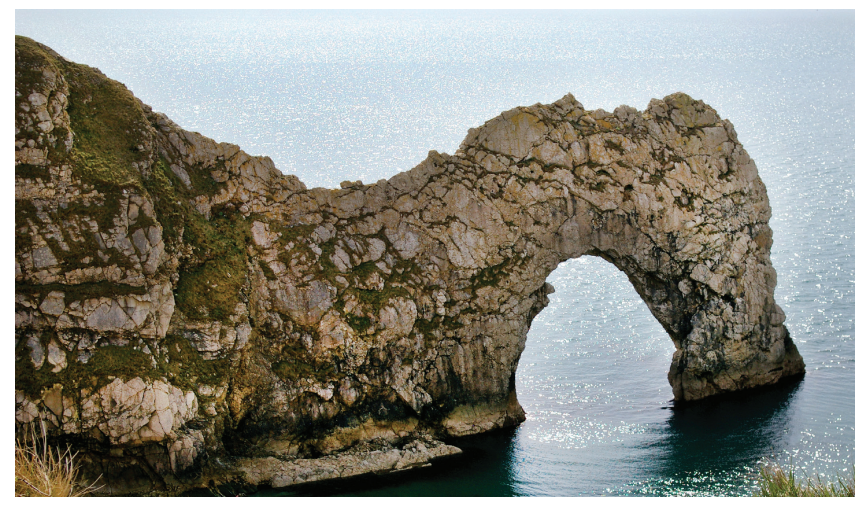

Figure 2a
Durdle Door, Dorset, England
Study Figure 2a in the Resource Booklet.
Identify the landform shown in Figure 2a.
arch
beach
spit
stack
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
State one type of mass movement process.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Explain one way that constructive waves can affect beaches.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
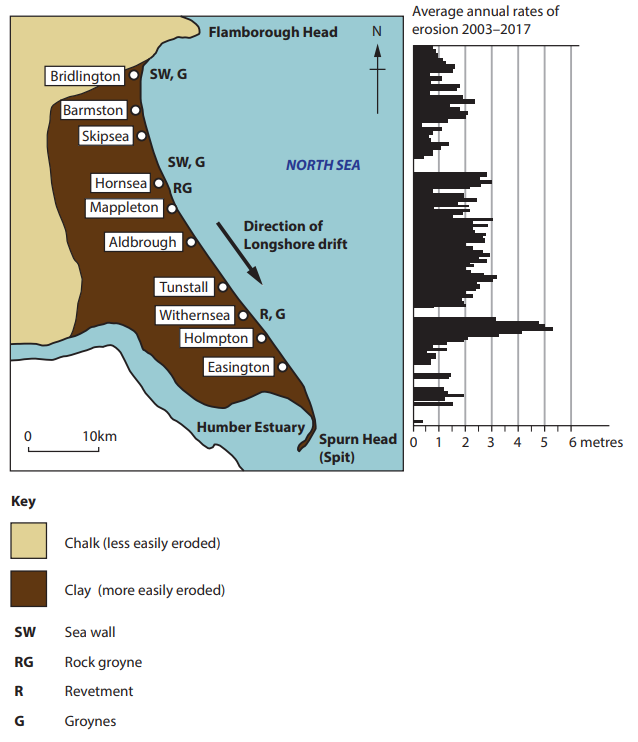
Figure 2b
Coastal erosion along the Holderness coastline in England
Study Figure 2b in the Resource Booklet.
Examine how different physical processes and human activities may have affected the rates of erosion shown in Figure 2b.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?