Butane (C4H10) is a saturated hydrocarbon used as a fuel in camping stoves.
Butane is a member of the alkane homologous series. State two characteristics of a homologous series.
Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of butane gas.
A mass of 5.25 g of butane gas is burned completely in oxygen. The carbon dioxide gas produced is collected at a temperature of 50 °C and a pressure of 105 kPa.
Calculate the volume of carbon dioxide gas produced, in dm3.
(The ideal gas constant R = 8.31 J K-1 mol-1)
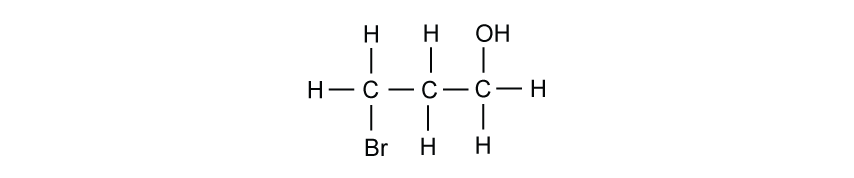
Butane exists as structural isomers. The isomer, 2-methylpropane, is also used as a fuel.
Draw the skeletal formula of 2-methylpropane.
The enthalpy of combustion of 2-methylpropane is -2869 kJ mol-1.
Use the mean bond enthalpies in the table to calculate the enthalpy of combustion for butane (C4H10) and suggest a reason, based on bonds, why the values for the two isomers are different.
Bond | Bond Enthalpy / kJ mol⁻¹ |
|---|---|
C–H | 413 |
C–C | 347 |
O=O | 498 |
C=O | 805 |
O–H | 464 |
Was this exam question helpful?