Gradients, Tangents & Normals (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Finding gradients
How do I find the gradient of a curve at a point?
The gradient of a curve at a point is the gradient of the tangent to the curve at that point
Find the gradient of a curve at a point by substituting the value of
at that point into the curve's derivative function
For example, if
then
So the gradient of
when
is
and the gradient of
when
is
Although your GDC won't find a derivative function for you, it is possible to use your GDC to find the value of the derivative of a function at a point, using
Worked Example
A function is defined by .
(a) Find .
Answer:

(b) Hence show that the gradient of when
is 20.
Answer:
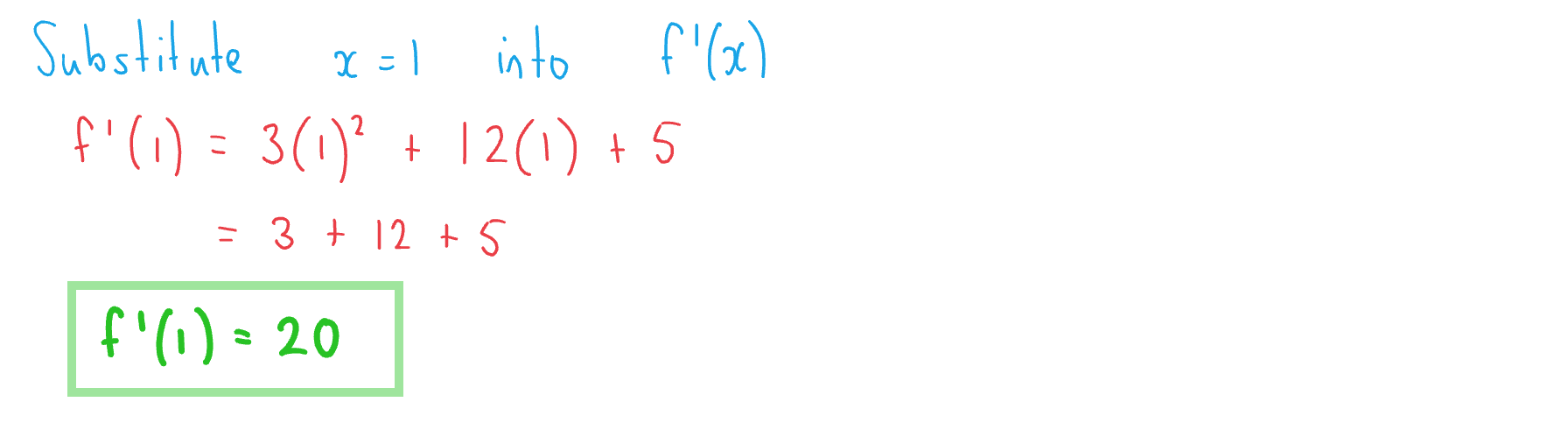
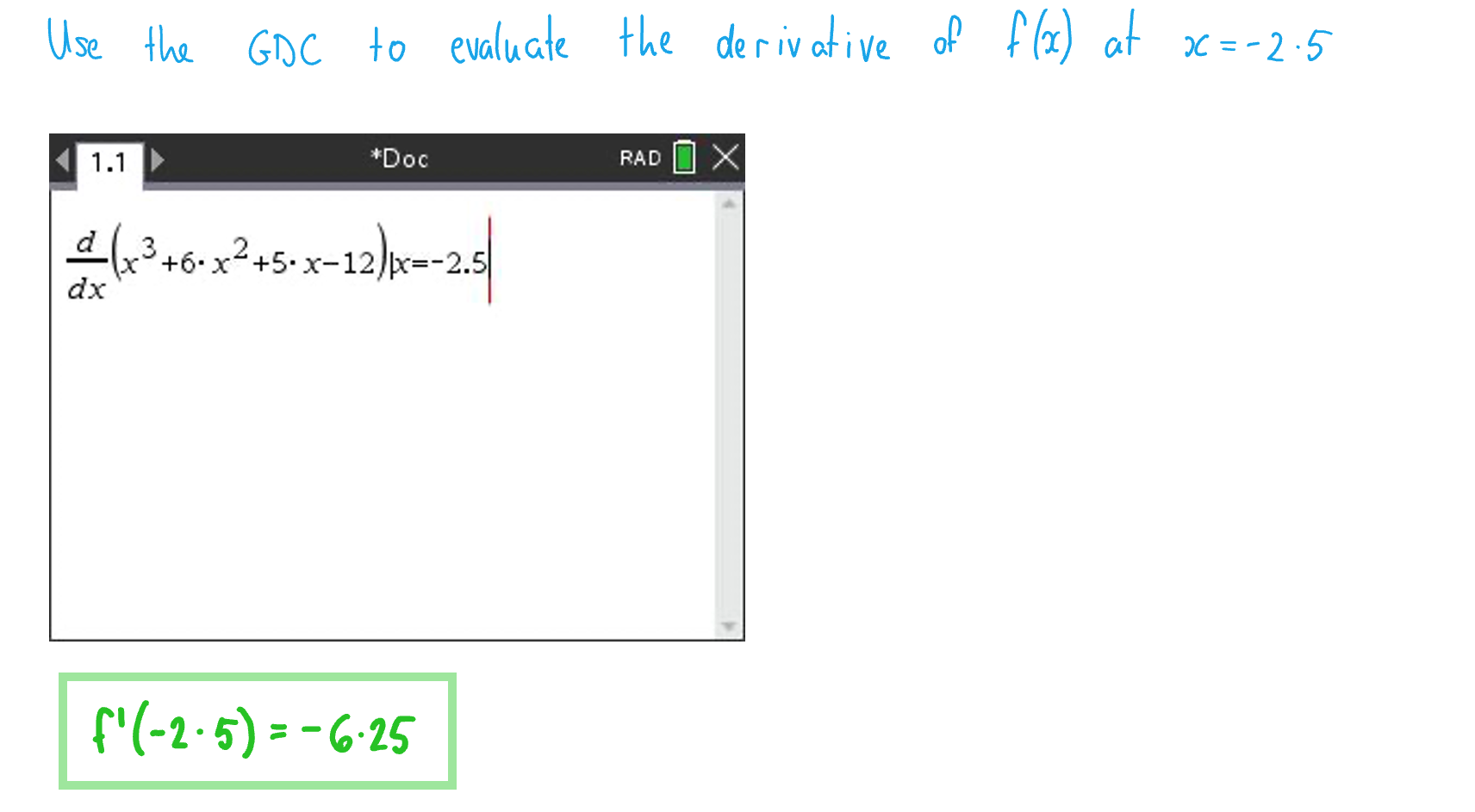
(c) Find the gradient of when
.
Answer:
Did this video help you?
Tangents & normals
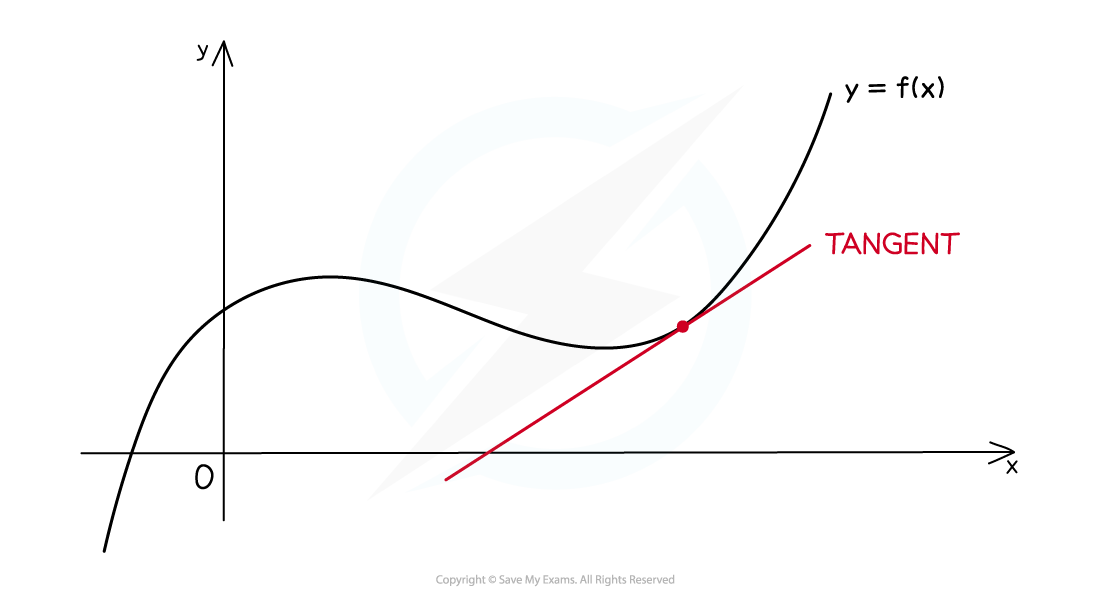
What is a tangent?
At any point on the graph of a (non-linear) function, the tangent is the straight line that touches the graph at the point without crossing through the graph
Its gradient is given by the derivative function
How do I find the equation of a tangent?
To find the equation of a straight line, a point and the gradient are needed
The gradient,
, of the tangent to the function
at
is
To find the equation of the tangent to the function
at the point
substitute the gradient,
and point
into the equation of a line
This gives:
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You could also substitute into , but it is usually quicker to substitute into
.
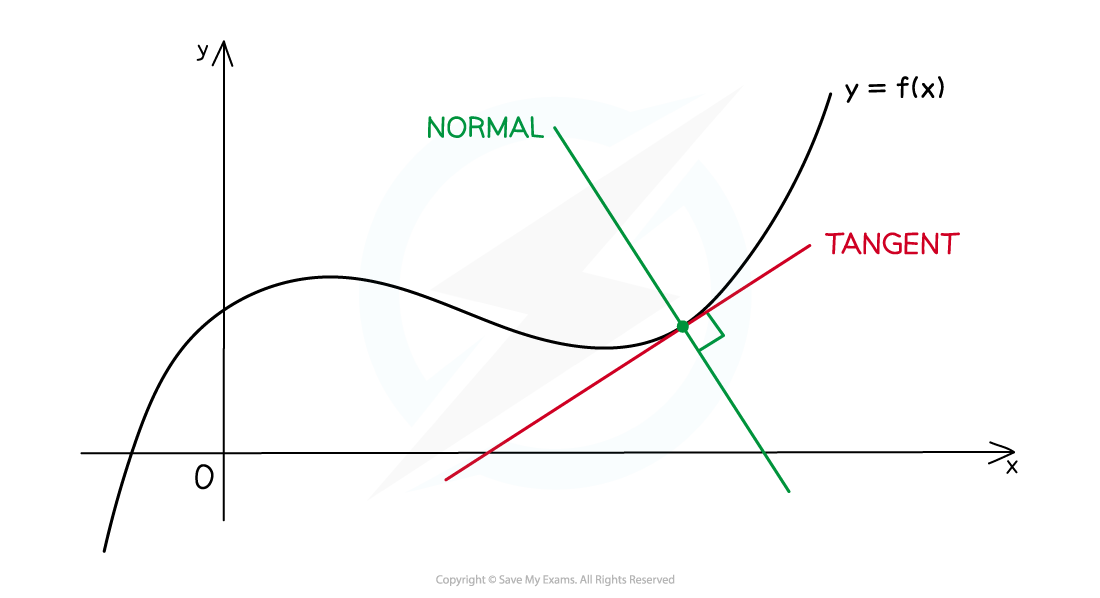
What is a normal?
At any point on the graph of a (non-linear) function, the normal is the straight line that passes through that point and is perpendicular to the tangent
How do I find the equation of a normal?
The gradient of the normal to the function
at
is
Therefore find the equation of the normal to the function
at the point
by using
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are not given the formulas for the equation of a tangent or the equation of a normal.
However both can be derived from the equations of a straight line which are given in the formula booklet.
Worked Example
The function is defined by
a) Find an equation for the tangent to the curve at the point where
, giving your answer in the form
.
Answer:

b) Find an equation for the normal at the point where , giving your answer in the form
, where
,
and
are integers.
Answer:


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
