Adding & Subtracting Vectors (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
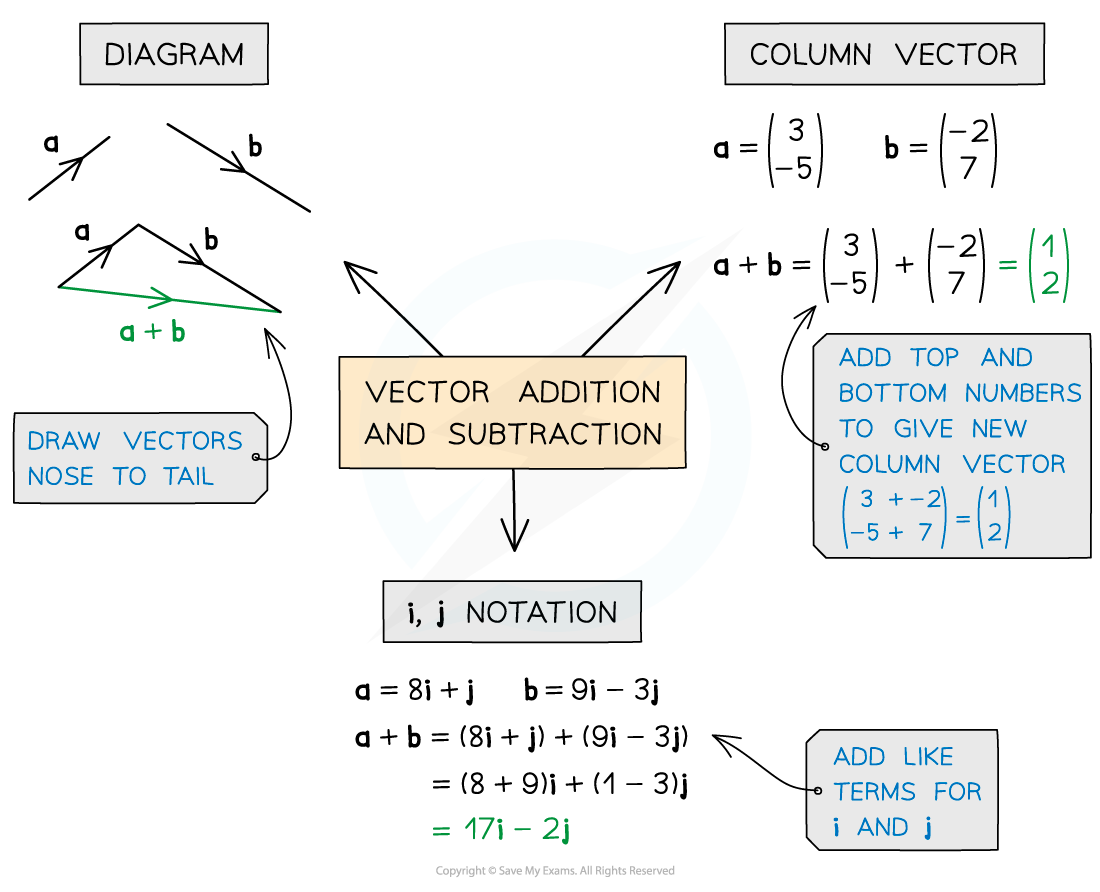
Adding & subtracting vectors
How are vectors added and subtracted numerically?
The sum of two or more vectors is called the resultant of the vectors
The resultant is also a vector
To add two vectors, you add together the corresponding components
To subtract two vectors, you subtract together the corresponding components
It is easy to add and subtract column vectors
For example,
Collect like-terms if working with vase vectors
For example, (2i + j – 5k) – (i + 4j + 3k) = (i – 3j – 8k)
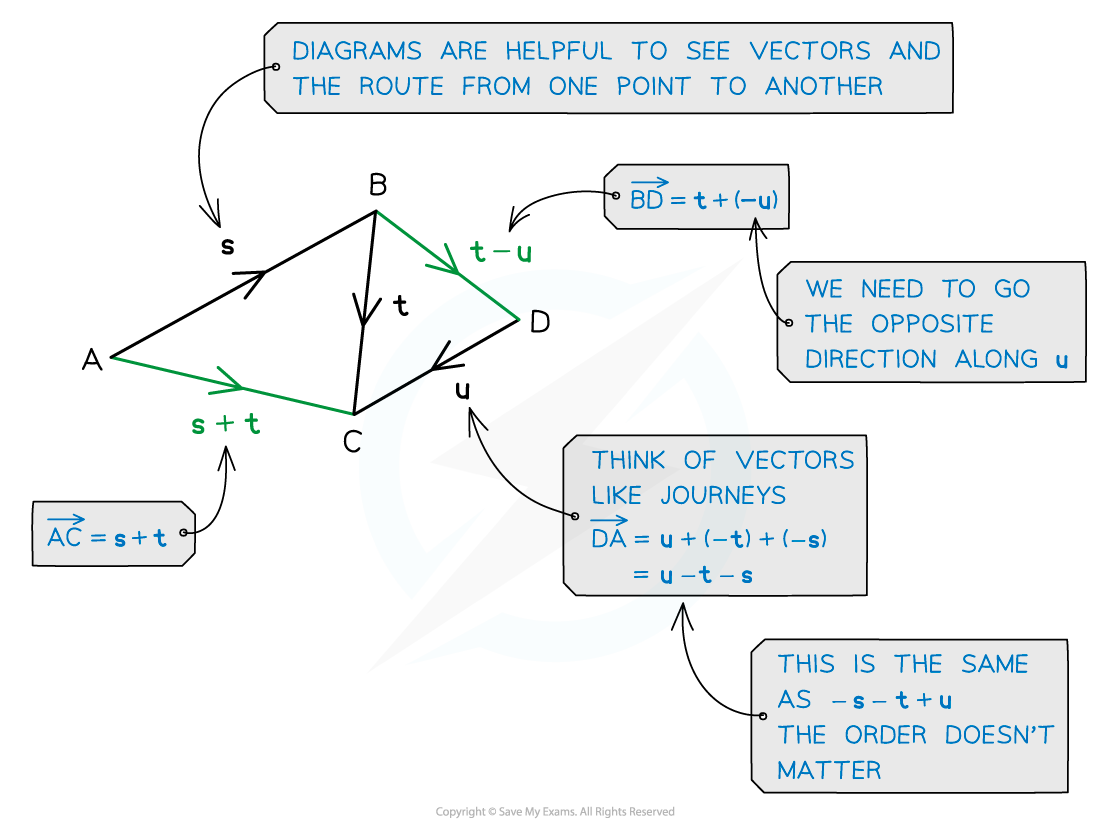
How are vectors added and subtracted geometrically?
Vectors can be added geometrically by joining the end of one vector to the start of the next one
The resultant vector will be the shortest route from the start of the first vector to the end of the second
If the two vectors have the same starting position
The second vector can be translated to the end of the first vector to find the resultant vector
This results in a parallelogram with the resultant vector as the diagonal
Subtracting a vector is the same as adding a vector with its direction reversed
For example, a – b = a + (-b)
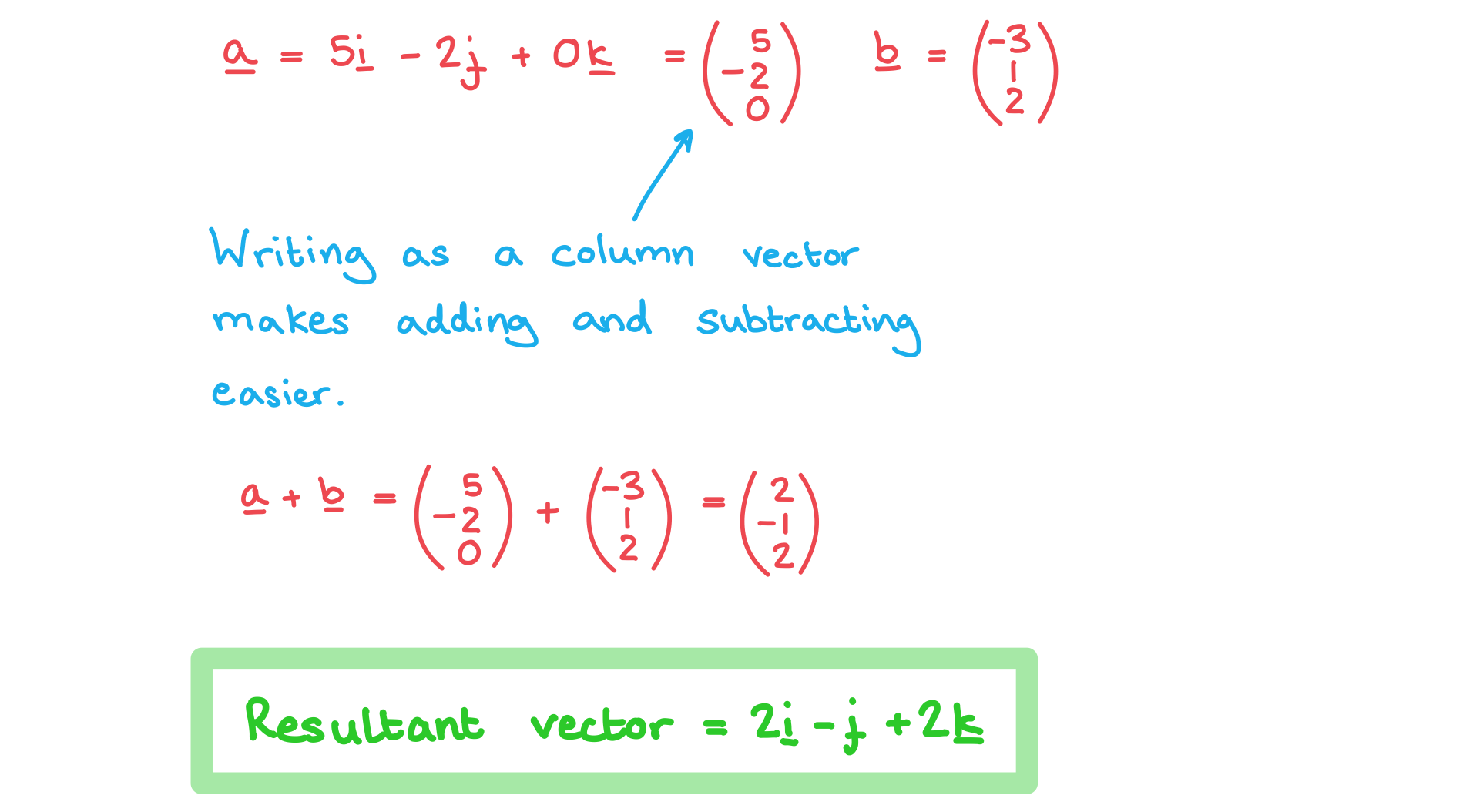
Worked Example
Find the resultant of the vectors a = 5i – 2j and b = .

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?