Position & Displacement Vectors (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Position vectors
What is a position vector?
A position vector describes the position of a point in relation to the origin
The position vector of point A is written with the notation
The origin is always denoted O
The individual components of a position vector are the coordinates of the point
For example, the point with coordinates (3, -2, -1) has position vector
Worked Example
Determine the position vector of the point with coordinates (4, -1, 8).

Did this video help you?
Displacement vectors
What is a displacement vector?
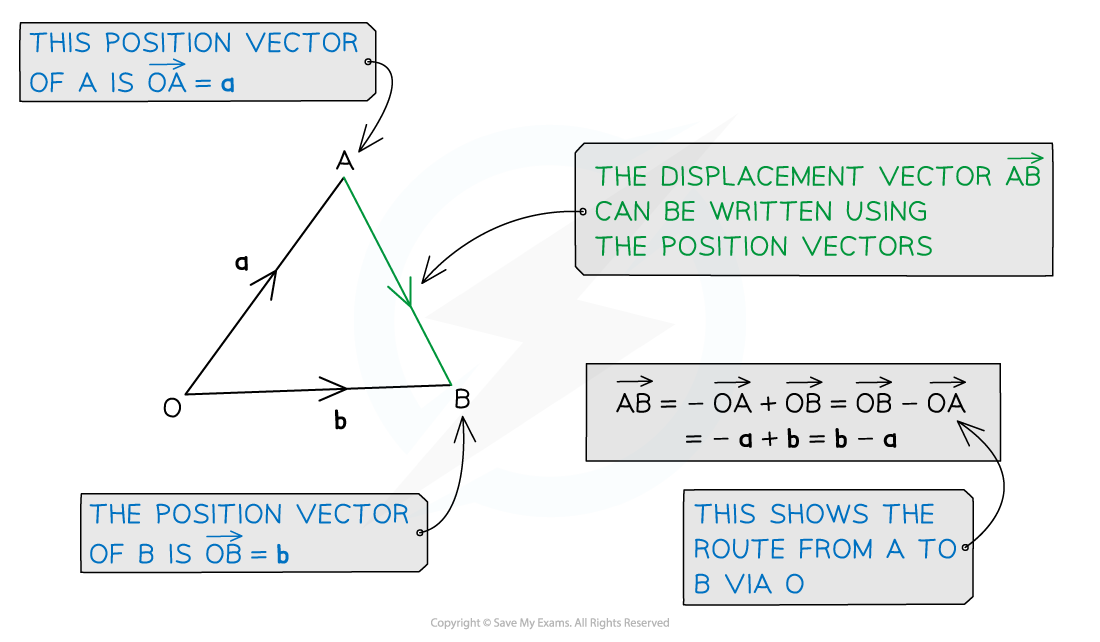
A displacement vector describes the shortest route between any two points
The displacement vector of point B from the point A is written with the notation
A position vector is a displacement vector of a point from the origin
A displacement vector between two points can be written in terms of the displacement vectors using a third point
For example,
A displacement vector can be written in terms of its position vectors
For example,
can be written in terms of
and
This can be rewritten as
Worked Example
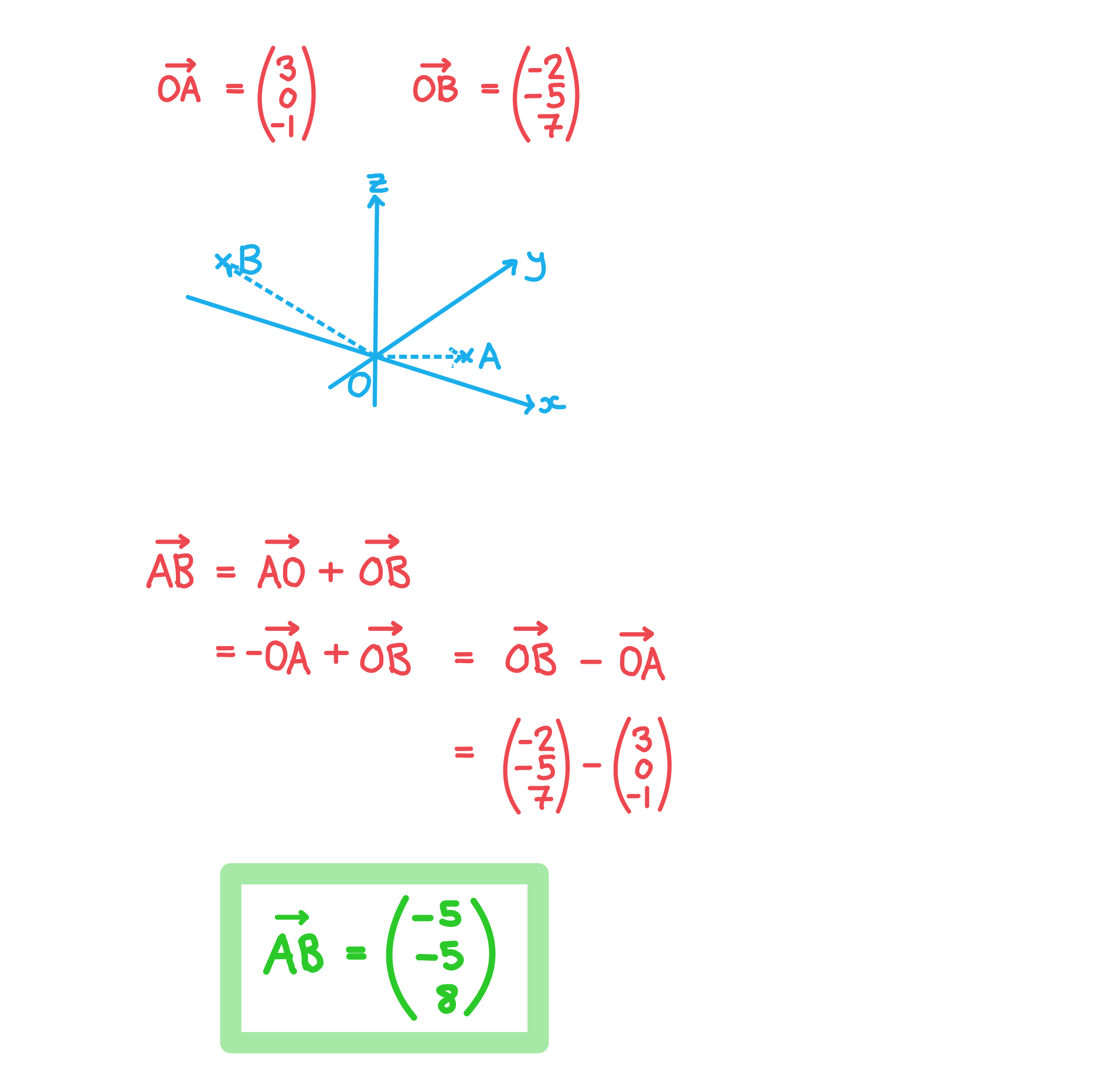
The point A has coordinates (3, 0, -1) and the point B has coordinates (-2, -5, 7). Find the displacement vector .

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?