The Vital Role of ATP (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
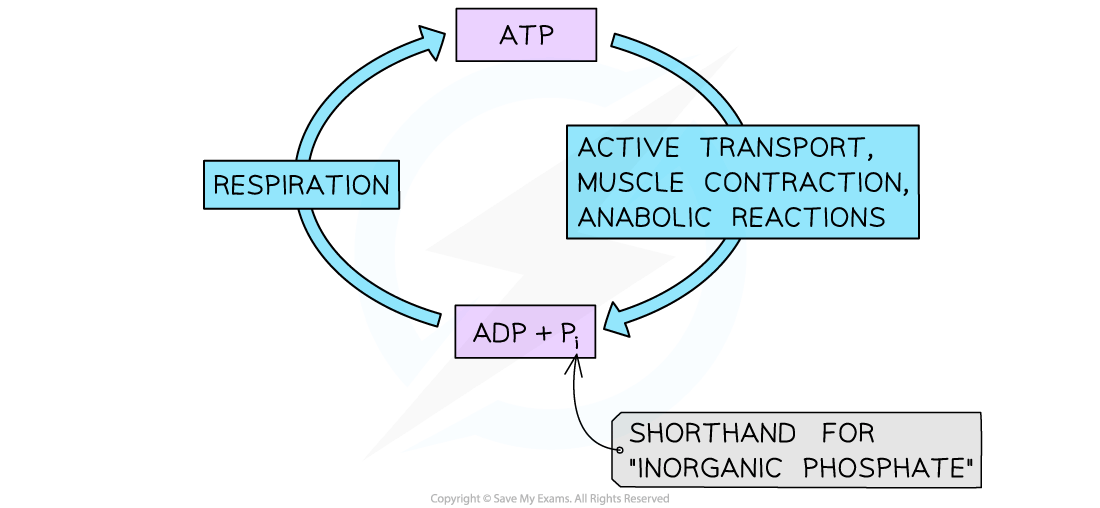
The vital role of ATP
All organisms require a constant supply of energy to maintain their cells and stay alive
This energy is required
In anabolic reactions to build larger molecules from smaller molecules
To move substances across the cell membrane in active transport, or to move substances within the cell
In animals, energy is required
For muscle contraction
In the conduction of nerve impulses
In all known forms of life, ATP from respiration is used to transfer energy in all energy-requiring processes in cells; this is why ATP is known as the universal energy currency
Energy is released from ATP when it is broken down to ADP and inorganic phosphate
This process is reversed during respiration to make ATP and maintain a supply of energy
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide
The monomers of DNA and RNA are also nucleotides
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always state that ATP is the immediate source of energy for cellular processes — not glucose.
In exam questions, students often say that cells “use glucose for energy”, but this is inaccurate. Glucose is first broken down in respiration to produce ATP, and ATP (not glucose) is the molecule that directly releases energy for processes like active transport, muscle contraction, and nerve impulse transmission.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
