Modulus Transformations (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Modulus transformations
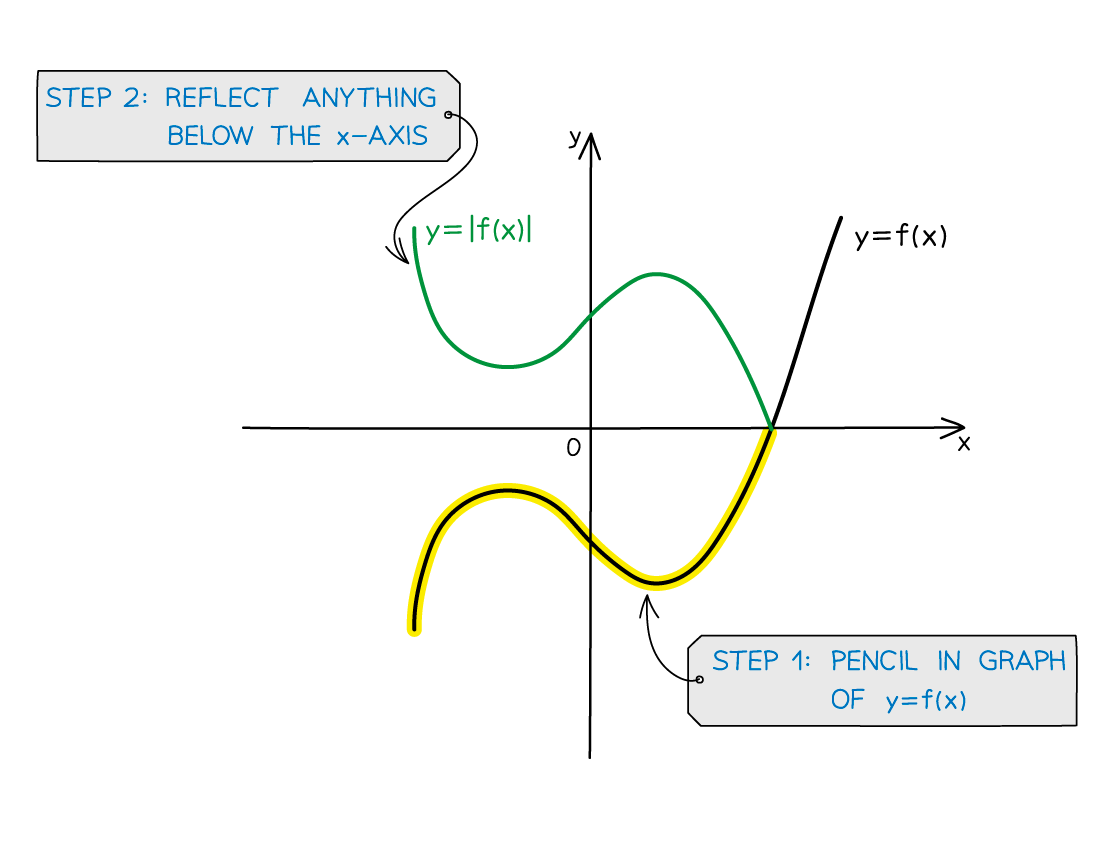
How do I sketch the modulus of a function y = |f(x)|?
To sketch
STEP 1
Sketch the parts ofthat are on or above the
-axis
STEP 2
Sketch the reflections in the-axis of any parts below
Examiner Tips and Tricks
No part of the graph should be below the
-axis.
How do I sketch a function of mod x, y = f(|x|)?
To sketch
STEP 1
Keep the part ofon, or to the right of, the
-axis
get rid of any part that is to the left
STEP 2
Reflect the right-hand side in the
-axis to create a left-hand side
This will create a symmetric graph about the
-axis
What are some differences between y = |f(x)| or y = f(|x|)?
It helps to remember that
can never go below the
-axis
whereas
can
is always symmetric about the
-axis
whereas
does not have to have any lines of symmetry
How do I sketch transformations of y = |f(x)|?
To sketch
first sketch
without modulus signs
then apply a vertical stretch of scale factor
followed by a vertical translation of
then take the modulus (using the rules above)
To sketch
sketch
(as above)
then apply a vertical stretch of scale factor
followed by a vertical translation of
How do I sketch transformations of y = f(|x|)?
To sketch
sketch
(using the rules above)
then apply a vertical stretch of scale factor
followed by a vertical translation of
How do I sketch y = |f(ax+b)| or y = f(|ax+b|)?
To sketch
first sketch
which factorises to
i.e. first apply a horizontal stretch to
of scale factor
becomes
followed by a horizontal translation of
to the left,
i.e.
becomes
which is
then take the modulus of
using the rules above
To sketch
factorise it to
i.e. first apply a horizontal stretch of scale factor
to
becomes
followed by a horizontal translation of
to the left,
i.e.
becomes
which is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When sketching transformed modulus graphs, make sure the corners (cusps) where parts of the graph have been reflected are drawn sharply.
Worked Example
The diagram below shows the graph of .

(a) Sketch the graph of .

(b) Sketch the graph of .


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?