Aerobic Respiration (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
The mitochondria
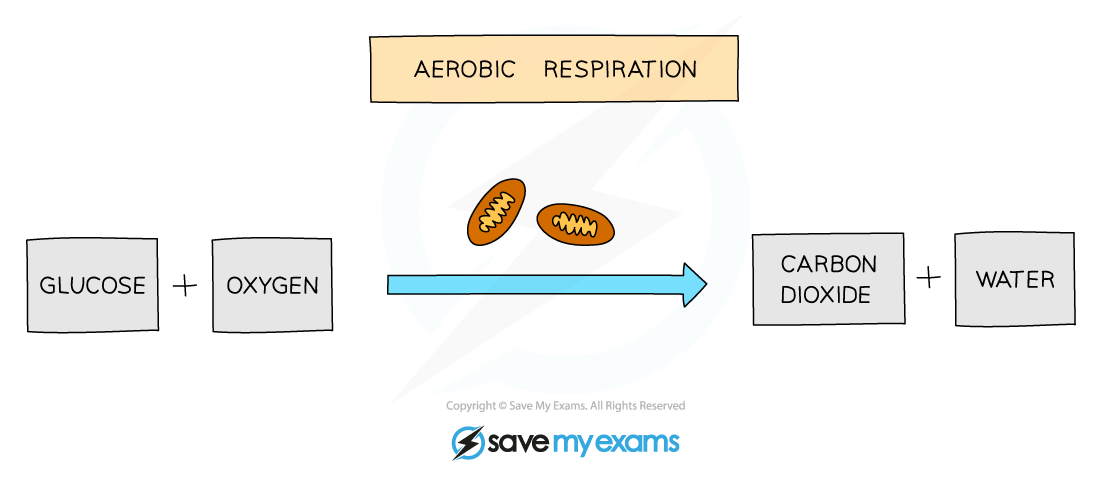
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and takes place in cellular organelles called mitochondria (singular = mitochondrion)
The structure of the mitochondrion is such that aerobic respiration can occur efficiently to generate ATP
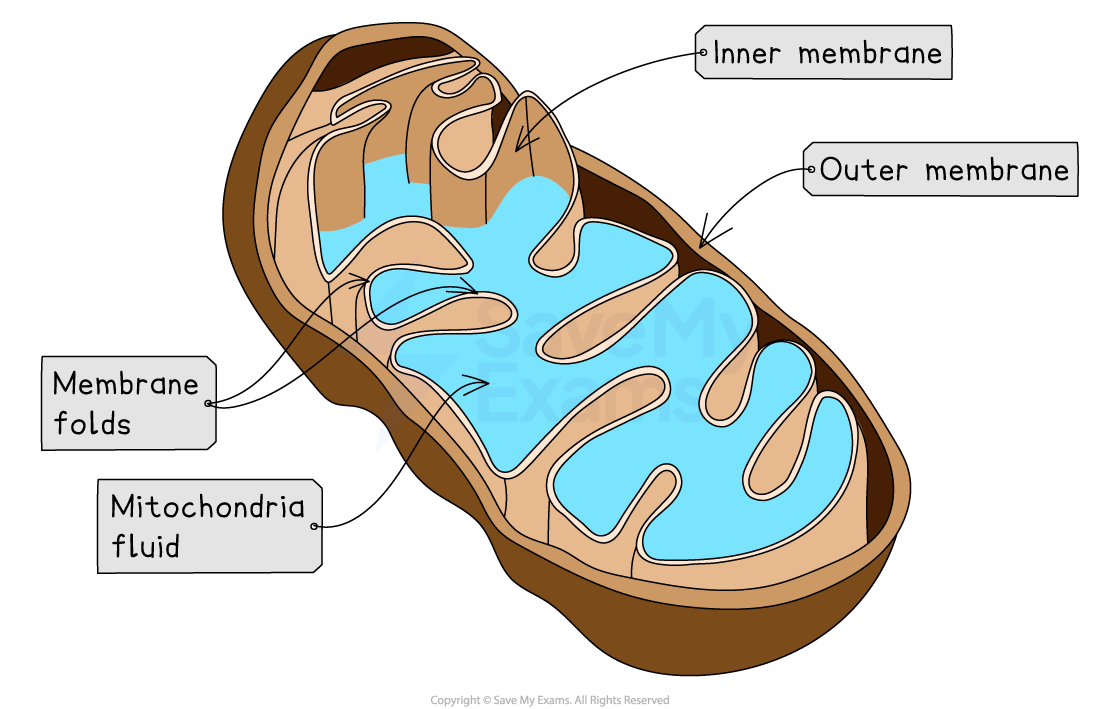
Each mitochondrion has the following structures:
A double membrane
A folded inner membrane for a large surface area
This is where respirations occur
An inner fluid-filled space
This contains enzymes essential for respiration
Many cells that require a large supply of ATP (such as sperm cells, nerve cells and muscle cells) have a large number of mitochondria
The process of aerobic respiration
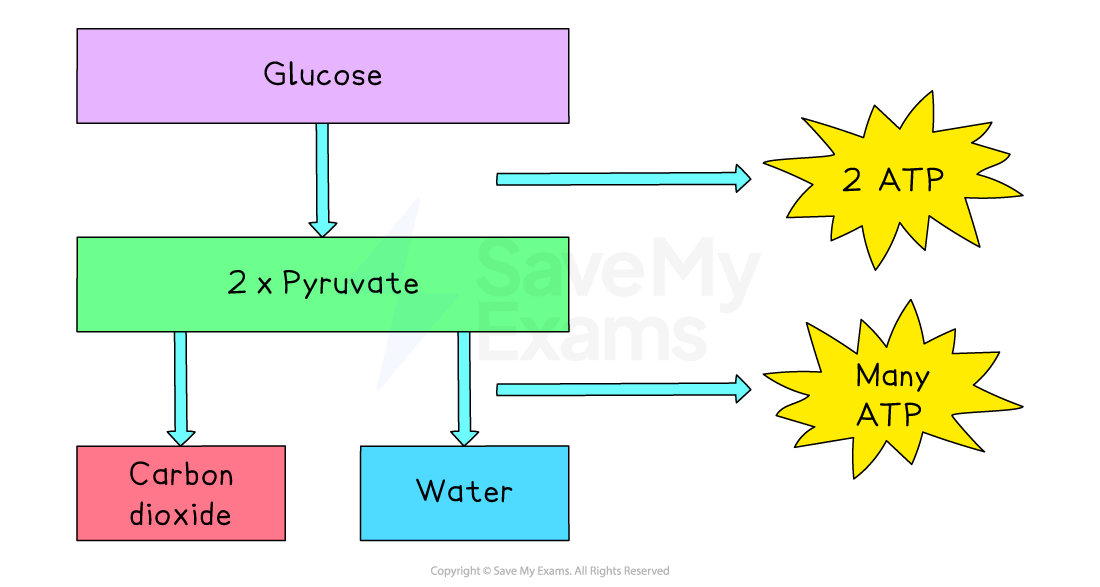
Aerobic respiration takes place over several reactions
Initially, glucose enters a cell and is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate
This releases enough energy to make two ATP molecules
This stage occurs in the cytoplasm rather than in mitochondria
If oxygen is present, each pyruvate is broken down (by enzyme-controlled reactions) completely into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
This process releases lots of energy
Enough energy is released to make a large number of ATP molecules
These enzyme-controlled reactions take place in the mitochondria
The word equation for aerobic respiration
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is important to use correct language when describing energy. You will not gain marks if you write about energy being 'made' or 'produced'. Energy can only be released or transferred, which, in the case of respiration, can be used to make or produce ATP.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
