Fermentation (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
Fermentation in animal cells
Fermentation is also known as anaerobic respiration
It refers to respiration in the absence of oxygen
The fermentation reactions take place in the cytoplasm of cells, rather than in the mitochondria
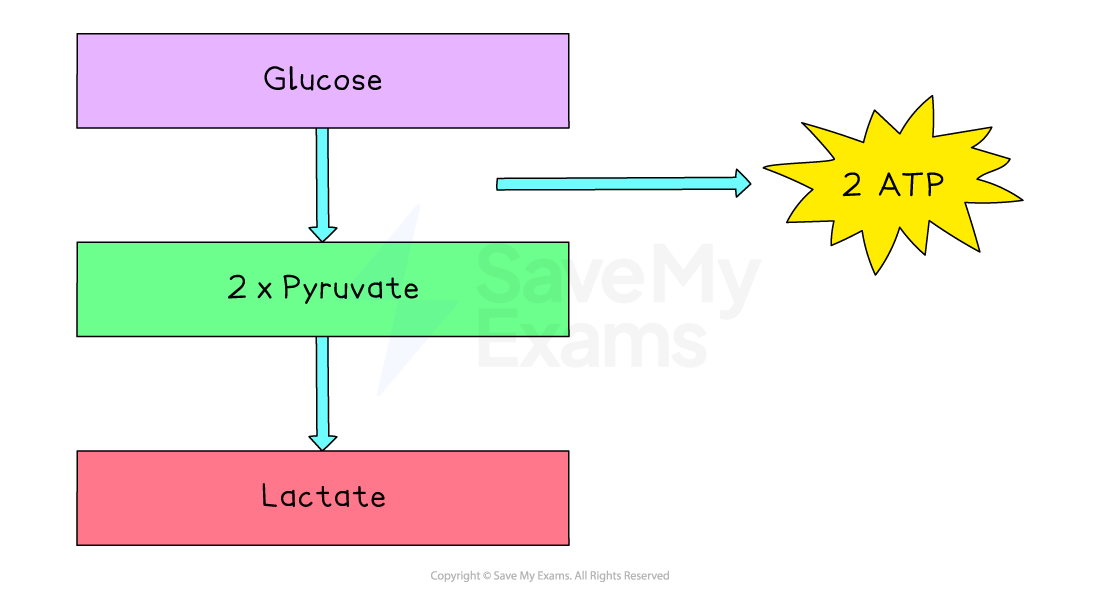
Fermentation starts in the same way as aerobic respiration
A molecule of glucose is broken down to two molecules of pyruvate, releasing enough energy to yield two molecules of ATP
In the absence of oxygen, the two pyruvate molecules are converted into lactate (lactic acid) instead of carbon dioxide and water
From one glucose molecule, four molecules of ATP are produced, but two are used to start the process, therefore giving a net gain of only two ATP molecules overall
This is much less than aerobic respiration
This is why anaerobic respiration is less efficient
Fermentation in plant and yeast cells
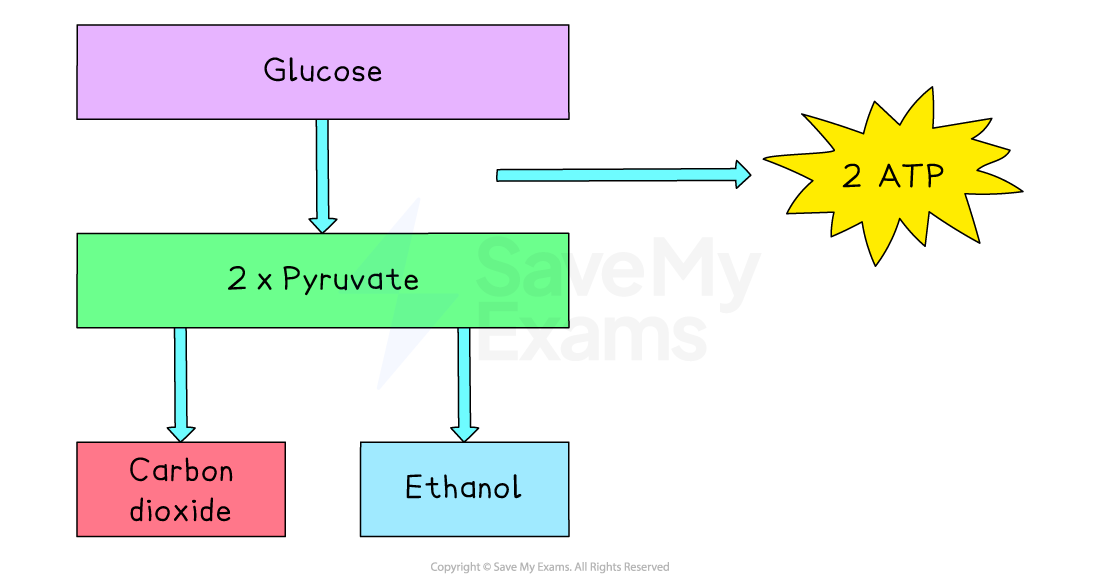
In plant and yeast cells, the process of fermentation is different from that of animal cells
Glucose is again broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, which releases a net gain of two molecules of ATP
Remember that four molecules of ATP are produced, but two are used to start the process
The two pyruvate molecules are converted to carbon dioxide and ethanol (alcohol)
No extra ATP is made during the conversion to carbon dioxide and ethanol
The products of fermentation in plant and yeast cells are used commercially to make bread rise and to brew alcoholic drinks

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
