Osmosis (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
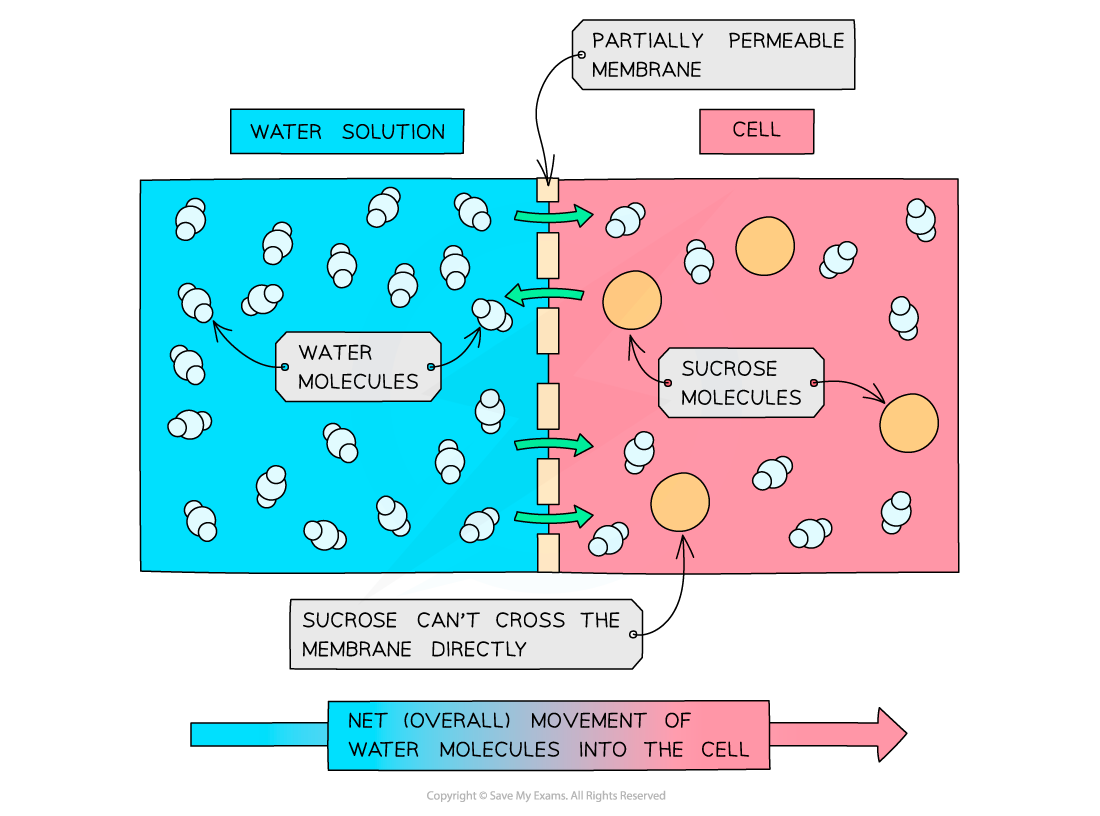
The process of osmosis
Osmosis is a type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules
Osmosis can be defined as:
the movement of water molecules from a higher water concentration to a lower water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
Note that a selectively permeable cell membrane can also be described as partially permeable
Solution | Alternative description | Direction of osmosis |
|---|---|---|
High water concentration E.g. the highest possible water concentration is found in pure water | Low solute concentration Dilute solution | Water will move out of a solution with a higher water concentration into a solution with a lower water concentration |
Low water concentration E.g. a concentrated sugar solution | High solute concentration | Water will move into a solution with a lower water concentration from a more dilute solution |
Osmosis in plant & animal cells
Plant and animal cells are surrounded by selectively permeable cell membranes; this means that water can move in and out of cells by osmosis
Osmosis affects animal and plant cells in different ways
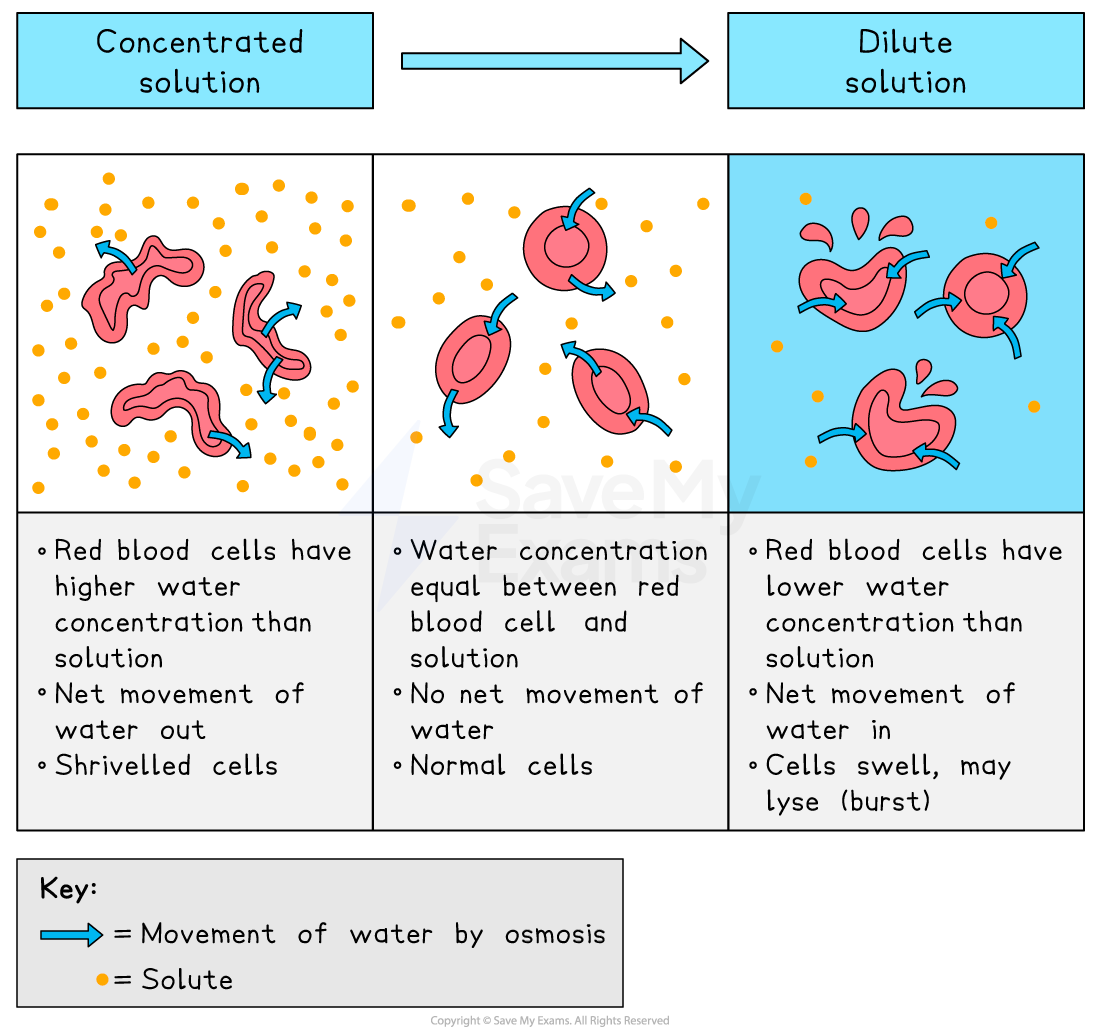
Animal cells
Animal cells can burst or shrink as follows:
animal cells placed in a strong sugar solution will shrink
the cell cytoplasm has a higher water concentration than the surroundings
water moves out by osmosis
cell volume decreases
animal cells placed in distilled water will burst
the cell cytoplasm has a lower water concentration than the surroundings
water enters by osmosis
cell volume increases
Maintaining a stable water potential in animal tissues is essential to prevent cell damage
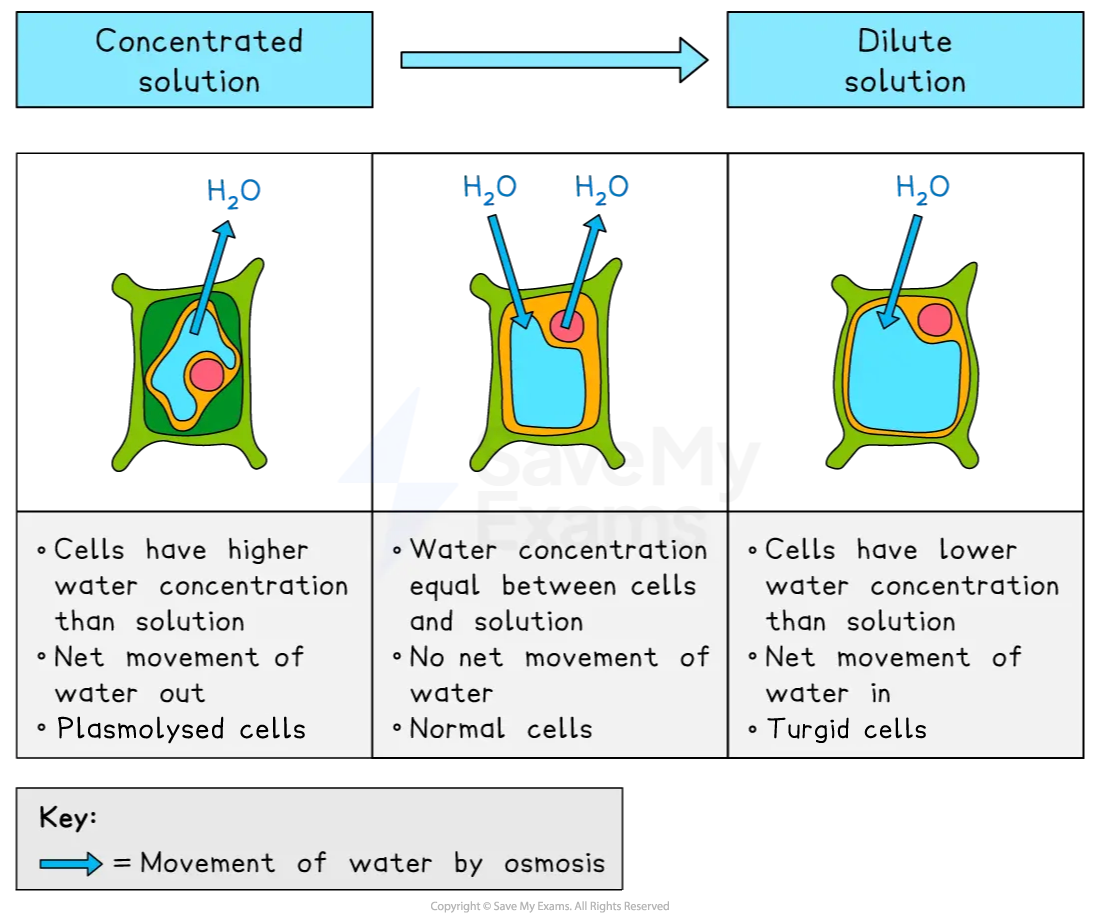
Plant cells
The effect of osmosis on plant cells differs to animal cells due to the presence of plant cell walls
Cell walls are rigid so maintain cell shape even when the volume of the cytoplasm changes
Plant cells can become turgid or plasmolysed as follows:
plant cells placed in a strong sugar solution will become plasmolysed
the cell cytoplasm has a higher water concentration than the surroundings
water moves out by osmosis
cytoplasm volume decreases
cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall
plant cells placed in distilled water will become turgid
the cell cytoplasm has a lower water concentration than the surroundings
water enters by osmosis
cytoplasm volume increases
cytoplasm pushes against the cell wall

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
