Exchange Surfaces (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
The need for exchange
For the body to function, cells need a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients for respiration, which releases energy in the form of ATP
Oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream in the lungs, where it diffuses from the alveoli into the blood
Nutrients, such as glucose and amino acids, are absorbed from digested food in the small intestine and enter the bloodstream through the villi
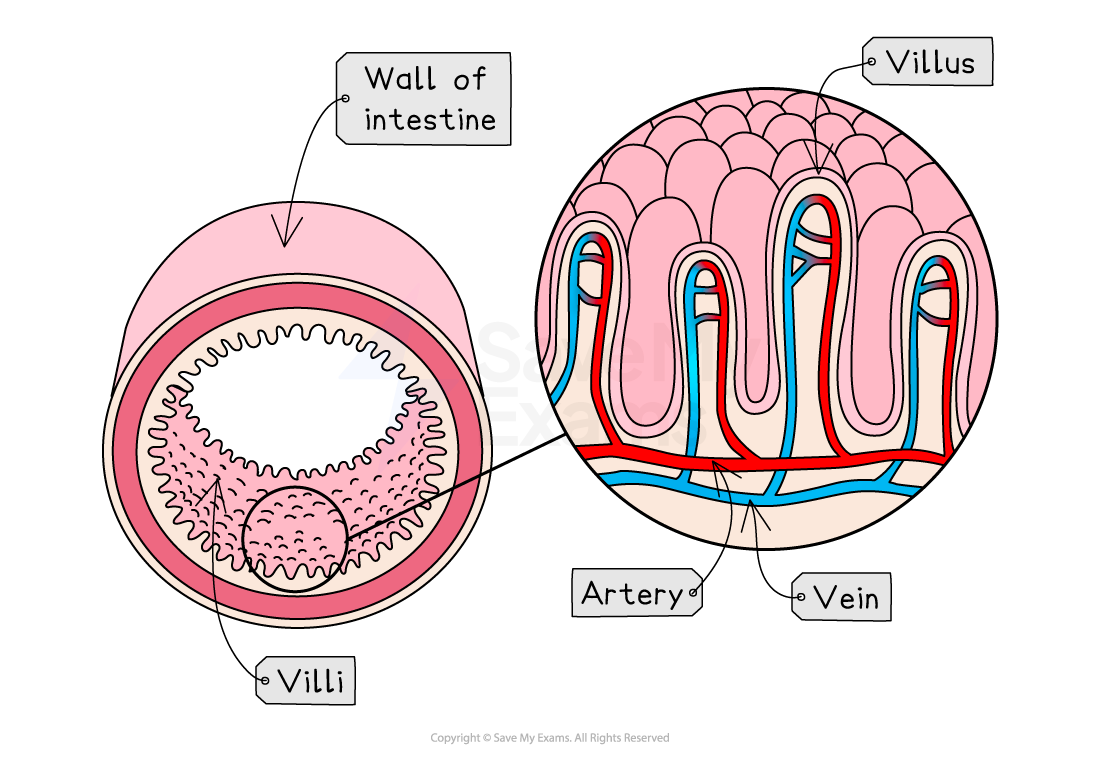
Delivery to the cells
Once key nutrients and oxygen have been absorbed into the bloodstream, they must then be delivered to the respiring cells
The heart pumps oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood via arteries, arterioles and capillaries
Oxygen is carried by red blood cells
Nutrients are carried in the blood plasma
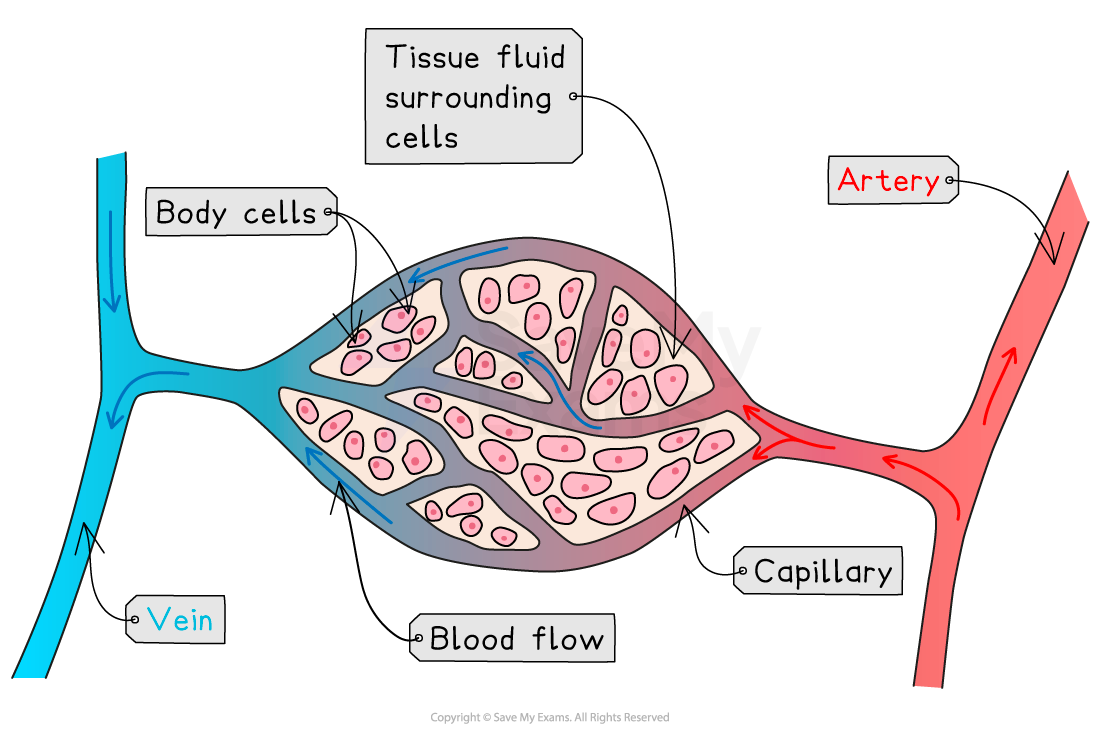
At the capillaries in tissues, substances move between blood and cells, mostly by diffusion
Removing waste
Waste materials, such as carbon dioxide from respiration, diffuse from cells into capillaries
Other waste substances include urea, excess ions and excess water
Once in the blood, carbon dioxide is mostly carried dissolved in plasma
At the lungs, carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli and is exhaled during breathing
Ventilation maintains a low concentration of carbon dioxide in the alveoli to ensure that diffusion continues
Capillary networks
Capillary networks surround tissues, so substances can move between the blood and cells efficiently
Substances that move into the cells include:
oxygen
glucose
amino acids
water
minerals
Substances that move out of the cells include:
carbon dioxide
urea
some water
Capillary networks are adapted to maximise the efficiency of exchange because they have:
very thin walls: the capillary endothelium is one cell thick, which provides a short diffusion distance
a narrow lumen: the capillary lumen is narrower than the diameter of a red blood cell, slowing blood flow and giving more time for exchange
a large total surface area: there are many capillaries, so that the total surface area of the capillary network is very large, allowing for fast exchange of materials

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
