Gas Exchange (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
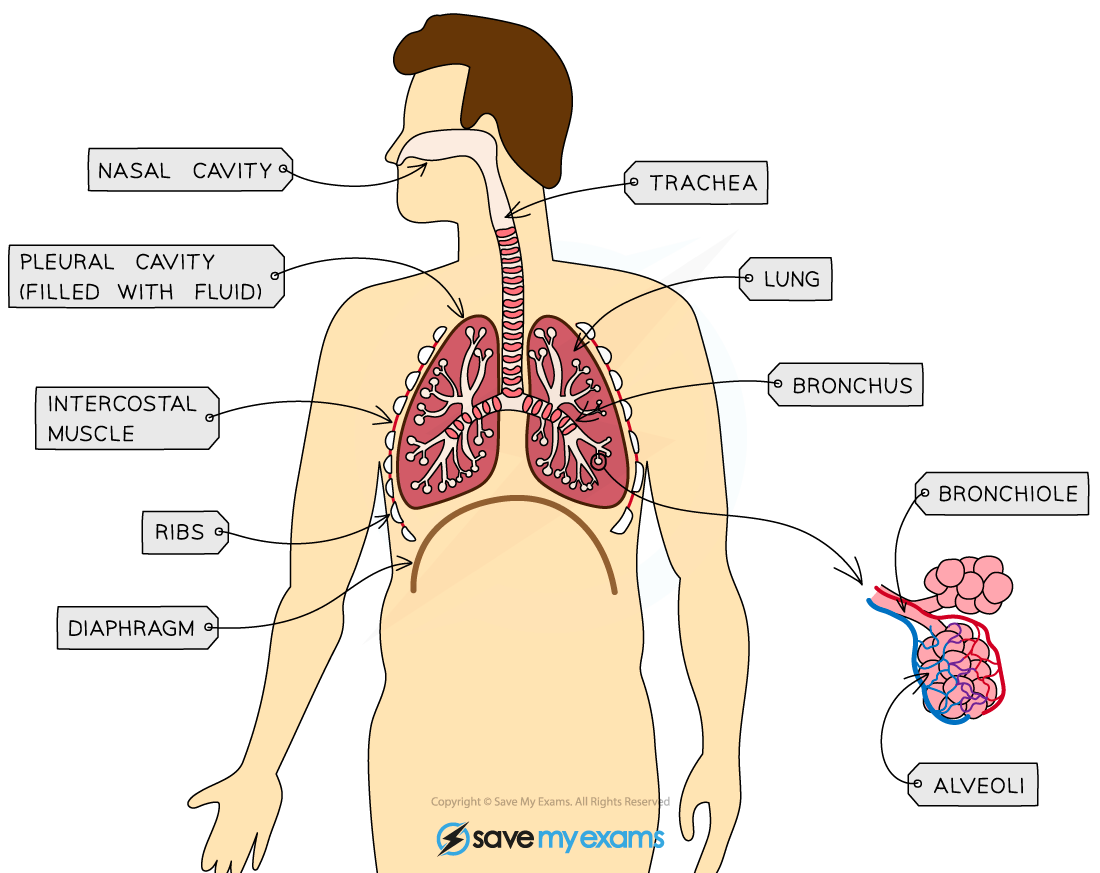
The lungs
The lungs are organs found within the thorax; they are the site of gas exchange
The main structures of the lungs include the:
trachea: the windpipe that carries air from the mouth and nose to the lungs
bronchi: two tubes branching from the trachea, each leading to a lung
bronchioles: smaller tubes that branch from the bronchi and carry air to the alveoli
alveoli (singular alveolus): many tiny air sacs at the ends of bronchioles that provide a large surface area for gas exchange
The lungs are surrounded by the pleural cavity and are protected by the ribs
Ventilation of the lungs is controlled by the action of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles
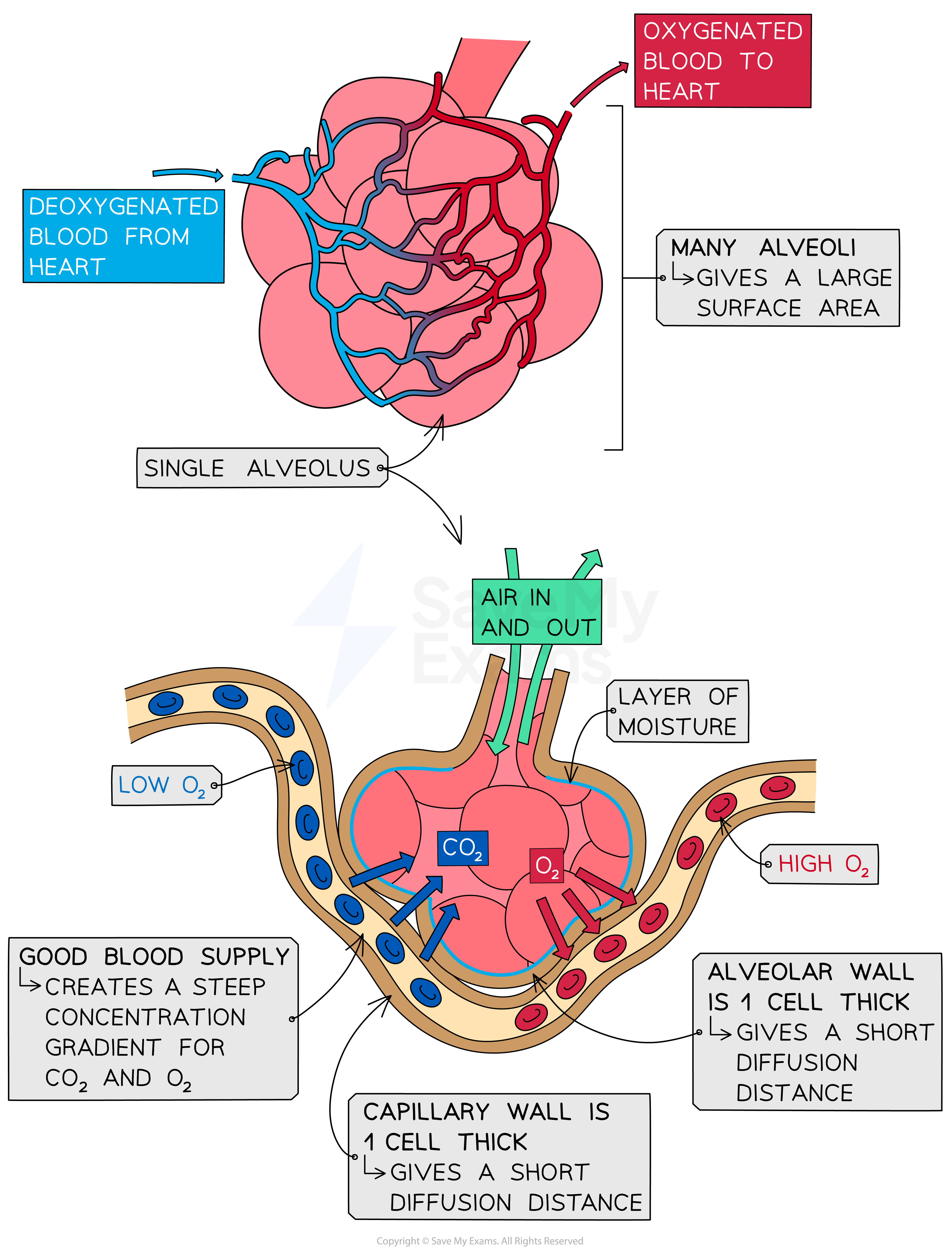
Adaptations of alveoli
The structural features of alveoli mean that they are well adapted for gas exchange:
Feature | Adaptation |
|---|---|
Many alveoli | A large surface area for gas exchange |
Thin walls | Diffusion distance is very short, speeding up gas exchange |
Well ventilated | Maintains high levels of oxygen and low levels of carbon dioxide in the alveolar air space, meaning there is a steep concentration gradient for diffusion of gases |
Many capillaries | Ensure a constant supply of blood that is high in carbon dioxide and low in oxygen, again to maintain concentration gradients for diffusion |
A layer of moisture lines each alveolus | Gases dissolve, speeding up diffusion |

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
