Nutrient Absorption (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
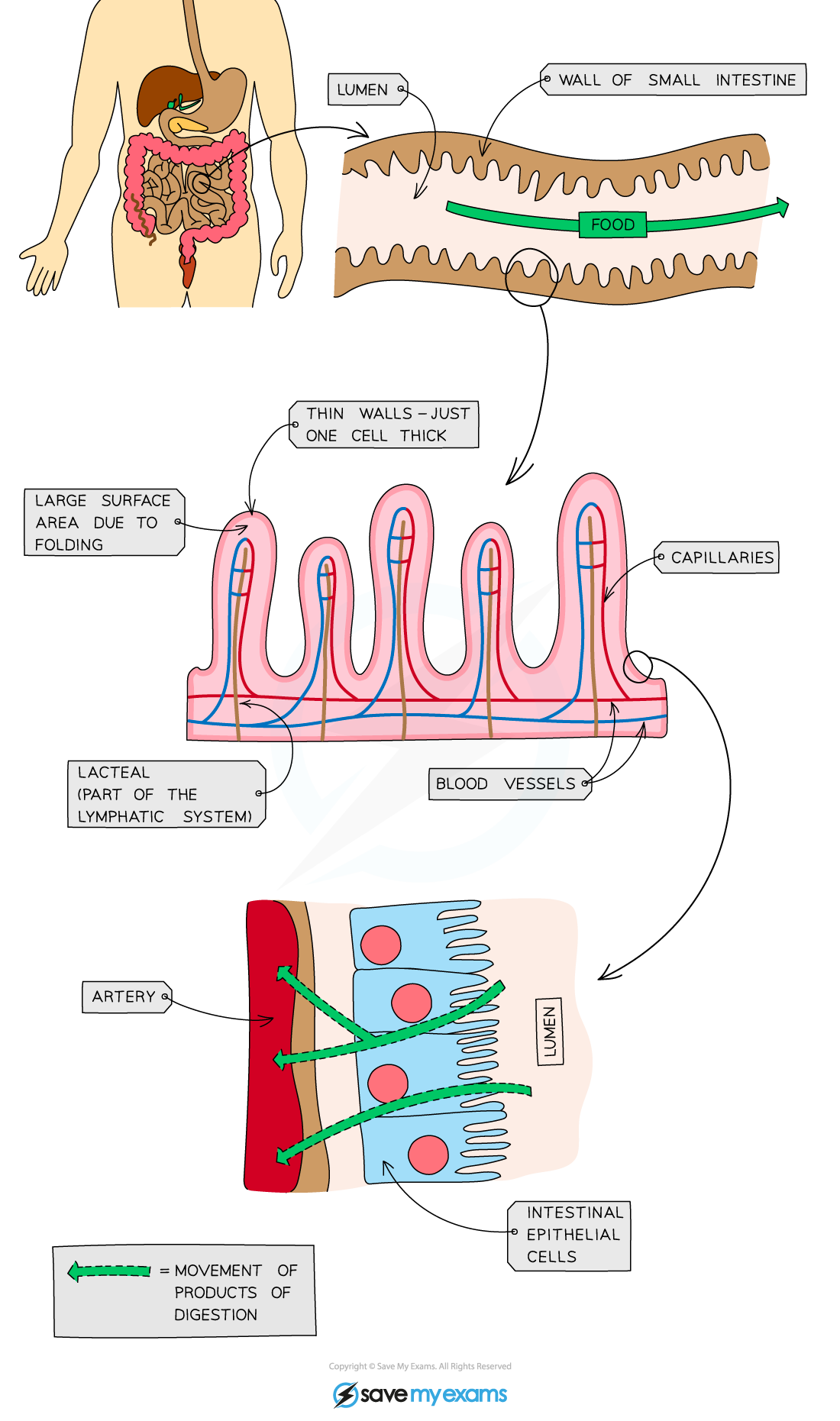
The small intestines
The small intestine is a tube in the abdomen, located between the stomach and large intestine; in the small intestine:
enzymes complete digestion
villi absorb the products of digestion
Absorption is the movement of small, digested food molecules from the digestive system into the blood
Absorption of small soluble molecules occurs by diffusion and active transport
The small intestine has adaptations that increase its surface area
Tt is very long
Its surface is made up of millions of villi
Adaptations of villi
Villi are finger-like projections lining the small intestine; their role is to aid in absorption of the products of digestion
The adaptations of villi include:
large surface area
There are many villi, so the collective surface area is large
Microvilli on the surface of each individual villus further increases the surface available for absorption
short diffusion distance
The wall of a villus is only one cell thick
steep concentration gradient
The villi contain a network of blood capillaries that transport glucose and amino acids away from the small intestine; this maintains the concentration gradient between the intestine and the blood
A lacteal runs through the centre of each villus to transport fatty acids and glycerol away from the small intestine; this maintains the concentration gradient between the intestine and the lacteal

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
