Mitosis (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
The importance of mitosis
Mitosis is defined as nuclear division, giving rise to genetically identical cells
Mitosis is used for:
growth
repair of damaged tissues
replacement of dead or damaged cells
asexual reproduction
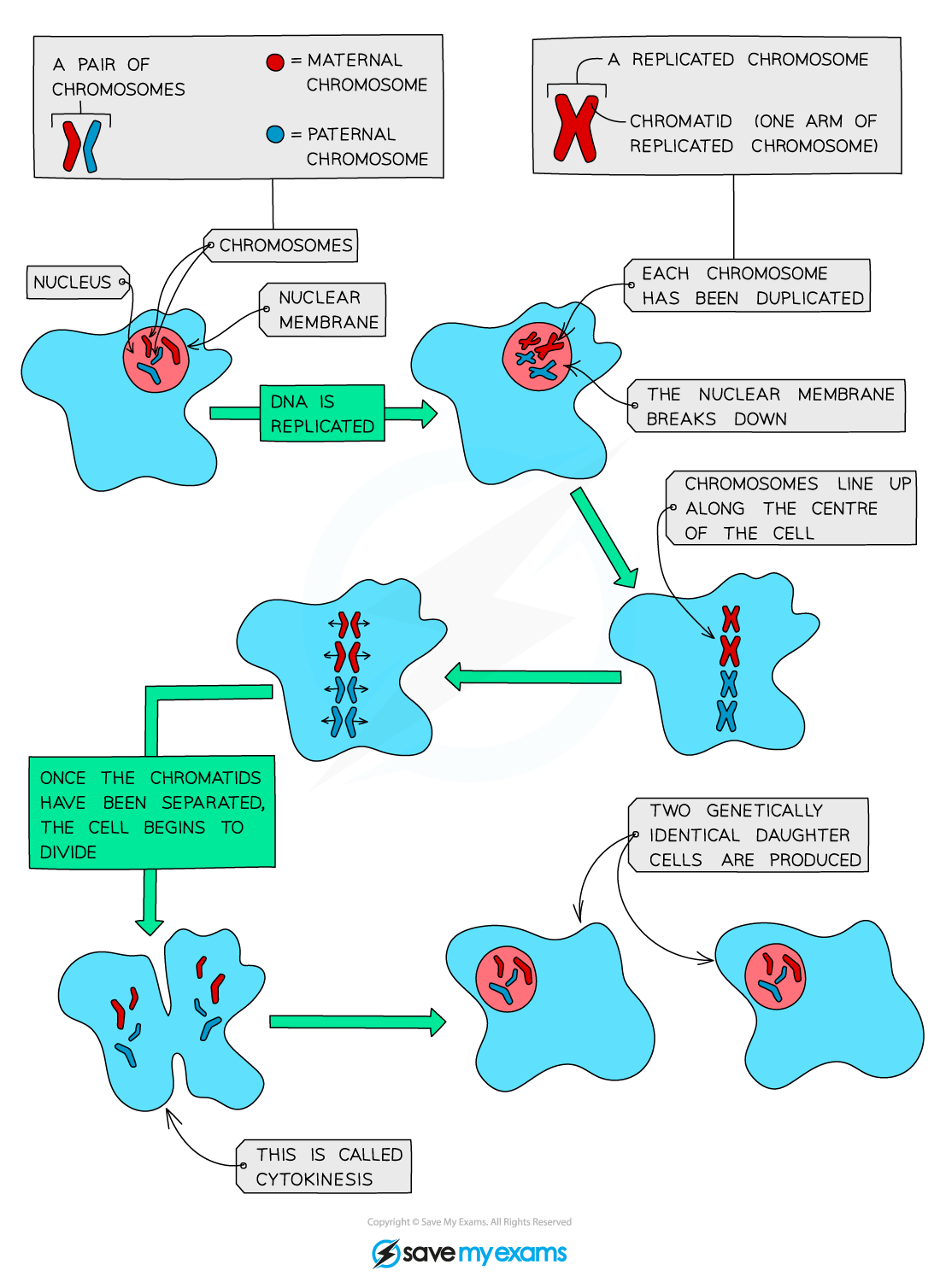
Most body cells have two copies of each chromosome
We describe these cells as diploid
Before a cell divides, each chromosome duplicates its DNA, forming two identical chromatids joined together
During mitosis, the chromatids are separated so that each new daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes
This ensures that both new cells remain diploid, maintaining the correct chromosome number for body cells
The stages of mitosis
Before mitosis, each chromosome in the nucleus of a cell has one chromatid
The chromatids copy themselves exactly during DNA replication
Each chromosome now has two chromatids (two identical DNA molecules joined together)
It’s still counted as one chromosome until the chromatids separate during mitosis
DNA replication must occur before mitosis begins
During mitosis, different stages occur to create two identical daughter cell
The stages are as follows:
Chromosomes condense (becoming visible) and the nuclear membrane breaks down
Chromosomes then line up along the equator of the cell
Spindle fibres split the chromosomes in half, pulling one chromatid to each pole (end) of the cell
A new nuclear membrane forms around the two separated chromatids
After mitosis, the cell divides into two cells, with an identical copy of each of the chromosomes in each cell
As mitosis results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells, the daughter cells have the same chromosome number as the parent cell
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are not expected to know the names of the stages of mitosis, but you must ensure you understand the steps that occur, paying particular importance to the key terms: chromatids, equator and spindle fibres.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
