Blood Vessels (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
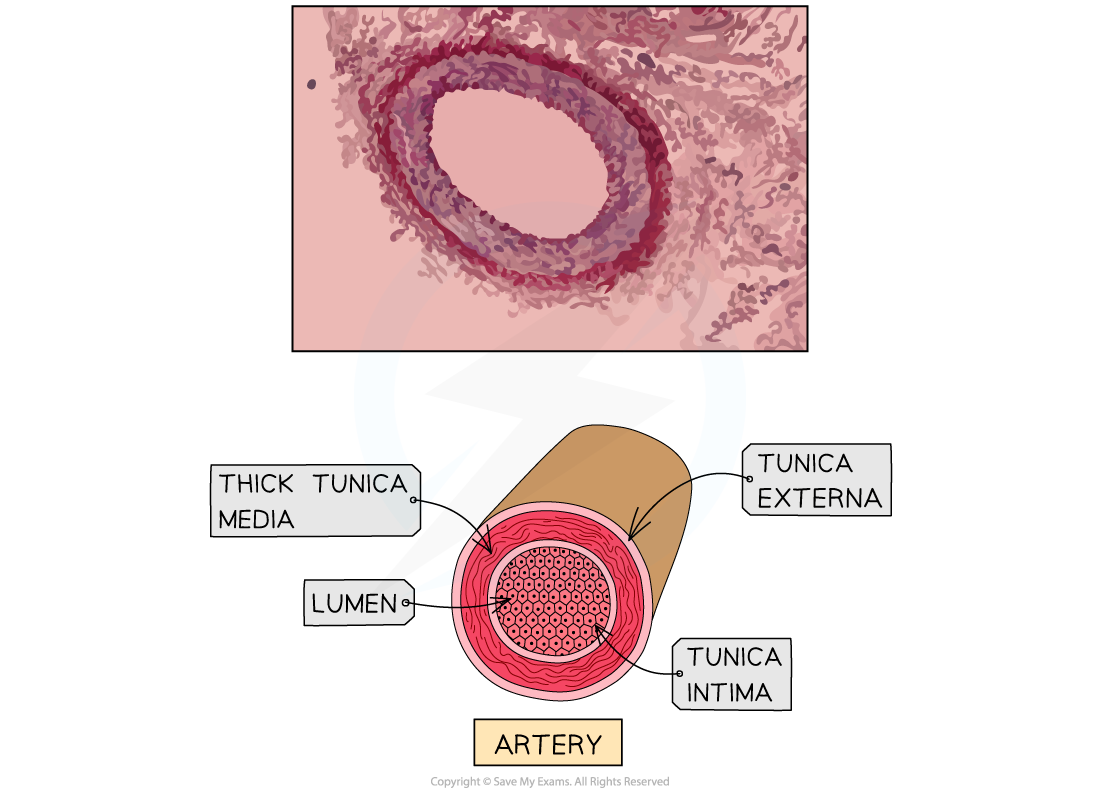
Arteries
Arteries are part of three different blood vessels found in the circulatory system
Arteries carry blood away from the heart at high pressure
Blood is oxygenated in all arteries apart from the pulmonary artery which carries deoxygenated blood
The walls of arteries are thick and muscular and contain elastic fibres to withstand the high pressure
Arteries have a narrow lumen to help maintain high pressure
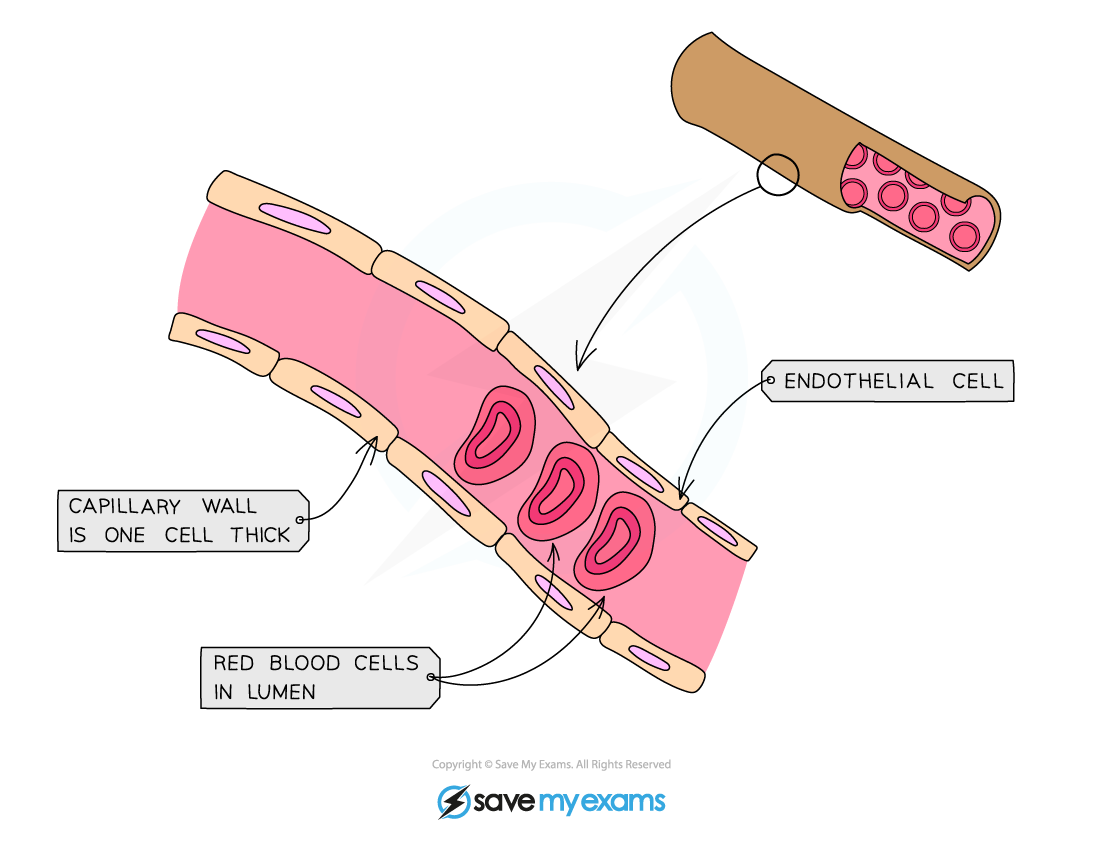
Capillaries
Capillaries form extensive networks that carry blood through tissues and organs, connecting arteries to veins
They are the site of exchange between the blood and body cells, allowing oxygen and nutrients to enter cells and carbon dioxide and other wastes to leave
Adaptations of capillaries maximise the efficiency of exchange in the following ways:
Their walls are only one cell thick and contain small gaps that let fluids and dissolved substances pass through easily
Capillaries have a very narrow lumen which slows blood flow, giving more time for exchange
The large surface area of the capillary networks increases the efficiency of diffusion
Capillaries carry oxygenated blood from arteries to body cells and deoxygenated blood from the cells to veins
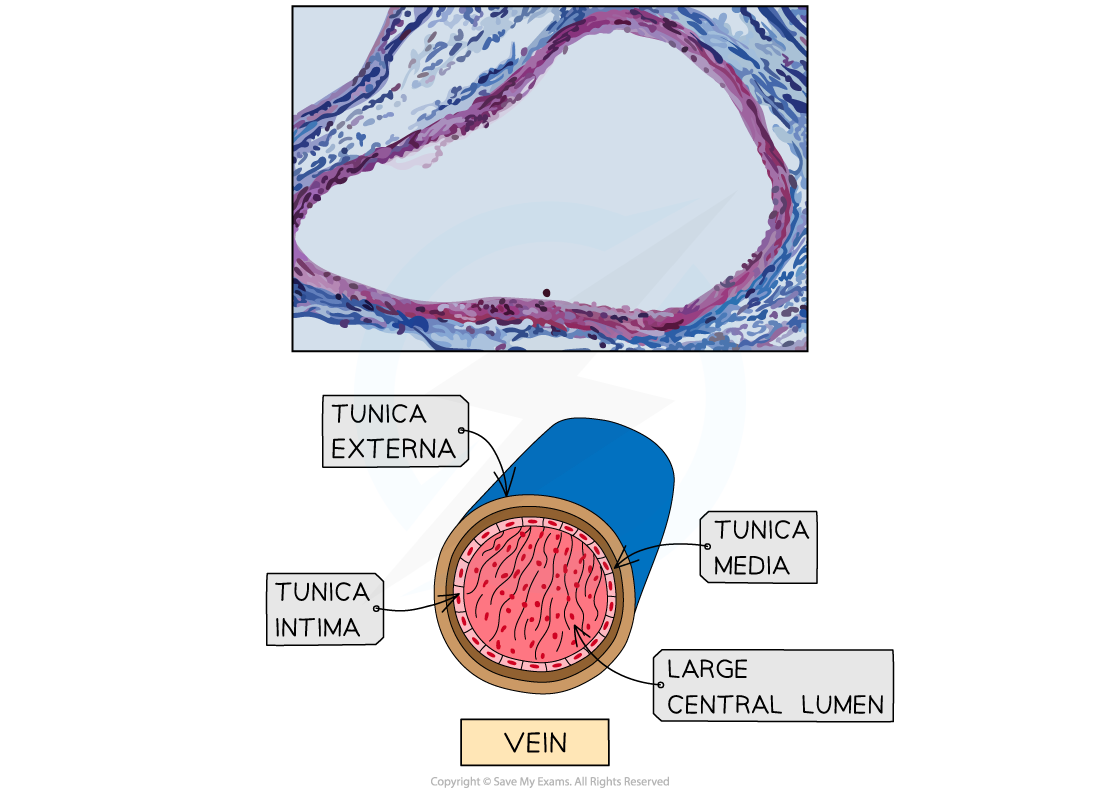
Veins
Veins carry blood towards the heart at low pressure
Veins transport deoxygenated blood away from the body
The single exception to this is the pulmonary vein, which carries oxygenated blood
The walls of veins are thin in comparison to arteries
Veins have a wide lumen
Valves in veins prevent blood from flowing backward
Comparing the blood vessels
Feature | Arteries | Capillaries | Veins |
|---|---|---|---|
Direction of blood flow | Carry blood away from the heart | Carry blood to and from cells in tissues | Carry blood towards the heart |
Type of blood carried | Oxygenated (except pulmonary artery) | Carry oxygenated blood from arteries to cells and deoxygenated blood from cells to veins | Deoxygenated (except pulmonary vein) |
Blood pressure | High | Decreases as blood passes through the capillary network | Low |
Wall thickness | Thick and muscular, with elastic fibres to withstand high pressure | One cell thick to allow efficient exchange | Thin layers of muscle and elastic fibres compared to arteries |
Lumen size | Narrow to maintain high pressure | Very narrow (just wide enough for one red blood cell) | Wide to ease flow at low pressure |
Presence of valves | Absent | Absent | Present, to prevent backflow |
Main function | Transport oxygenated blood quickly from the heart to the tissues | Allow exchange of materials (O₂, CO₂, nutrients, waste) between blood and tissues | Return deoxygenated blood to the heart |

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
