White Blood Cells (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
Function of white blood cells
The body's immune system is highly complex
White blood cells are part of the immune system and are involved in destroying pathogens
Pathogens include bacteria, viruses and fungi
Once a pathogen has entered the body, the role of the immune system is to prevent the infectious organism from reproducing and to destroy it
White blood cells make up less than 1% of total blood volume
There are two main types
phagocytes
lymphocytes
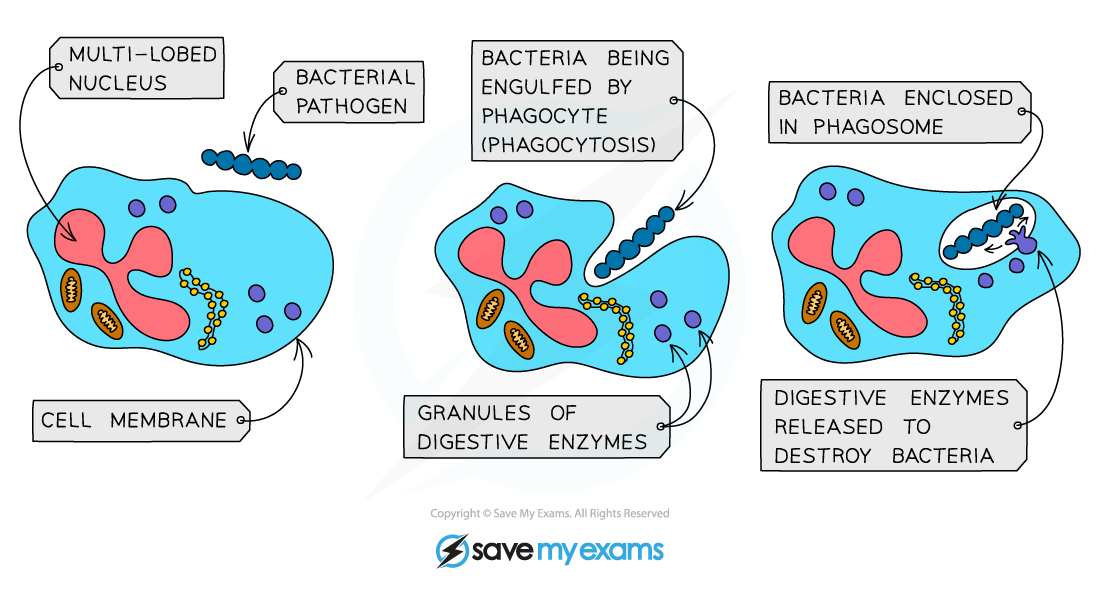
Phagocytes
Phagocytes carry out phagocytosis
They have a sensitive cell surface membrane that can detect chemicals produced by pathogens
Once they encounter a pathogen, phagocytes will engulf it and release digestive enzymes to digest it
This is a non-specific immune response
Lymphocytes
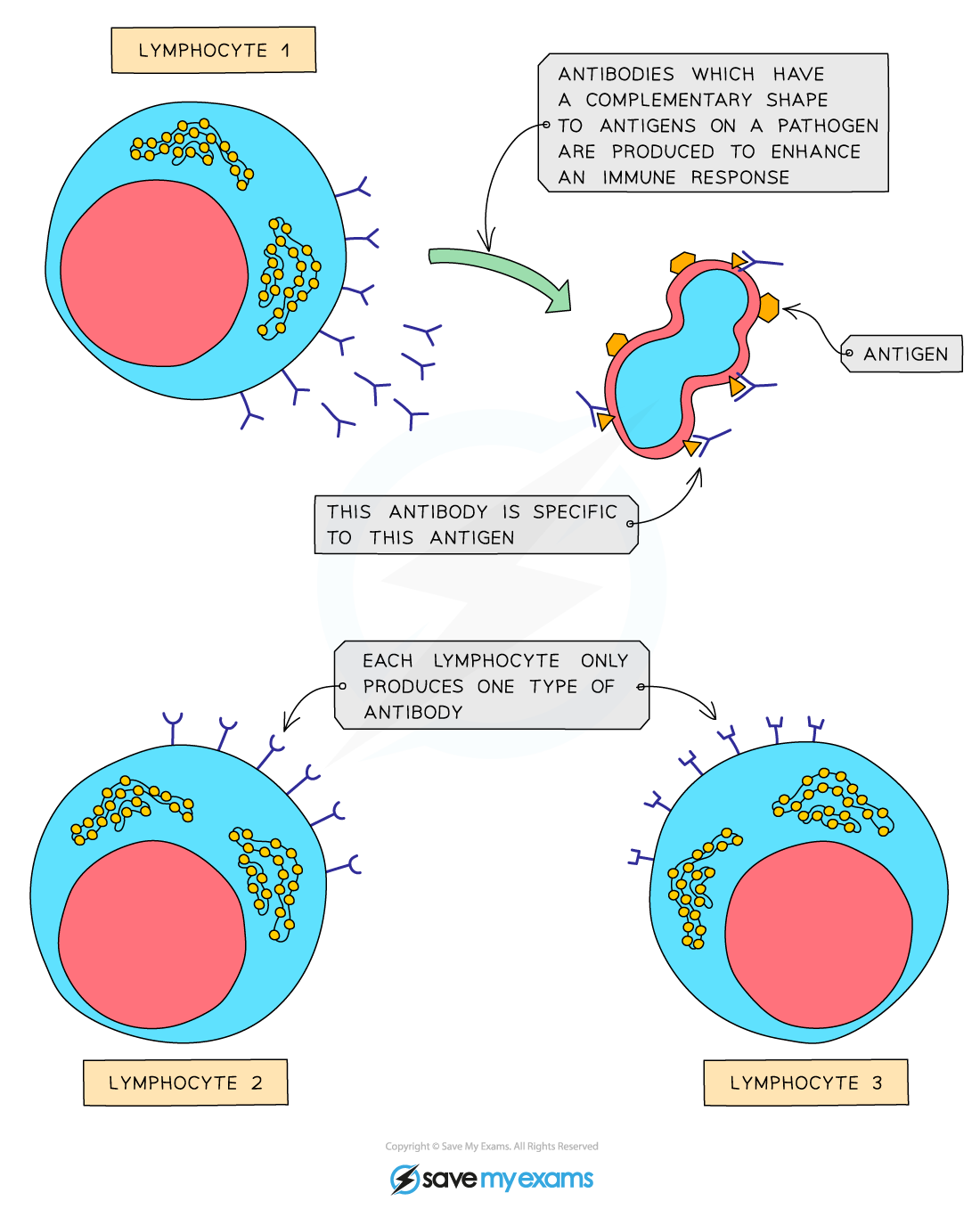
Lymphocytes are white blood cells that produce antibodies
Antibodies are proteins with a shape that is specific (complementary) to the antigens on the surface of the pathogen
An antigen is a marker on the surface of a cell or pathogen that the body sees as foreign and causes the immune system to respond
Lymphocytes provide a specific immune response, as the antibodies produced will only fit one type of antigen

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
