Key Terms in Genetics (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
Key terms in genetics
Genes and alleles
A gene is a short length of DNA found on a chromosome that codes for a particular characteristic (expressed by the formation of different proteins)
Alleles are variations of the same gene
We have two copies of each chromosome; therefore, we have two copies of each gene and therefore two alleles for each gene
One of the alleles is inherited from the mother and the other from the father
This means that the alleles do not have to ‘say’ the same thing
For example, an individual has two copies of the gene for eye colour, but one allele could code for brown eyes and one allele could code for blue eyes
Alleles can be dominant or recessive
A dominant allele only needs to be inherited from one parent for the characteristic to show in the offspring
A recessive allele needs to be inherited from both parents for the characteristic to show in the offspring
Genotype and phenotype
Genotype is the combination of alleles that control each characteristic
The phenotype refers to the observable characteristics of an organism (seen just by looking - e.g.eye colour, or found – e.g. blood type)
Phenotype occurs as the result of both genotype and environmental influences
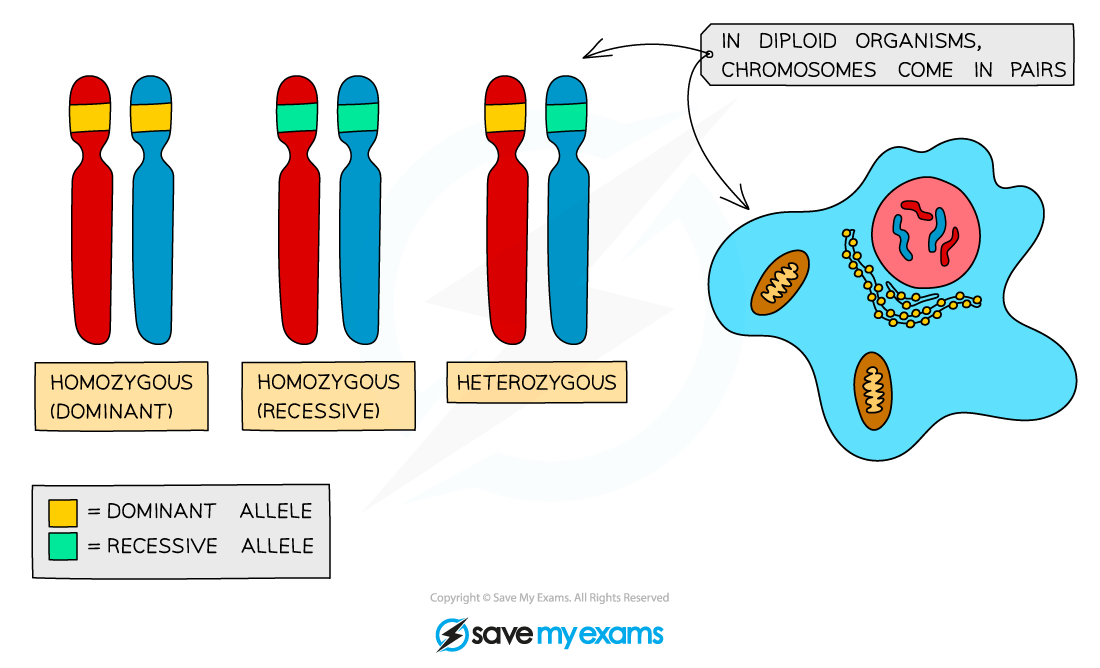
Homozygous and heterozygous
Alleles are often given a lettered code, such as Bb or BB or bb, to easily represent the genotype
When completing genetic diagrams, alleles are abbreviated to single letters
The dominant allele is given a capital letter
The recessive allele is given the same letter, but lowercase
Homozygous is used to refer to genotypes where two alleles of a gene are the same (homo = same)
An individual could be
homozygous dominant (having two copies of the dominant allele): BB
homozygous recessive (having two copies of the recessive allele): bb
Heterozygous is used to refer to genotypes where the two alleles of a gene are different (hetero = different): Bb
P, F1 and F2 generations
In inheritance, the P generation (parental generation) refers to the original pair of organisms that are crossed in a genetic experiment
These are the true-breeding (pure-bred) parents with known genotypes
The F₁ generation is the first generation of offspring produced from two parent organisms (P generation)
The F₂ generation is the offspring produced when two individuals from the F₁ generation are crossed
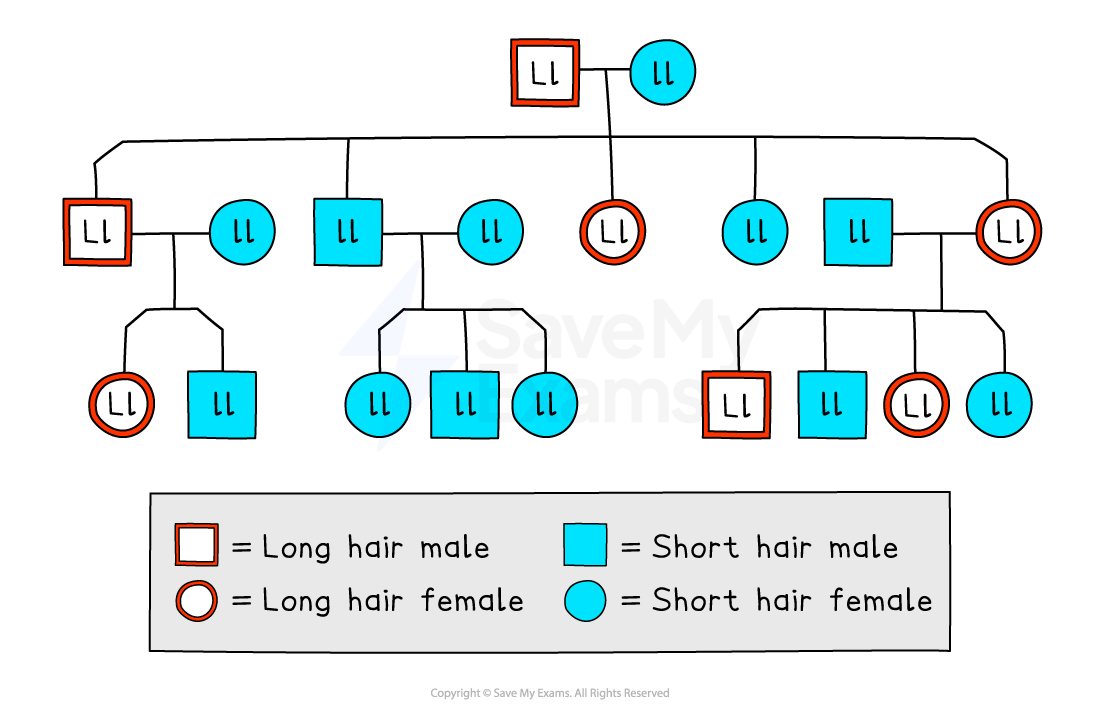
Family trees (also referred to as pedigree charts) can be used to identify phenotypes and their genotypes of different generations
They can be used to trace the pattern of inheritance of a specific characteristic (usually a disease) through generations of a family
Interpreting a family tree
Family trees, or pedigree charts, use standard genetic symbols to trace how a particular trait is inherited through several generations within different family groups
They can be interpreted as follows:
Males are indicated by a square shape, and females are represented by circles
Horizontal lines between males and females show that they have produced children (which are shown underneath each couple)
In the diagram below, affected individuals are red, and unaffected individuals are blue
The family tree below shows:
both males and females are affected
every generation has affected individuals
one family group that has no affected parents or children
the other two families have one affected parent and affected children as well
Summary of key terms
Key term | Definition |
|---|---|
Gamete | Sex cells e.g. egg and sperm cells in animals or pollen and ovum in plants |
Chromosome | Thread-like structures of DNA carrying genetic information in the form of genes. Found in the nucleus of cells |
Gene | Short lengths of DNA are found on chromosomes. They code for specific proteins |
Allele | Different versions of a gene |
Dominant | An allele that is always expressed even if only one copy is present |
Recessive | An allele that is only expressed if two copies (and no dominant alleles) are present |
Homozygous | A genotype with two of the same alleles for a particular gene |
Heterozygous | A genotype with two different alleles for a particular gene |
Genotype | The combination of alleles that control a characteristic |
Phenotype | The observable characteristics of an organism that result from genotype and environmental influences |
P, F1 & F2 generation | P is the parental generation, F1 is the first generation of offspring from P generation cross. F2 is the generation of offspring from a cross between two of the F1 generation |

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
